Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects multiple systems. Myelopathy is one of 19 neuropsychiatric syndromes related to SLE defined by the American College of Rheumatology. Although infrequent, it is a severe manifestation, leading to motor and sensory deficits, and sphincter dysfunction. The pathogenesis is not clearly known, but may be related to arterial thrombosis and vasculitis. Diagnosis is based on clinical findings, laboratory tests and the use of gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. The standard therapy is the combination of intravenous cyclophosphamide and glucocorticoids. In refractory disease, other treatments such as plasmapheresis or rituximab have been used.
El lupus eritematoso sistémico (LES)es una enfermedad autoinmune crónica que afecta múltiples sistemas. La mielopatía es uno de los 19 síndromes neuropsiquiátricos relacionados al LES, definidos por el Colegio Estadounidense de Reumatología. Aunque infrecuente, es una manifestación grave que cursa con déficit motor y sensitivo, y disfunción de los esfínteres. La fisiopatogenia no se conoce claramente, pero podría estar relacionada con trombosis arterial y/o vasculitis. El diagnóstico se basa en los hallazgos clínicos, los exámenes de laboratorio y el uso de la resonancia magnética con gadolinio. El tratamiento estándar es la combinación de ciclofosfamida y glucocorticoides por vía intravenosa. En casos refractarios se han utilizado otros tratamientos, como plasmaféresis o rituximab.
Acute myelitis (AM) involves inflammation of the spinal cord and is characterized by neuronal and axonal damage, which provokes paralysis or paresis, sensory deficit and autonomic dysfunction. The incidence in the general population is 1–4 cases per 1 million population per year.1 Of the multiple causes of AM, systemic autoimmune diseases play a major role and, among them, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is one of those most frequently related.2
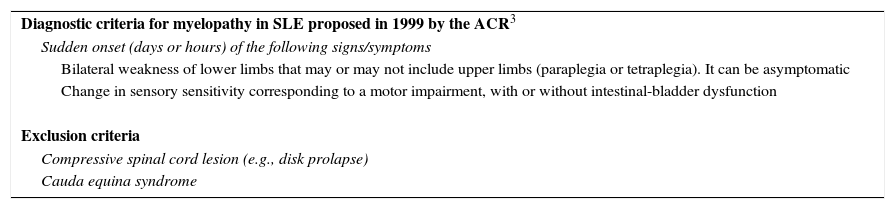
Myelopathy due to SLE is one of the 19 associated neuropsychiatric syndromes defined by the American College of Rheumatology (ACR)3 (Table 1). Taking into account the common neurological manifestations, such as headache, mood disorder and cognitive dysfunction, myelopathy is one of the least common neuropsychiatric syndromes (between 1% and 2% of the patients).4 In the majority of the cases it occurs within the first 5 years after the onset of SLE4 and, in nearly half of the cases, is the initial manifestation,4,5 with a recurrence rate of between 18% and 50%.4–6
Diagnostic Criteria for Myelitis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
| Diagnostic criteria for myelopathy in SLE proposed in 1999 by the ACR3 |
| Sudden onset (days or hours) of the following signs/symptoms |
| Bilateral weakness of lower limbs that may or may not include upper limbs (paraplegia or tetraplegia). It can be asymptomatic |
| Change in sensory sensitivity corresponding to a motor impairment, with or without intestinal-bladder dysfunction |
| Exclusion criteria |
| Compressive spinal cord lesion (e.g., disk prolapse) |
| Cauda equina syndrome |
ACR, American College of Rheumatology; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus.
The pathophysiology is not yet fully known. Based on pathological and serological findings, it has been proposed that small vessel vasculitis and thrombosis would be the 2 major mechanisms most directly responsible for the neuronal and axonal damage.4,7–9 Depending on the type of spinal cord compromise (extensive or limited), one of the mechanisms will better explain the manifestations than the other. In the case of transverse myelitis, the frequent involvement at the thoracic level4,8 (a region with vessels of a smaller caliber than the spinal cord vasculature and, thus, more vulnerable to thrombosis) and the presence in serum of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL),4,8 are features that indicate that thrombosis will have a preponderant pathogenic role.4,8–10 However, this mechanism would not explain longitudinal myelitis with continuous compromise.6
A number of reports indicate an important association between aPL and myelopathy in lupus,4,8,9 although the prevalence of positive serology is not much greater than that of patients with no spinal cord involvement.4,9,10 The most probable mechanism of action is thrombosis. It has also been proposed that aPL could have a direct cytotoxic effect, which would correlate with the presence of oligoclonal bands in aPL-positive patients.6,9,10 Another mechanism could involve the so-called “cooperation between antibodies”9: ischemia would induce the synthesis of aquaporin-4 with the subsequent development of lupus myelitis associated with the neuromyelitis optica (NMO) spectrum mediated by anti-aquaporin-4 immunoglobulin (Ig) G (AQP4-IgG) or another type of antibody.9,10
Despite the above, the role of aPL is debatable.9,10 A systematic review9 compared aPL-positive and aPL-negative patients in terms of the rate of relapses and overall clinical course. Paradoxically, thoracic involvement was observed more frequently among patients who were negative for aPL. Another fact to be considered is that according to a large number of published reports,4–6,8,9 only anticardiolipin (aCL) antibodies and/or lupus anticoagulant were determined, but their exact values were not expressed or were provided using nonstandard units and in the absence of information on cutoff values (in accordance with the classification criteria for antiphospholipid syndrome, the value is 40IU measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay [ELISA]11). Moreover, there is no information on the isotypes studied: for example, in a nonspecific manner, IgM aCL antibody positivity can be found in a number of processes. Another oversight of the articles is that, in general, the patients being studied have only undergone aPL determination once, and the possibility of its being a transient phenomenon has not been ruled out.11
Although no specific pathogenic role has been attributed to anti-Ro/SSA antibody, its association with recurrent myelitis is well known.12 This antibody has been identified in patients with MNO and in transverse myelitis even in the absence of a diagnosis of Sjögren's syndrome.13 Curiously, in one of the largest series of lupus myelitis9 it was observed that patients with recurrent disease were more frequently anti-Ro/SSA-positive than those with monophasic disease (single episode).
Another pathophysiological mechanism proposed is the change in the blood–brain barrier due to autoantibodies,12 especially in cases of overlapping with NMO, although there are no consistent findings to validate this hypothesis.12
The lack of gadolinium uptake in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in certain cases of myelitis suggests a hemodynamic pathophysiological mechanism: spinal cord inflammation, when produced in a rigid anatomic space, would generate progressive venous hypertension (due to compression of the dorsal venous plexus) with the consequent reduction of the perfusion gradient between the radicular arteries of the spinal cord and the venous plexus of the pia mater, generating spinal cord ischemia.9 This mechanism, not yet confirmed, would not explain the initial inflammatory process.
Clinical ManifestationsAlong general lines, the onset is acute and progresses over hours or days, although in many cases, the nadir occurs within the first 24h.9,14 It can be preceded by general symptoms like fever, headache and vomiting,6,9 and, later by a short period that begins with paresthesia and paresis of the lower limbs. This is generally severe, and can lead to paraplegia or, less frequently, to tetraplegia, sensory deficit and sphincter dysfunction, which is expressed as urinary and fecal incontinence.4–6,8,9
Motor involvement is almost always bilateral, although not necessarily symmetrical, and the severity is variable, and can range from mild paresis to tetraplegia.4–6,8,14 The most common motor deficit is spastic paraparesis.4,8
The sensory loss, like the motor dysfunction, is bilateral—with signs of differing severity—ranging from anesthesia (below the level of the spinal cord lesion) to the achievement of exclusive dissociation of thermal analgesia.4,6,8,15 The thoracic segment is the region most frequently affected (from T5 to T8, especially T7)4–6,8 and is usually well defined.
The autonomic nervous system is often compromised, including urinary retention and intestinal paralysis, which leads to bladder and fecal incontinence.4,11 There can be reduced vasomotor function, resulting in pallor and a cold sensation in the limbs.
Acute myelitis can be accompanied by other neurological manifestations. Optic neuritis (ON) is associated with relative frequency4,5,9 (20%–50%). Others less widespread are depression, memory impairment, seizures, psychosis and ophthalmoplegia.4,6
Longitudinal MyelitisFor years it was thought that SLE-related longitudinal myelitis was an uncommon mode of presentation of this neurological disorder.15,16 However, a systematic review found that it was the form most frequently encountered.16 This is probably because of improvements in the quality of MRI, which would enable a better visualization of spinal cord lesions.14 In the majority of the cases, more than 4 segments were affected,10,14 and the lesions viewed with MRI were continuous or patchy.15 Cervical and mid-thoracic segments (T5–T8) were found to be those most widely affected.6 Although it normally develops in cases of SLE in which there are high indices of activity, up to one third occur with low or no activity.15
From the clinical point of view, the most common manifestations (80%–90%) are sensory and motor deficits and urinary sphincter dysfunction. The level of impairment is variable: it can range from a mild urinary disorder to anesthesia of the lower limbs, paraplegia and even tetraplegia. Physical examination nearly invariably shows sensory loss and abnormal reflexes (hyporeflexia or areflexia).6,15,16 Up to 30% of the patients have trunk involvement in the form of cranial nerve paralysis.6 In turn, in a systematic review of myelitis secondary to lupus and aPL, the authors found that 80% of the patients in which ON was associated with lupus myelitis had extensive involvement (more than 3 spinal segments).10 In comparison with transverse myelitis (in which less than 4 segments are affected), the neurological compromise is more severe and there is more evidence of systemic inflammatory activity (e.g., in cerebrospinal fluid [CSF]). Although the prognosis is similar (only 14% had complete recovery), sensory deficit, even after treatment, is more frequent.6
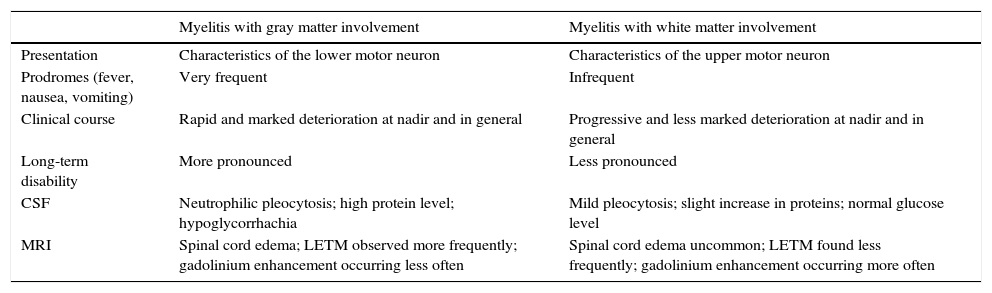
White and Gray Matter InvolvementAn article8 that analyzed a cohort of 22 patients with AM and SLE reported the presence of 2 well-differentiated profiles of spinal cord compromise: a profile with involvement of the spinal cord gray matter, characterized by flaccidity and hyporeflexia, and another that affected the white matter that was associated with spasticity and hyperreflexia (Table 2). The involvement of the gray matter represented a hyperacute onset, and was extremely severe from the very first moment (the clinical nadir was reached within 6h); it had a poor response to immunosuppressive therapy and occurred in the setting of a high index of SLE activity. It was associated with prodromal symptoms like urinary retention and fever, which could be taken into account for an early diagnosis. The compromise of the white matter was less serious, and strength was preserved; the course was more indolent (and the clinical nadir was not reached until after 72h) and it occurred in the presence of low or no SLE activity. Curiously, this report showed that among the patients with white matter compromise there was a large proportion (45%) that met the criteria for NMO or had anti-NMO antibodies, forming part of the NMO spectrum (81.8%).
Differences Between Myelitis With Gray Matter and With White Matter Involvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
| Myelitis with gray matter involvement | Myelitis with white matter involvement | |
|---|---|---|
| Presentation | Characteristics of the lower motor neuron | Characteristics of the upper motor neuron |
| Prodromes (fever, nausea, vomiting) | Very frequent | Infrequent |
| Clinical course | Rapid and marked deterioration at nadir and in general | Progressive and less marked deterioration at nadir and in general |
| Long-term disability | More pronounced | Less pronounced |
| CSF | Neutrophilic pleocytosis; high protein level; hypoglycorrhachia | Mild pleocytosis; slight increase in proteins; normal glucose level |
| MRI | Spinal cord edema; LETM observed more frequently; gadolinium enhancement occurring less often | Spinal cord edema uncommon; LETM found less frequently; gadolinium enhancement occurring more often |
| Recurrence | Very rare | More than 70% of the patients |
|---|---|---|
| Previous optic neuritis | No | Frequent |
| Seropositivity for NMO and/or NMO-IgG | No | Frequent |
| Increased SLE activity | Common | Uncommon |
CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; LETM, longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis; NMO, neuromyelitis optica; NMO-IgG, anti-aquaporin-4 antibody; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus.
Magnetic resonance imaging with gadolinium is considered to be the diagnostic method of choice to confirm any type of myelitis,1,2,17 including that associated with lupus,4,8 as well as to rule out other causes of noninflammatory spinal cord lesions, such as compression.8 While different MRI sequences can be used for the detection of spinal cord lesions, short tau inversion recovery (STIR) and T2-weighted sequences are those most sensitive for the detection of spinal cord lesions.17 According to current recommendations, MRI should be performed of the entire spinal cord regardless of the clinical manifestations1,2 and of the encephalon after alternative diagnoses have been ruled out. The latter include multiple sclerosis (MS), which is very infrequently associated with SLE.18 Computed tomography is not recommended for the diagnosis of myelitis because of its lack of sensitivity,1,2 although it is useful to rule out compression as a cause of myelopathy.1,2
The most common finding is a hyperintense lesion in T2-weighted MRI, generally in the central region, with or without spinal cord swelling, indicative of edema. In most cases, the lesions are enhanced by contrast.16 The number of foci is related to the extension of the area affected: in transverse myelitis, only one focus is usually visualized in T2-weighted sequences,5 whereas in longitudinal involvement, several segments can be found to have an increased signal intensity, especially when the compromise is patchy.6 In cases of spinal cord atrophy, MRI shows attenuation of the signal.4 It must be taken into account that lesions may not be observed at the onset in 30% of the patients,4,15,16 but develop days later.15 Obviously, this is related to the magnetic field strength utilized (Tesla units) and, in order to increase the yield, it is recommended that it not be lower than 1.5T.1,2 Therefore, if MRI produces no image, it should be repeated 2–7 days after the onset of the condition.1 In treated patients, there may be a reduction in the number of images with a hyperintense signal, although this is not necessarily correlated with clinical improvement.14,15
Up to 30% of the patients will have lesions in the brain and trunk,5,6 sometimes indistinguishable from those of other demyelinating diseases, such as MS, although findings in brain MRI can aid in achieving the initial diagnosis. For example, subcortical lesions predominate in antiphospholipid syndrome and in SLE, whereas periventricular lesions and those affecting the corpus callosum are more common in MS.18
Laboratory TestsLaboratory tests can show an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein level, leukopenia, lymphopenia and anemia.4,5 Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) are positive from the time of onset in 95% of the cases,5,8 and anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies5,6,8 and/or hypocomplementemia6 are observed in more than 50%, which demonstrates the importance of these determinations in cases of SLE in association with myelopathy.8 As was mentioned above, there is a prevalence of 50% of patients who are seropositive for aPL. This determination is useful for the diagnosis of SLE in those individuals who have no prior diagnosis of SLE or in cases in which secondary antiphospholipid syndrome is suspected (e.g., spinal cord infarction).
The study of the CSF is a fundamental tool for confirming the diagnosis of myelitis (of any type) and for ruling out infection.1,17 The findings in CSF may be quite variable: they range from normality (20%–33%)4,5 to a fluid with signs of bacterial meningitis,9 with pleocytosis, hypoglycorrhachia and an increase in proteins, although in longitudinal involvement, pleocytosis is nearly always seen to consist predominantly of polymorphonuclear cells.6 Before treatment has begun, the analysis of a second sample of the CSF shows more marked evidence of inflammation.6 There can also be oligoclonal bands, especially in patients who are seropositive for aPL.10
The determination of anti-NMO (IgG type) in serum helps to distinguish patients with myelopathy in SLE associated with NMO,5,12,19 especially in cases of extensive myelitis5,12,19 or involvement of the white matter.9 It has been observed that seropositivity for anti-NMO antibodies persists even after immunosuppression therapy with glucocorticoids and/or cyclophosphamide.9
Differential DiagnosticMyelopathy in lupus should be differentiated from compressive causes (e.g., tumors), infections,1,2,17 demyelinating diseases such as MS18 or NMO12,13,18,19 and idiopathic myelitis.1,2,14 On occasion, the differential diagnosis at onset is problematic as a large percentage of cases of SLE commence with myelopathy, making them indistinguishable from other causes even with laboratory tests and, in these situations, the diagnosis is retrospective.
Neuromyelitis Optica and Myelopathy in LupusAlthough the diagnostic criteria of the ACR3 do not include the determination of anti-NMO antibodies in the evaluation of patients with myelopathy and lupus, a number of authors propose that it be performed because of their implication in the prognosis and therapeutic measures.5,12,13,19 We have no clinical data that can specifically distinguish the 2 conditions: spinal cord compromise can be impossible to differentiate in cases of white matter involvement or of longitudinal myelitis.5,9,13,19 At the present time, it is suggested that they are 2 different disorders that can coexist12,19 due to common genetic and environmental factors that have a role in predisposition.12 However, in cases of recurrent longitudinal myelitis with no previous diagnosis of SLE (especially if it is accompanied by ON), this coexistence is not that clear: some interpret this condition to be NMO,12,19 although patients are positive for autoantibodies like ANA or anti-Ro antibodies, others define it as myelopathy related to SLE and white matter involvement5 and others as an association of the 2 disorders but in early stages of the development of SLE.13 This points to the need for multidisciplinary efforts12,13 to reach the correct diagnosis.
TreatmentThe guidelines issued by the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR)20 on the treatment of neuropsychiatric manifestations in lupus recommend the early commencement (ideally within the initial hours of the onset of the disease) of intravenous methylprednisolone and cyclophosphamide (grade A recommendation). Even in cases in which the findings in the CSF suggest meningitis, treatment should be begun with high-dose glucocorticoids while the microbiological studies are being performed. However, because of the small prevalence of myelitis in SLE, there is little evidence on the optimal treatment.5,21 There is only 1 randomized clinical trial21 dealing with the treatment of severe neurological involvement in SLE that demonstrates the utility of intravenous glucocorticoids alone or in association with cyclophosphamide, this combination being the most effective,22 although the subgroup of patients with myelitis was too small to provide significant differences. A recent report on myelitis in SLE showed that patients who did not receive intravenous cyclophosphamide had a worse neurological outcome. Thus, the combination of intravenous glucocorticoids and cyclophosphamide is considered to be the standard therapy.5,20 The doses utilized in published reports4–6,22 were: 1-g pulses of intravenous methylprednisolone for 3 days together with intravenous cyclophosphamide at a dose of 0.75–1g/m2 body surface area monthly for 6 months to 1 year and, thereafter, every 3 months to 1 year, together with oral prednisone for 6 months to 1 year at a dose of 1mg/kg body weight/day starting 4 days after beginning the treatment, with a gradual decrease after 1–3 months. In refractory cases, between 6 and 10 sessions of plasmapheresis can be added,4–9 although it does not seem to improve the prognosis.4 Intravenous immunoglobulin has also been used as induction therapy or in cases of refractoriness, alone or accompanying the standard treatment, with a variable reponse.5,6,9 Anticoagulation, although employed in cases of myelitis in aPL-positive patients,4,6,8,16 showed no evidence of contributing to the therapeutic benefit of immunosuppression.10
Due to the high rate of recurrence, EULAR recommends subsequent maintenance of immunosuppression, although less intense (level of evidence 2, grade D recommendation). Low-dose glucocorticoids,4,5,8,16,22 azathioprine5,6,8,16 and mycophenolate mofetil5 have been used. Hydroxychloroquine would reduce the number of relapses.5
For more than 10 years, we have seen reports that indicate the utility of rituximab in severe or refractory lupus,23 with serious neuropsychiatric manifestations that do not respond to intravenous glucocorticoids or cyclophosphamide. There are studies of its use in cases of severe myelitis (in the lack of a response to induction or frequent relapse), alone or in combination with glucocorticoids, with varying results.5,6 The dose employed is 375mg/m2 a week for 4 weeks or 1000mg separated by 2 weeks.5,6,23,24 Despite its efficacy, more than 50% of the patients have a relapse within 1 year,23,24 and it is suggested that the cycle be repeated 6 to 12 months later.23,24
Aside from drug therapy, the patients have to start early rehabilitation and other measures in order to avoid the complications of sequelae (e.g., decubitus ulcers, urinary tract infection due to neurogenic bladder).5
Disease Course and Prognostic FactorsBetween 14% and 27% of the patients achieve complete resolution with treatment.4–6,8 Reports on partial recovery or its absence vary widely (14%–73% and 5%–64%, respectively4–6,8). Recurrence is common: between 18% and 50% of the patients4–6 will have at least another episode within the first year even with optimal treatment.4,6
There are a number of short-term and long-term prognostic factors regarding the outcome and risk of relapse.
Clinical manifestations: the significance of the neurological deficit and the need for urinary catheterization are factors that predict severe disability 6 and 12 months after an episode, respectively.5 Gray matter involvement, despite intense immunosuppression, is associated with a poorer prognosis.9
Imaging: MRI findings showing the presence of lesions,4 as well as their number4,17 and extension,6,16,17 are associated with a poorer prognosis in terms of response to medication and subsequent disability. However, a report that compared patients with spinal cord involvement affecting more than 4 segments with those in whom the compromise was less severe found no significant difference in the response to treatment, although the sensory deficit persisted in the former group.10
Laboratory tests: it has been seen that patients with abnormal CSF have a poorer neurological prognosis.10 Anti-NMO seropositivity is associated with a risk of relapse within 1 year of 60%.12
Therapeutics: the failure to add cyclophosphamide to the initial treatment is linked to a worse neurological prognosis, which predicts disability.5 Moreover, the lack of hydroxychloroquine administration and inadequate maintenance therapy (less than 2 years and/or at doses lower than those recommended) are associated with relapses within 1 year.
Ethical DisclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflict of InterestThe authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Doctor Carmen Lessa (Head of the Immunology and Histocompatibility Department of Hospital Carlos Durand, Buenos Aires, Argentina).
Doctor Mónica Perassolo (Head of the Neurology Department of Hospital Carlos Durand, Buenos Aires, Argentina).
Doctor José Luis di Pace (Physician in the Neurology Department of Hospital Carlos Durand, Buenos Aires, Argentina).
We thank them for their support and advice regarding the publication of this report.
Please cite this article as: Chiganer EH, Hryb JP, Carnero Contentti E. Mielitis y lupus: clínica, diagnóstico y tratamiento. Revisión. Reumatol Clin. 2017;13:344–348.