To determine the impact of the disease in patients with PsA in daily clinical practice and to evaluate its relationship with its axial activity.
MethodsA cross-sectional study was conducted in consecutive patients attended from January 2021 to December 2021 who met the CASPAR criteria, with clinical of inflammatory back pain and positive axial imaging, with or without peripheral involvement. Demographic, clinical, analytical data, HAQ index, PsAID12 and activity index (BASDAI and ASDAS-PCR) were also collected. Patients were divided into two groups, those with high impact and those with low impact according to PsAID results. Continuous variables are shown as median (Q1–Q3) and categorical variables as percentages and frequencies.
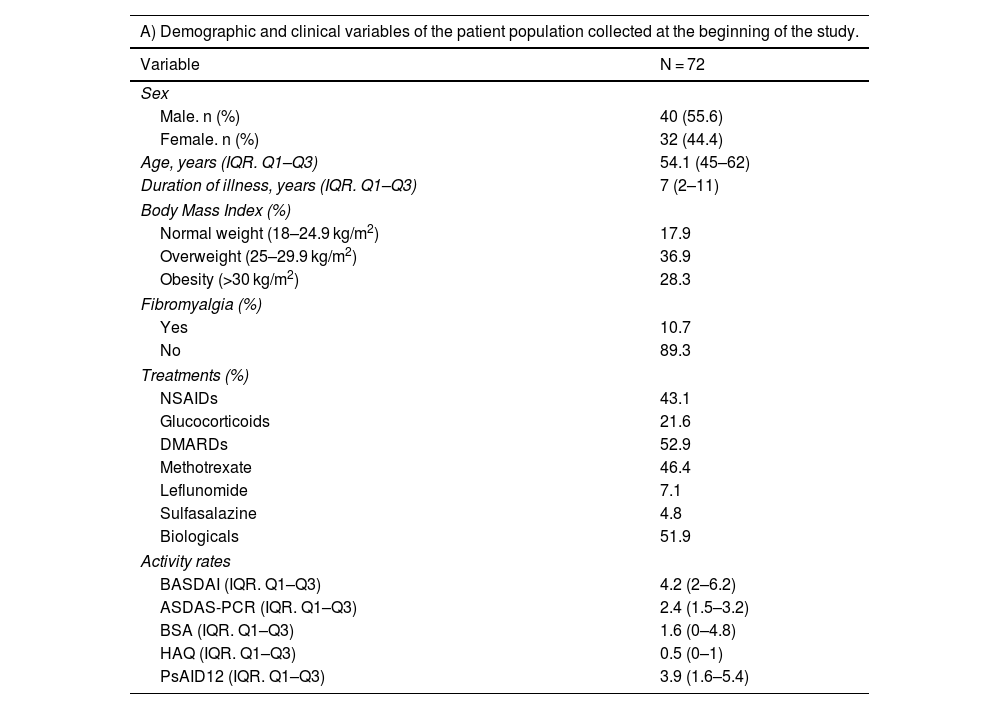
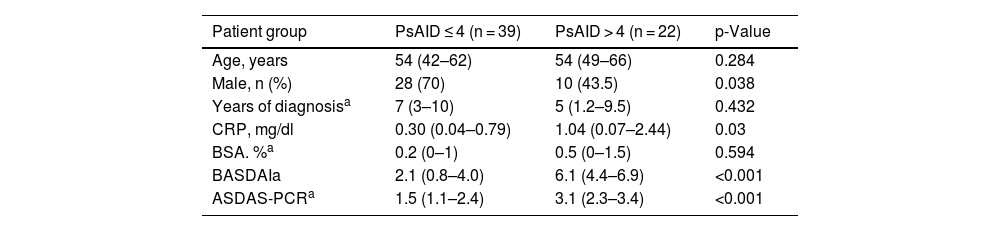
ResultsOf the 269 patients evaluated with PsA, 72 patients with axial involvement were included, 40 men (55.6%), with a median age of 54.1 years and disease duration of 7 years. 28.3% of the patients were obese and serum CRP level was 0.45 mg/dl (0.08–1.10). BASDAI was 4.2 (2.0–6.2) and ASDAS-PCR was 2.4 (1.5–3.2), which translates into 39.6% of patients in low activity or remission. The median PsAID total score was 3.9 (1.6–5.4), evaluated in 61 patients. The patients who achieved a PsAID12 ≤ 4 were 63%, mostly men and with lower CRP levels than PsAID ≥ 4 patients. In addition, low impact measured by the PsAID12 was associated with low results in BASDAI and ASDAS-PCR.
ConclusionsAxial involvement reflected lower impact of the disease measured by PsAID12 and it is correlated with low activity measured by BASDAI and ASDAS-PCR.
Determinar el impacto de la enfermedad en pacientes con artritis psoriásica (APs) en la práctica clínica diaria, y evaluar su relación con la actividad axial.
MétodosSe realizó un estudio transversal multicéntrico en pacientes consecutivos vistos desde enero 2021 hasta diciembre 2021 que cumplieron con los criterios CASPAR, con clínica dolor lumbar inflamatorio y prueba de imagen positiva, con o sin afectación periférica. También se recogieron datos demográficos, clínicos, analíticos, índice Health Assessment Questionnaire, PsAID12 e índices de actividad axial (BASDAI y ASDAS-PCR). Se dividió a los pacientes en 2 grupos según el alto o bajo impacto del cuestionario PsAID. Las variables continuas se mostraron como mediana (Q1–Q3) y las categóricas como porcentajes y frecuencias.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 72 pacientes con afectación axial de los 269 evaluados con APs, 40 varones (55,6%), con una mediana de edad de 54,1 años y duración de la enfermedad de 7 años. El 28,3% de los pacientes eran obesos y el nivel sérico de PCR fue de 0,45 mg/dl (0,08–1,10). El BASDAI fue de 4,2 (2,0–6,2) y el ASDAS-PCR de 2,4 (1,5–3,2), estando en baja actividad o remisión el 39,6%. La mediana de la puntuación total de PsAID fue de 3,9 (1,6–5,4), evaluado en 61 pacientes. Los pacientes que alcanzaron un PsAID12 ≤ 4 fueron el 63%, predominantemente varones, presentaron valores de PCR menores y se asoció a una menor puntuación de BASDAI y ASDAS-PCR.
ConclusionesLos pacientes con afectación axial reflejaban un bajo impacto de la enfermedad medido por PsAID12 y este se correlacionaba con baja actividad medido por BASDAI y el ASDAS-PCR.