The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors and comorbidities in a cohort of Mexican Mestizo rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients.
MethodsWe performed an observational and cross-sectional study involving the RA cohort of our Cardio-Rheumatology Clinic in a teaching hospital. The cohort includes patients aged 40–75 years old who fulfilled the ACR/EULAR classification criteria for RA, patients were recruited from August 2014 to July 2023. Cardiovascular risk factors and comorbidities were defined as a diagnosis included in the patient's medical record or the use of treatment for these conditions.
Results523 patients with RA were included; the majority were women (92.3%). The median age was 55 (48.9–61.0) years. The most prevalent cardiovascular risk factors were overweight (219, 42%), obesity (157, 32.0%), dyslipidemia (165, 31.5%), and hypertension (164, 31.3%). We also detected, that 12.1% of patients without a diagnosis of hypertension had elevated blood pressure, hyperglycemia was reported in 17.2%, and lipid profile alterations were present in 70.6% of patients with no previous diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia, respectively.
ConclusionCardiovascular risk factors are prevalent in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Overweight, obesity, and dyslipidemia were the most prevalent cardiovascular risk factors in our cohort. Alterations in the lipid profile were reported in half of the patients with no previous diagnosis of dyslipidemia.
El objetivo de este estudio fue determinar la prevalencia de los factores de riesgo cardiovascular y las comorbilidades en una cohorte de pacientes mestizos mexicanos con artritis reumatoide (AR).
MétodosSe realizó un estudio observacional y transversal que incluyó a la cohorte de AR de nuestra clínica preventiva de cardio-reumatología en un hospital universitario. La cohorte incluyó pacientes de 40 a 75 años, que cumplían los criterios de clasificación ACR/EULAR para AR, los pacientes fueron reclutados desde agosto de 2014 hasta julio de 2023. Los factores de riesgo cardiovascular y las comorbilidades se definieron como un diagnóstico incluido en la historia clínica del paciente o el uso de tratamiento para estas condiciones.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 523 pacientes con AR; la mayoría eran mujeres (92,3%). La mediana de edad era de 55 (48,9-61,0) años. Los factores de riesgo cardiovascular más prevalentes fueron el sobrepeso (219, 42,0%), la obesidad (157, 32,0%), la dislipidemia (165, 31,5%) y la hipertensión (164, 31,3%). También se detectó que el 12,1% de los pacientes sin diagnóstico de hipertensión presentaban presión arterial elevada, la hiperglucemia se registró en el 17,2%, y las alteraciones del perfil lipídico estaban presentes en el 70,6% de los pacientes, sin diagnóstico previo de diabetes mellitus tipo 2 y dislipemia, respectivamente.
ConclusionesLos factores de riesgo cardiovascular son prevalentes en los pacientes con artritis reumatoide. El sobrepeso, la obesidad y la dislipidemia fueron los factores de riesgo cardiovascular más prevalentes en nuestra cohorte. Se observaron alteraciones del perfil lipídico en la mitad de los pacientes sin diagnóstico previo de dislipidemia.
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are at an increased risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, reducing life expectancy compared to the general population.1 Hispanic population, in general, has an increased incidence of traditional cardiovascular risk factors, due to behavioral, genetic, and environmental factors that independently impact the risk profile of this population.2 In Mexico, there is a high prevalence of diseases associated with overweight and obesity, among the main ones are type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension.3 A specialized evaluation in a cardio-rheumatology clinic could help recognize and manage these risk factors, improving patient outcomes.4 The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors and comorbidities in a cohort of Mexican Mestizo RA patients.
Material and methodsWe performed an observational and cross-sectional study involving the RA cohort of our Cardio-Rheumatology Clinic in a teaching hospital. This cohort includes patients aged 40 to 75 years old who fulfilled the American College of Rheumatology/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (ACR/EULAR) 2010 classification criteria for RA, patients were recruited from August 2014 to July 2023. Exclusion criteria included a previous diagnosis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular event, or peripheral arterial disease), overlap syndromes (defined as the fulfilled criteria for two or more connective tissue disease formally diagnosed by a rheumatologist in the patient's clinical record), or pregnancy. Patients with missing laboratory results were taken as elimination criteria.
All patients underwent a complete medical history including traditional cardiovascular risk factors (diabetes, hypertension, smoking, dyslipidemia), and a family history of heart disease. The disease activity was assessed using DAS28-PCR, taking high disease activity as >5.1 points. The presence of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia was defined as a diagnosis included in the patient's medical record or the use of treatment for these conditions. Overweight and obesity were defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 25 to <30kg/m2, and a BMI of ≥30kg/m2, respectively. In patients without a previous diagnosis of hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and dyslipidemia, high blood pressure was defined as blood pressure ≥140/90mmHg; hyperglycemia was defined as fasting glucose ≥100mg/dL; and alterations of lipid profile were stated as total cholesterol (CT)>200mg/dL, triglycerides (TGL)>150mg/dL, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C)<40mg/dL, or low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C)>100mg/dL.
The Research and Ethics committee of our institution approved this study with registration number MI14-006. The study was conducted following the ethical standards outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki and its subsequent amendments.
The distribution was evaluated with the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Normally distributed variables were described with mean and standard deviation (SD) and the 25th and 75th percentiles (p25–p75) were used to report variables without normal distribution. Comparisons were done using Student's T test, Mann–Whitney's U test, and Chi-square test, accordingly. A p-value of ≤0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS version 25 (IBM, New York, USA).
ResultsFive hundred and sixty-one patients with RA were included in the cardio-rheumatology preventive clinic. Of these 561 patients, 20 were excluded because not have a complete specific serology, and 18 for incomplete lipid profiles. The remaining 523 patients were included in the analysis.
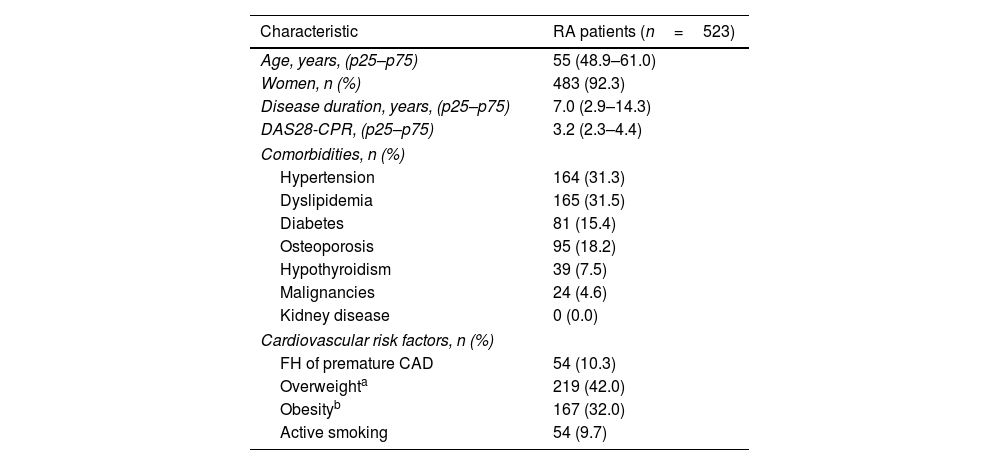
Five hundred twenty-three patients with RA were included; the majority were women (92.3%). The median age was 55 (48.9–61.0) years. The most prevalent cardiovascular risk factors were overweight (42%), obesity (32.0%), dyslipidemia (31.5%), and hypertension (31.3%). A total of 54 patients (10.3%) reported a family history of cardiovascular disease, and 51 patients (9.7%) were referred to be active smokers at the time of inclusion (Table 1).
Cardiovascular risk factors and comorbidities in RA patients.
| Characteristic | RA patients (n=523) |
|---|---|
| Age, years, (p25–p75) | 55 (48.9–61.0) |
| Women, n (%) | 483 (92.3) |
| Disease duration, years, (p25–p75) | 7.0 (2.9–14.3) |
| DAS28-CPR, (p25–p75) | 3.2 (2.3–4.4) |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | |
| Hypertension | 164 (31.3) |
| Dyslipidemia | 165 (31.5) |
| Diabetes | 81 (15.4) |
| Osteoporosis | 95 (18.2) |
| Hypothyroidism | 39 (7.5) |
| Malignancies | 24 (4.6) |
| Kidney disease | 0 (0.0) |
| Cardiovascular risk factors, n (%) | |
| FH of premature CAD | 54 (10.3) |
| Overweighta | 219 (42.0) |
| Obesityb | 167 (32.0) |
| Active smoking | 54 (9.7) |
RA, rheumatoid arthritis; FH, family history; CAD, cardiovascular disease.
Regarding RA characteristics, the median disease duration was 7.0 (2.9–14.3) years, and the median disease activity, measured by DAS28-CRP, was 3.2 (2.3–4.4). A total of 481 (91.9%) patients used synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (sDMARDs) as treatment, and 42 (8.0%) patients used biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs). Only 2 (0.4%) patients were using JAKs at inclusion. A total of 311 (59.8%) patients were receiving glucocorticoid therapy, with a median prednisone dose of 5.0mg (5.0–7.5). Disease duration greater than ten years was reported in 199 (38.0%), and seropositivity for anti-citrullinated peptide citrullinated peptides or rheumatoid factor in 446 (85.2%). Comparisons were made between patients with high disease activity versus those without. Patients with high disease activity do not have higher levels of TC (p=0.374), C-LDL (p=0.431), TGL (p=0.309), and glucose (p=0.485). Nor were they found to have higher weight (p=0.294) and systolic blood pressure values (p=0.058).
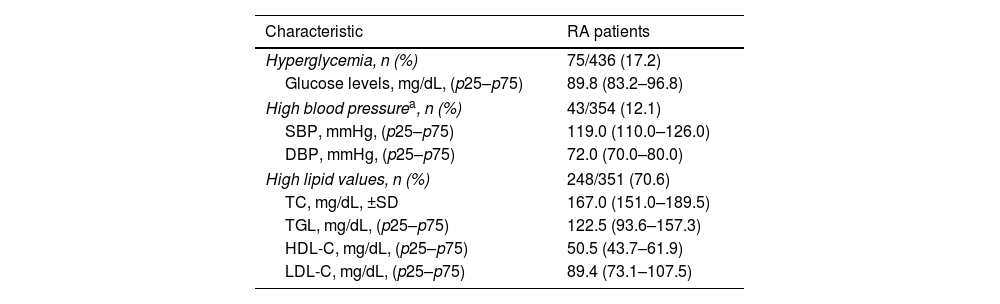
In patients without a previous diagnosis of hypertension (n=354), we found high blood pressure in 43 (12.1%); in those without a diagnosis of diabetes (n=436), we documented hyperglycemia in 75 (17.2%); and 248 (70.6.0%) RA-patients presented alterations in lipid profile without a previous diagnosis, the most frequent alteration being low levels of HDL-C (n=159, 45.2%), followed by high levels of LDL-C (n=117, 33.3%) (Table 2).
Alterations in clinical and laboratory values without diagnosis in RA patients.
| Characteristic | RA patients |
|---|---|
| Hyperglycemia, n (%) | 75/436 (17.2) |
| Glucose levels, mg/dL, (p25–p75) | 89.8 (83.2–96.8) |
| High blood pressurea, n (%) | 43/354 (12.1) |
| SBP, mmHg, (p25–p75) | 119.0 (110.0–126.0) |
| DBP, mmHg, (p25–p75) | 72.0 (70.0–80.0) |
| High lipid values, n (%) | 248/351 (70.6) |
| TC, mg/dL, ±SD | 167.0 (151.0–189.5) |
| TGL, mg/dL, (p25–p75) | 122.5 (93.6–157.3) |
| HDL-C, mg/dL, (p25–p75) | 50.5 (43.7–61.9) |
| LDL-C, mg/dL, (p25–p75) | 89.4 (73.1–107.5) |
RA, rheumatoid arthritis.
Patients with RA have a reduced life expectancy of up to 10 years compared to the general population, despite a similar prevalence of comorbidities.1 Our results indicate a significant prevalence of comorbidities, with 52.3% of patients presenting at least one comorbidity associated with increased cardiovascular risk (such as diabetes, hypertension, or dyslipidemia). This finding is lower than the prevalence observed in our previous report from the cohort which included 225 patients and showed that 63.5% of them had at least one comorbidity.5 In addition, 27.5% of patients had comorbidities that are not considered traditional cardiovascular risk factors (osteoporosis, renal disease, cancer, or hypothyroidism).
Lipid abnormalities contribute to accelerated atherosclerosis and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of increased mortality in patients with RA.6 Dyslipidemia was the most common comorbidity (31.5%, n=165) in our cohort, similar to the reported in the COMORA study and Mexican general population (average of 32%, and 30.4%, respectively).7,8
Hypertension was our patients’ second most common comorbidity (31.3%, n=164). Compared to our 2017 results,5 the prevalence of hypertension increased by 1.5% but remained lower than the prevalence reported in the COMORA study and the Mexican general population, (40.4% and 47.8%, respectively).7,9
Patients with RA have the equivalent cardiovascular risk to patients with diabetes mellitus10 and adverse prognosis for macro and microvascular complications.11 In our cohort, the prevalence of diabetes was 15.4%, higher than the reported in the COMORA study (average of 14%) with the highest reported in the USA (21%),7 but similar to the Mexican general population (15.7%).3
The prevalence of active smoking was lower in our patients compared to the Mexican general population, and the international average (9.7% vs. 19.5% vs. 13.2%, respectively).7,12 However, our 2017 study reported a lower prevalence (8.9%) for active smoking, which is of concern because the prevalence of tobacco use decreased in all age groups from 2005 to 2015 and is expected to continue to decrease in all age groups until 2025.13
Overall, 74.0% of patients were overweight or obese, close to the prevalence reported for the Mexican general population (75.2% in 2018).14 The COMORA study reported an international average of 50% for both overweight and obesity.7 This may be related to our cohort's high prevalence of cardiovascular risk-related comorbidities since countries with lower prevalence had non-cardiovascular-related comorbidities.5
According to the 2015/2016 update of the EULAR recommendations for cardiovascular disease risk management in patients with RA, a complete evaluation should encompass the determination of a cardiovascular risk profile that includes smoking status, gender, age, blood pressure, lipid levels, diabetes mellitus and screening for subclinical atherosclerosis.10 However, the identification and management of cardiovascular risk factors has been reported to be lower in RA patients managed by rheumatologists only, compared with primary care physicians.15 This may be due to several reasons. One is that rheumatologists may focus predominantly on treating the rheumatic disease instead of preventing care. In addition, many rheumatology practices do not have staff specialized to perform preventive screening tools. Furthermore, the time allocated to each visit may hinder preventive care and comorbidity diagnosis.16
In our cohort, 12.1% of patients without a diagnosis of hypertension had elevated blood pressure, hyperglycemia was reported in 17.2% of patients without a previous diagnosis of diabetes, and lipid profile alterations were present in 70.6%. Evaluation of RA patients in a specialized cardio-rheumatology clinic could improve the quality of care for rheumatic patients through prevention and early detection of cardiovascular comorbidities.16
Few studies evaluate the prevalence of cardiovascular comorbidities in Mexican-Mestizo patients. In the study by Vega-Morales D., patients with RA showed a lower prevalence of cardiovascular comorbidities, with hypertension as the most common one (21% vs. 31% in our cohort). The difference could be due to their population's lower use of glucocorticoid therapy since 23% of their patients were currently using prednisone vs. 59.3% in our population, and a lower mean age (53.7 vs. 55 years).17 Regarding the COMORA study, just 50.7% of their sample were overweight or obese which was the most prevalent comorbidity in our population. This discrepancy might be due to the sociodemographic differences between each group, since COMORA does not include the Mexican-Mestizo population.
The high prevalence of hypertension in the COMORA study may be explained by their higher disease activity levels demonstrated by their DAS-28 in comparison to ours.7 A previous prospective cohort study, where hsCRP levels are associated with future risk of developing hypertension and the association of arterial stiffness and chronic inflammatory diseases, which leads to increased blood pressure,18 reiterates this statement.
The disagreement between our results and previous studies regarding the correlation between higher disease activity levels and an increased prevalence of cardiovascular comorbidities may be due to being a small sample of higher disease activity patients who are receiving integral cardiovascular evaluation and treatment in our Cardio-Rheumatology Clinic population.
This study has some limitations that must be noted. First, our population was recruited from a single center that serves a population predominantly of low income. This factor could contribute to the low use of bDMARDs, due to their high cost and the high prevalence of steroid use. In addition, they were mostly women (92.3%) which could have been a determinant for some risk factors and comorbidities.
ConclusionCardiovascular risk factors are prevalent in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Overweight, obesity, and dyslipidemia were the most prevalent cardiovascular risk factors in our cohort. Lipid profile alterations were reported in half of the patients with no previous diagnosis of dyslipidemia. Healthcare professionals should be aware of the increased cardiovascular risk and the prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in patients with RA, so the search for such risk factors should be an important part of patient management, as they could improve patients’ quality of life.
Author contributionsAll authors contributed to the study's conception and design. The idea for the article was performed by JA-CG and V-GG. The literature search was performed by V-GG and AL-GA. The work was critically revised by DA-GD, IJ-CP, JR-AL, JA-CG, and RI-AR. The first draft was written by V-GG and AL-GA, and all commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Compliance and ethical standardsThe manuscript does not contain clinical or patient data.
Funding statementNo specific funding was received from public, commercial, or not-for-profit bodies to carry out the work described in this article.
Statement and declarationsNone.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
None.