To assess the effectiveness and safety of Baricitinib and Tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients in “real world” conditions.
MethodsA single centre retrospective study was performed including RA patients who had initiated treatment with Baricitinib or Tofacitinib from September-2017 to January-2020. Demographic, clinical, laboratory, efficacy and safety variables were collected from baseline and at months 1, 3, 6, 12, 18 and 24. Effectiveness was evaluated by changes from the baseline in DAS28, SDAI, HAQ and acute phase reactants. Safety analysis included adverse events due to any cause, including infection or intolerance. Infection was considered severe if it implied hospitalization. Statistical analysis consisted in Bayesian mixed ordinal regression models including the monotonic effect of each visit and Kaplan–Meier survival curves.
ResultsOverall, 98 patients were included. A significant reduction of disease activity scores was noted in both groups. No difference between either treatment was detected in terms of effectiveness even in first line, after bDMARD failure, in monotherapy nor combined therapy. A total of 54 adverse events were recorded of which 18 were considered relevant. The incidence of infection, including Herpes Zoster, was similar in both groups. No patients in either group suffered any tuberculosis, thromboembolic event, malignancy, death or cardiovascular adverse events.
Survival analysis did not show any difference between groups.
ConclusionBaricitinib and Tofacitinib are both comparable in terms of effectiveness and safety in real world conditions.
Evaluar la efectividad y seguridad de baricitinib y tofacitinib en los pacientes con artritis reumatoide (AR) en condiciones del «mundo real».
MétodosSe realizó un estudio retrospectivo unicéntrico que incluyó a los pacientes de AR que habían iniciado tratamiento con baricitinib o tofacitinib de septiembre de 2017 a enero de 2020. Se recopilaron las variables demográficas, clínicas, de laboratorio, de eficacia y seguridad a nivel basal, y transcurridos uno, 3, 6, 12, 18 y 24 meses. La efectividad se evaluó mediante los cambios desde el punto basal en cuanto a DAS28, SDAI, HAQ y los reactantes de fase aguda. El análisis de seguridad incluyó los episodios adversos debido a cualquier causa, incluyendo infección o intolerancia. Se consideró infección grave cuando se produjo hospitalización. El análisis estadístico consistió en modelos mixtos de regresión ordinaria de Bayes incluyendo el efecto monotónico de cada visita y las curvas de supervivencia de Kaplan-Meier.
ResultadosEn total se incluyeron 98 pacientes. Se observó una reducción significativa de la actividad de la enfermedad en ambos grupos. No se detectó diferencia alguna entre ninguno de los tratamientos en términos de efectividad incluso en primera línea, tras el fallo de bDMARD, en monoterapia ni en terapia combinada. Se registró un total de 54 episodios adversos, de los cuales se consideraron relevantes 18. La incidencia de la infección, incluyendo herpes zoster, fue similar en ambos grupos. Ningún paciente de cualquiera de los grupos padeció episodios adversos tales como tuberculosis, episodio tromboembólico, malignidad, muerte ni episodios adversos de tipo cardiovascular.
El análisis de supervivencia no reflejó diferencia alguna entre los grupos.
ConclusiónBaricitinib y tofacitinib son comparables en términos de efectividad y seguridad en condiciones del mundo real.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, autoimmune disease that is characterized by persistent synovitis, systemic inflammation and circulating autoantibodies that can lead to structural damage, irreversible disability, a higher cardiovascular risk and several other comorbidities.1,2 Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) reduce synovitis and systemic inflammation. The leading conventional synthetic DMARD (csDMARD) is methotrexate but other first line therapies include Leflunomide, Sulfasalazine or Hydroxychloroquine.3 Unfortunately, those therapies, even in combination with short-term glucocorticoids are insufficient to control the disease in 3 out of 4 patients.1,4 The combination of DMARDs, starting with biological DMARD (bDMARD) or oral targeted DMARDs is encouraged in cases with poor prognosis factors.3 However, in spite of all those interventions, some patients experience an insufficient disease control or have unacceptable side effects.1
The role of inflammatory cytokines has been well established, especially through the inhibition of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) or IL-6.1 Moreover, many of the cytokines involved in RA pathogenesis, such as IL6, interferons or the gamma-chain signaling cytokines such as IL-15 and IL-7 are produced through the Janus kinases (JAKs) after binding to their surface receptors and the activation of the signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT).1,5,6 Currently, there are two JAK inhibitors available for the treatment of RA, Baricitinib and Tofacitinib which show similar adverse effect profile than the biological DMARDs,7 however herpes zoster virus reactivation and thromboembolic events seems to be more frequent in patients taking JAK inhibitors.1,8 The same as the other bDMARD, JAKi are more efficacious when combined with a conventional DMARD than as with monotherapy,1 however, as seen with IL-6 receptor inhibitors (Tocilizumab and Sarilumab) monotherapy with JAKi had shown good results on the randomized control trials (RCTs).9,10 Additionally, Baricitinib was the first drug with a study being superior to an anti TNF in RA.11
JAKi represents a valuable addition to the pharmacotherapy arsenal against RA and this is of great benefit to patients in the same way that methotrexate or biological therapies were in the past. Therefore, further studies of patient profiles should be interesting so as to give a patient focused, predictive and personalized rheumatology health care. Whether several RCTs have evaluated the safety and efficacy of Baricitinib and Tofacitinib, the objective of this study is to explore the performance of both drugs in “real life” conditions.
Patients and methodsStudy design and populationA single center retrospective study was performed. Inclusion criteria were adult patients who fulfilled the ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria12 and had initiated treatment with Baricitinib or Tofacitinib from September-2017 to January-2020 in agreement with current EULAR guidelines.3 Previous use of other bDMARD was allowed. Treatment was according to the manufacturer's drug information.13,14
Treatment decision was the choice of the rheumatologist based on disease activity, safety issues and patient factors3 after which, the proposal goes to a multidisciplinary prescription committee composed of rheumatologists, nurses and a pharmacist for agreement.
In clinical routine, after a basal visit each patient was visited at the first and third month, continued by a biannual follow up. A rheumatology specialized nurse met the patient at the basal visit reinforcing adherence, complementing disease, side effects and treatment information and also promoting a healthy lifestyle.15–17
Written informed consent was obtained from all the patients.
Outcome measuresDemographic, clinical and laboratory parameters were collected. Laboratory determinants included Rheumatoid Factor (RF), determined by immunoturbidimetry (Roche Diagnostics, cut-off point 10UI/L) and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) assessed by fluoroenzyme immunoassay (Phadia 250, negative 7; dubious 7–10; positive >10). Body Mass Index (BMI), disease activity, functional capacity and efficacy assessments were conducted at baseline and throughout the study period. Adverse events and treatment interruptions were collected.
Effectiveness assessmentEffectiveness was evaluated according to changes from the baseline in DAS28, SDAI and HAQ18 which altogether represents the disease activity and functional capacity. Low disease activity (LDA) was considered if DAS28 value was between >2.6–3.2 and remission <=2.6.1
Laboratory markers included in the analysis were C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), RF and ACPA. Anyway, a complete blood count was collected at each visit.
Safety assessmentAdverse Events (AE) were considered to be any unfavorable or unintended sign (including an abnormal laboratory finding), symptom, or disease temporally associated with the treatment, as considered in Common Terminology Criteria for AE.19 Adverse events which were considered to be relevant if causes major functional impairment, required hospitalization or brought a discontinuation, whether temporary or permanent, of the drug.
Statistical analysisContinuous variables were summarized using mean (SD, standard deviation) and median (1st, 3rd quartiles). Categorical variables were summarized using absolute and relative frequencies (%).
To evaluate the evolution of SDAI, DAS28, HAQ between groups a Bayesian mixed ordinal regression model was adjusted including monotonic effects of each visit. To correct the non-independence of the observations, each individual was introduced to the model as a random factor. Survival between groups was explored using Kaplan–Meier curves and Log-rank test.
All statistical analyses were performed using software R (version 3.6.1) and packages brms (v2.12), survminer (0.4.6), clickR (0.4.48) and sure.
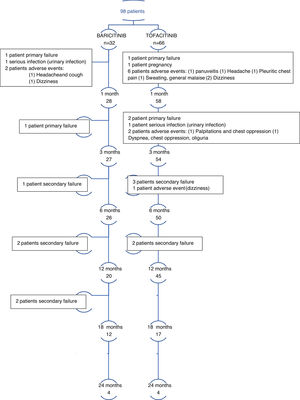
ResultsStudy participantsOverall, 98 patients were included in the study. At the moment of the study a total of 69 (70%) patients remained taking JAKi. 29 patients (30%) discontinued the treatment for the reasons outlined below. A total of 23 patients (24%) reached 18 months taking JAKi and 8 (8%) to month 24 at the moment of the analysis (Fig. 1 and Table S1 in the supplementary material).
Baseline demographic and disease characteristics were similar between the groups (Table 1). More seropositive patients were noted in Baricitinib group. Naïve patients and inadequate responders to prior bDMARD were also balanced between groups.
Demographic and baseline characteristics of the patients.
| Characteristic | All JAKi patientsn=98 (100%) | Baricitinib groupn=32 (32.65%) | Tofacitinib groupn=66 (67.35%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age – years | 54.1 (13.2) | 53.2 (13.1) | 55.4 (13.4) |
| Female sex – number (%) | 87 (88.78) | 31 (96.88) | 56 (84.85) |
| BMI – value (ds) | 24.59 (4.41) | 25.25 (5.57) | 24.02 (3.16) |
| Race – number (%) | |||
| Caucasian | 88 (89.8) | 26 (81.25) | 62 (93.94) |
| Asian | 1 (1.02) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.52) |
| Latin | 9 (9.18) | 6 (18.75) | 3 (4.55) |
| Erosive disease – number (%) | 89 (90.82) | 31 (96.88) | 58 (87.88) |
| Seropositivity – number (%) | 63 (64.29) | 25 (78.12) | 38 (57.58) |
| RF – median titter (1st, 3rd Q.) | 35 (10, 168) | 95 (17, 294) | 19 (10, 151) |
| ACPA – median titter (1st, 3rd Q.) | 139 (0.7, 340) | 192 (90, 340) | 33 (0.5, 340) |
| Extraarticular manifestations – number (%) | 11 (11.22) | 5 (15.62) | 6 (9.09) |
| Patients taking glucocorticoids – number (%) | 70 (71.43) | 22 (22.45) | 48 (48.98) |
| Mean glucocorticoid dosage – mg of prednisone or equivalent | 5 (0, 5) | 5 (0, 5) | 5 (0, 5) |
| Comorbidities – number (%) | |||
| High blood pressure | 32 (32.65) | 8 (25) | 24 (36.36) |
| Dyslipemia | 29 (29.59) | 9 (28.12) | 20 (30.3) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 5 (5.1) | 0 (0) | 5 (7.58) |
| Prior bDMARD– number (%) | |||
| Naïve patients | 28 (28.57) | 8 (25) | 22 (33.33) |
| 1 bDMARD failure | 24 (24.49) | 4 (12.5) | 20 (30.3) |
| 2 bDMARD failure | 13 (13.27) | 4 (12.5) | 9 (13.64) |
| 3 or more bDMARD failure | 28 (28.57) | 14 (43.75) | 14 (21.21) |
| DAS 28 – mean total score | 4.86 (1.05) | 4.88 (1) | 4.85 (1.08) |
| SDAI – mean total score | 24.98 (9.83) | 28.72 (9.55) | 23.32 (9.57) |
| HAQ – mean total score | 1.48 (0.52) | 1.56 (0.45) | 1.44 (0.54) |
| Acute phase reactants | |||
| CRP – mg/L | 6.1 (1.65, 19.1) | 9 (2.2, 19) | 5.65 (1.15, 19.12) |
| ESR – mm/h | 27 (16, 48.5) | 28.5 (16.75, 51) | 27 (14, 47) |
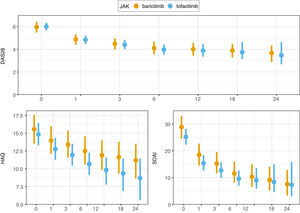
A significant reduction of disease activity scores was noted in both groups (Fig. 2 and Table S1 in the supplementary material). No differences between either group was detected in terms of effectiveness even in first line, after bDMARD failure, in monotherapy nor combined therapy. LDA was achieved in 16% of patients and remission in 9% at the first month point. After 3 months of treatment, 30% of patients were in remission and 13% with LDA. At month 6, 64% of patients were with LDA or in remission. These results are all represented in graphics 1–4 in the supplementary material. Response rates between groups were comparable. CRP, ESR, RF and ACPA did not differ significantly between groups.
First indication was noted in 30% of cases and 90% of patients were with LDA or remission at the 6 month point. However, 8 patients discontinued the treatment due to adverse events or intolerance. Monotherapy was registered in 29 cases (30%) and patients experimented remission in 26% of the cases at month 3. Combined therapy allowed remission in 36% of patients, but no statistical signification was achieved.
The clinical responses observed at month 6 were maintained and improved throughout the study period (Fig. 2).
SafetyOverall, a total of 54 AE were noted (55%) of which 18 were relevant (18%). All of them are shown in Table 2 and detailed per patient in Table S2. The incidence of infection and serious infection was higher in the Baricitinib group with no statistical signification. Two patients (one in each group) discontinued the treatment due to serious infection.
Safety profile throughout the study.
| All JAKi patients (100%)n=98 | Baricitinib group (32.65%)n=32 | Tofacitinib group (67.35)n=66 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Any adverse event (patient) | 54 (55.1%) | 20 (62.5%) | 34 (51.52%) |
| Relevant adverse event | 18 (18.36%) | 7 (21.87%) | 11 (16.67%) |
| Death | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Infection | |||
| Total events | 50 (51.02%) | 22 (68.75%) | 28 (42.42%) |
| Patient | 37 (37.75%) | 17 (53.3%) | 20 (30.3%) |
| Mild infection | 40 (40.81%) | 15 (46.87%) | 25 (37.88%) |
| Respiratory infection | 21 (21.42%) | 7 (21.87%) | 14 (21.21%) |
| Urinary tract infection | 8 (8.16%) | 5 (15.62%) | 3 (4.54%) |
| Candidiasis | 3 (3.06%) | 2 (6.25%) | 1 (1.51%) |
| Other | 8 (8.16%) | 1 (3.12%) | 7 (10.6%) |
| Serious infection | 7 (7.14%) | 5 (15.62%) | 2 (3.03%) |
| Pneumonia | 6 (6.12%) | 4 (12.5%) | 2 (3.03%) |
| Cellulitis | 1 (1.02%) | 1 (3.12%) | 0 (0%) |
| Herpes zoster (total) | 3 (3.06%) | 2 (2.04%) | 1 (1.02%) |
| Mono-metameric | 2 (2.04%) | 1 (3.12%) | 0 (0%) |
| Multy-metameric | 1 (1.02) | 1 (3.12%) | 1 (1.02%) |
| Adverse events | |||
| Mild | 5 | 1 | 4 |
| Headache | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Nausea and/or vomiting | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| Dizziness | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Serious | 11 | 2 | 9 |
| Chest pain, palpitations | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Headache, dizziness | 5 | 2 | 3 |
| Panuveitis | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Sweating, general malaise | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Polyarthralgia, nausea and vomiting | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Adverse events of special interest | |||
| Herpes zoster | 3 (3.06%) | 2 (2.04%) | 1 (1.02%) |
| Major cardiovascular adverse event | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Deep venous thrombosis | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Pulmonary artery embolism | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Treatment interruptions – number (%) | |||
| Temporary interruption (patients) | 32 (32.65%) | 15 (46.88%) | 17 (25.75%) |
| Temporary interruption (number) | 78 | 38 | 40 |
| Definitive discontinuation | 29 (29.59%) | 10 (10.2%) | 19 (19.39%) |
| Primary failure | 4 (4.08%) | 2 (2.04%) | 2 (2.04%) |
| Secondary failure | 11 (11.22%) | 5 (5.1%) | 6 (6.12%) |
| Adverse event | 11 (11.22%) | 2 (2.04%) | 9 (9.18%) |
| Infections | 2 (2.04%) | 1 (1.02%) | 1 (1.02%) |
| Pregnancy | 1 (1.02%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (1.02%) |
Mean values are expressed: mean (SD)/n (%). Median values are expressed: median (1st, 3rd Q.).
Herpes zoster infection was reported in 3 patients (2 in Baricitinib and 1 in Tofacitinib group) and was the reason for discontinuing the treatment in 2 patients who also developed postherpetic neuralgia. Only 2 patients developed mild and transitory hypertransaminasemia, one in each group. In one patient, mild leukopenia was detected while taking Tofacitinib but it was not necessary to discontinue the drug. Mild thrombocytopenia was detected in a single case taking Baricitinib and did not lead to discontinuation.
No patients in either group suffered any tuberculosis, thrombosis, malignancy, death attributed to infection or major cardiovascular adverse events.
A total of 78 temporary interruptions in 32 patients were registered. The main reasons were intolerance symptoms in 11 cases (11%) such as dizziness, nausea or headache (4 with Tofacitinib and 2 in Baricitinib group) and mild infections.
Definitive discontinuation was registered in 29 cases (30%), 10 in the Baricitinib group and 19 in the Tofacitinib group. Reasons for those interruptions were primary failure in 4 cases, secondary failure in 11 cases and AE in 11 cases (7 due to persistent dizziness, nausea or headache; chest pain in 2 cases; 2 cases of infection and panuveitis in 1 case).
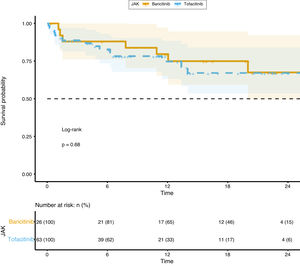
Survival analysis did not show any difference between groups (p=0.68) and it is represented in Fig. 3.
DiscussionThis study evaluates the performance of available JAKi Baricitinib and Tofacitinib in “real world” conditions, focusing on effectiveness and safety data. Real world evidence remains to be established to bridge the gap between RCT and rheumatology clinics.1,8 Baseline characteristics were sufficiently balanced between groups, however there was less absolute and relative seropositive patients in tofacitinib group. Ninety-eight patients were included in the study and overall retention of the drug was over 70%. In any case, results must be considered in the context of the different situation of the subjects included, since some patients are now starting their treatment, and others have been taking it for more than 2 years.
EffectivenessJAKi reduced the signs and symptoms of RA in most patients, however still many patients experience uncontrolled disease. Main changes in disease activity from baseline, seems to happen between 3 and 6 months after the drug commenced. After that, the scores tend to become stable. In contrast to the population included in RCT, our patients showed lower mean DAS28 score.20–22 It is remarkable that were more seronegative patients in Tofacitinib group, with few significance in our study, but a recent work explored this topic in particular analyzing data from phase III RCT, with slightly better results with Tofacitinib with seronegative than in seropositive arthritis.24
Monotherapy had similar results to combined therapy and first indications appear to be the best therapeutic scenario. Moreover, JAKi were also effective after biologic failure as seen in RCT and other series published.20–22,25–30
SafetySafety concerns have emerged with JAKi,6,7 however, this is under vigilance and at the moment there are no specific recommendations about screening, prevention or monitoring of infections between JAKi and bDMARD.8 In addition, based in these concerns, ACR guidelines still recommends Methotrexate as first line therapy instead of JAKi.31 Increased risk of herpes zoster seems to be a class effect of JAKi7,8 and in our cohort was only detected in 3 patients (3%) and seems to be similar to other studies published.8 Thromboembolic risk has been the other issue, especially with Baricitinib,25 but at the moment seems to be a rare serious event.8 In our study, fortunately no single a case of thrombotic related entities had been registered (DVT, PAE nor even MACE). Not any cases of malignancy was detected, as available evidence neither found an increased risk of them.7,8
The incidence of mild infections in our cohort was higher, but serious infection happened in only 7% of patients. In Baricitinib group we detected some more serious infection. Infections under JAKi seems to be as similar as prior documented with bDMARD.7,8,20–23 It is noteworthy that mild infections were the most frequent AE, and included uncomplicated upper respiratory tract infections and urinary infections. In spite of the number of AE recorded, JAKi was not required to be discontinued. More Serious infections were detected in the Baricitinib group (16% against 3%), and the majority of them were pneumonia.
Despite the data from RCT, treatment interruption was very frequent in our study. These could be related to the moderate presence of mild AE and the easiness of the JAKi posology which allows flexible and short interruptions. It is important to remark that mild adverse events (and temporary interruptions) were collected through 3 routes: Self-detected and reported in the next Rheumatology appointment, telematic attention (nurse or rheumatologist) or detected and managed in primary care and reported telematically or at the next appointment.
Study limitationsThe main limitation of our study is the short observational period in many patients that could underestimate the incidence of adverse events. Would be also interesting to analyze the steroid dose in relapses, treatment failure and AE. All those issues will be covered in further analysis.
ConclusionIn conclusion, Baricitinib and Tofacitinib are both comparable in terms of effectiveness and safety in real world conditions. The 70% of patients were taking the drug at the moment of the study of which 23 had been at least 18 months on a JAKi. The main cause of discontinuation in the first month was mild adverse events and lack of effectiveness after the third month of treatment. The 64% of patients achieved LDA or remission at the 6th month.
FundingNo funding source was required.
Conflict of interestAll the authors declare not to have any conflict of interest.
To Dr. Emilio Monte from the pharmacy department, to Dr. Cristina Aguado from the Medical Laboratory and to Carmen Nájera and Inés Cánovas for her daily effort and valuable help.
The authors are also grateful for the collaboration with English language revision to Mr. Paul Godfrey.
The following are the supplementary data to this article:
Table S1. Detailed disease activity data per visit. Table S2. Detailed adverse event per patient. Graphics 1–5. Graphics 1–4 shows the percentage of patients achieving remission or LDA in all patients (1), those who received Baricitinib (2) OR Tofacitinib (3) and in first indication (4). Graphic 5 represents the difference between monotherapy and combined therapy achieving remission or LDA. In all the panels only the patients that achieved that month of the study are represented.