Transitional care programs are developed to facilitate the passage of a young patient with a chronic disease to an adult clinic where he needs to learn how to get involved in his own care. Various models have been proposed to address this transition in a multidisciplinary process. This review will address, in an updated format, various aspects of the transition units. With this objective in mind, we developed a narrative overview of the available information in the literature on transition units (TU) in rheumatic diseases. The most relevant information is presented in different stages: description and recommendations for the management of the adolescent patient, guidelines and information on programs at TU, and a description of aspects that should be part of a TU. Although several transition programs have been described, we do not have enough information to know what the ideal one would be like. More research is needed in this field, focusing on variables such as quality of life, satisfaction, activity and chronic damage.
Las unidades de transición se encargan de facilitar el cambio de un paciente joven con una patología crónica a una consulta de adultos. Se han propuesto diversos modelos de transición que abordan este proceso de una forma multidisciplinar. En esta revisión se abordarán de una manera actualizada los distintos aspectos de las unidades de transición. Con este objetivo se ha realizado una revisión narrativa de los artículos disponibles en la literatura médica sobre unidades de transición (UT) en patología reumática. La información más relevante se presenta en distintos puntos: descripción y recomendaciones en el manejo del paciente adolescente, información sobre guías y programas de UT, y una descripción de aspectos que deberían ser parte de una UT. Aunque hay descritos varios programas de transición, no disponemos de suficiente información para saber cuál es el programa ideal. Es necesaria más investigación en este campo, haciendo hincapié en variables como calidad de vida, grado de satisfacción, actividad y daño crónico.
Transitional care is defined as the medical assistance process by which a young patient with a chronic disease develops skills and resources for health care during the transition from adolescence to young adult life.1 The transition process begins in early adolescence, but does not end until the young adult is fully integrated into an adult unit. On the other hand, transfer is a static process, which takes place only once and involves passing medical information from one specialist to another.2
Today, young people with rheumatic disease have better survival, although high morbidity could be avoided still, in part, with multidisciplinary management. The variable course of these diseases and the transition to teenage years are a major challenge for the physician. 45% of pediatric rheumatologists are reluctant to treat patients aged 18 years, and 28% are seen by adults rheumatologists treating patients below 17 years of age, according to a study conducted by the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).3 Both specialists must develop the skills necessary to enable the transfer of these patients. The lack of coordination between specialists and services, well documented in the literature, can lead to difficulties in the clinical management of these patients.
Another aspect to consider is that adolescence is a period in the development of the individual. Mental health professionals call attention to this age, as it is the time when individual identity develops approximately between 16 and 19 years.4 This is of great importance, since 50% of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) and depression must suffer their first episode between 15 and 25 years.5 Despite being a difficult period, the majority of adolescents with rheumatic disease do not receive appropriate advice and support. Only 14% of 5400 adolescents with special health care needs among U.S. respondents received appropriate guidance and support for the transition process to adult age.6
Despite the many recommendations and that rheumatologists agree on the need for these programs,7 studies in America and England show a low prevalence of these.8–10
In recent years, several professional groups and international agencies have attempted to create consensus recommendations and guidelines to try to remedy this situation. This review aims to review all available information in the literature on these guidelines and transition programs.
MethodsThis review was undertaken by a single person (IC). The selection of the items included have followed the recommendations of the Cochrane systematic reviews, adapted to a narrative review.11
The first approach is to transform the clinical question into epidemiological terms within the PICO concept (patient, intervention, comparator and outcome). Patients were defined as those falling within the adolescence period. The intervention would be included in a transitional unit. In this case, it would be compared and outcome measures of successful operation of these units defined, such as the degree of doctor and patient satisfaction and clinical efficacy. No particular study was selected because the majority of publications on the topic of interest are clinical practice guidelines, case reports, expert opinions or editorials.
From a clinical standpoint, we wanted to know all the information available in the literature on transitional units for rheumatic diseases as well as data concerning the operation of these units in clinical practice.
Systematic Search and Selection of ItemsWe conducted a search strategy for articles published between 1950 and January 2010 in MEDLINE, EMBASE and the Cochrane Library, using the terms described in Annex 2. We also sought information in the abstracts presented at the EULAR (European League Against Rheumatism) and ACR meetings, available on the official website of each agency. The search was limited to a population of adolescents, children and young adults. We included articles in English and Spanish.
The initial selection was conducted by reviewing the title and abstract of each article obtained with the search strategy and identified articles that met the inclusion criteria. These criteria were: adolescent or pediatric population, diagnosis of rheumatic pathology and those including information relevant to a transition unit. After a careful reading of the articles, the information needed was gathered to develop the narrative review. Some items were additionally obtained by reviewing the references of articles already included.
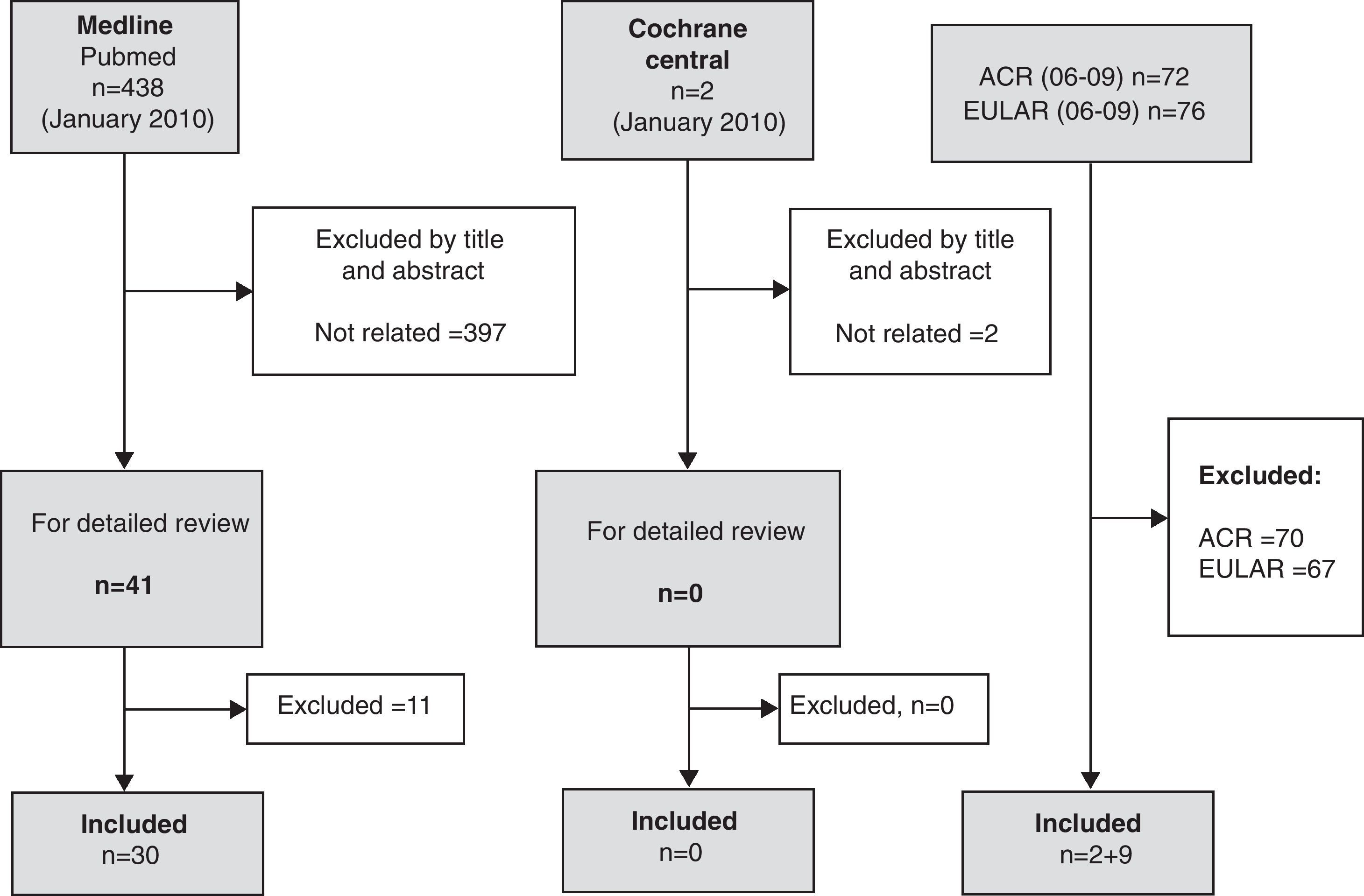
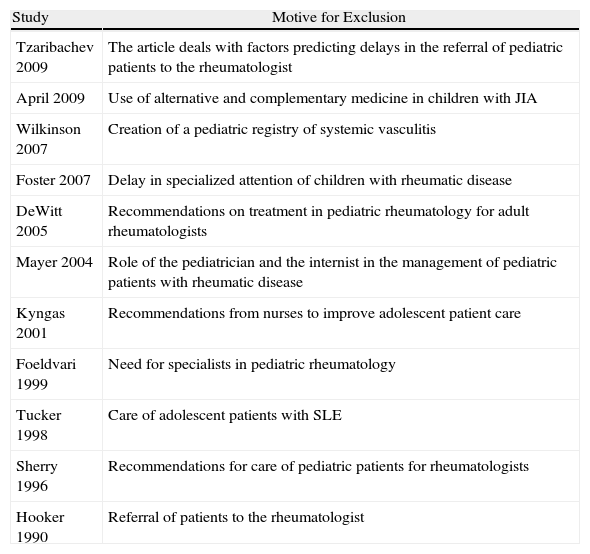
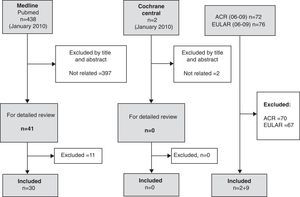
ResultsA total of 41 references were included for a more detailed review. Of these 11 were excluded, the reasons for exclusion are listed in Table 1. The number of items obtained in addition by reviewing the bibliographies of included articles, was 16. From this selection of items we developed this narrative review (Fig. 1).
Excluded Articles and Motives for Exclusion.
| Study | Motive for Exclusion |
| Tzaribachev 2009 | The article deals with factors predicting delays in the referral of pediatric patients to the rheumatologist |
| April 2009 | Use of alternative and complementary medicine in children with JIA |
| Wilkinson 2007 | Creation of a pediatric registry of systemic vasculitis |
| Foster 2007 | Delay in specialized attention of children with rheumatic disease |
| DeWitt 2005 | Recommendations on treatment in pediatric rheumatology for adult rheumatologists |
| Mayer 2004 | Role of the pediatrician and the internist in the management of pediatric patients with rheumatic disease |
| Kyngas 2001 | Recommendations from nurses to improve adolescent patient care |
| Foeldvari 1999 | Need for specialists in pediatric rheumatology |
| Tucker 1998 | Care of adolescent patients with SLE |
| Sherry 1996 | Recommendations for care of pediatric patients for rheumatologists |
| Hooker 1990 | Referral of patients to the rheumatologist |
Results of the literature search and disposition of relevant articles. A total of 438 articles were found on Pubmed that could be related to the topic. After an exhaustive title and abstract review, 397 were excluded, leaving 41 for a more detailed review. After this detailed review, 30 references were included for analysis and 11 abstracts. In addition, a total of 16 references were obtained through a bibliography search of the included articles.
The rheumatic diseases during adolescence are of particular interest because musculoskeletal symptoms represent the third most common cause of primary care consultation at this age.12 On the other hand, a third of JIA adolescente13 debut in this age range and 15%–20% of cases of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) begin in childhood or adolescence, being more aggressive, more renal and meriting immunosuppressive treatment or steroids more often.14
The adolescent patient is complicated for several reasons. Adolescence is the only period in which the doctor does not deal directly with an adult and during childhood attention is focused on the parents. Some behaviors are typical of the adolescent and their management are difficult, such as tardiness or missing appointments, inattention, failure to follow recommended guidelines or defiant attitudes. Sometimes the adolescent identifies the physician as a parent to be separated from, in order to seek their own independence. On the other hand, this type of pathology at this age has a great physical, emotional and psicological15 impact.
Another aspect to consider is the difference in priorities between the adolescent and their caregivers. A clear example is when the teen chooses not to take steroids because they are concerned about side effects that may impair their physical appearance. Chronic damage and even death as a consequence of not taking medication are abstract concepts to them and it is even more difficult to convince them of the need for treatment when their disease is in remission.16
Adolescent medicine is a subspecialty recognized in the U.S. and specific training programs exist in Canada (http://www.mcs.bc.ca/ntiah.htm). Although in other countries it is not recognized as such, there are teenage patient education initiatives, as is the case of England (http://e-lfh.org.uk/projects/ah/team.html).
Recommendations for the Management of the Adolescent PatientSome recommendations may be useful when facing adolescent patient care:
- 1.
Promote mutual respect, for many teens the key determinants of the functioning of a transition unit in rheumatology are the qualities and personality of the physician.17
- 2.
Confidentiality for adolescent patients is difficult if they suspect that the information provided will be forwarded to parents.
- 3.
Avoiding bias when assessing the adolescent.
- 4.
Continuity and consistency: young patients need about 4 or 5 visits to begin to trust their physician.18
- 5.
Independence for visits without their parents in congenital heart disease patients has proven a success factor in transition19 units. Another important aspect is sufficient time for the patient, as quick reference can create anxiety in adolescents. The Royal College of Pediatrics and Child Health suggests that the time devoted to the adolescent patient should be longer than the adult-oriented or even children.20
- 6.
Treat important health issues, such as substance abuse, sexuality and emotional and mental stability. A useful tool for psychological exploration that can be used in routine clinical practice is the HEADSS assessment, acronym adapted by McDonagh21 for the rheumatic patient and includes an assessment of family relationships (Home), level of education and/or expectations of future (Education) general exercise (Exercise), interests, friendships and aspirations (Activities, Affect, Ambition), drug and substance abuse (Drugs), driving (Driving) and diet or weight management (Diet), sleep hygiene (Sleep) and sexuality, especially contraception recommendations under some treatments (Sex). It is important to note that young patients are often reluctant to start these conversations, so the rheumatologist involved must take the lead in advising on these issues.
Although the recommended age for the transfer of the patient is between 16 and 18 years,22 the transition process should begin at age 11, since benefits can be seen at this age8 and the patient is more responsive, a quality that is lost entering adolescence.23 The transition process must be flexible given the heterogeneity of the adolescent patient and the heterogeneity of rheumatic diseases. For example, patients with JIA have not only a physical developmental delay24 but also delayed psychosexual, social and vocacional25 development.
Coordinator of the Transition UnitA coordinator of the unit designed specifically for this purpose should be named. It is not clear which member of the multidisciplinary team would be most suitable in principle, depending on available resources. The coordinator would be responsible for reviewing, updating and evaluating the functioning of the unit. This work is important because it described a lack of communication between specialists, family and patients.26
Transition ProgramThere are many differences between pediatric and adult consultations, and it is important that young adults learn to be able to interact properly with the new doctor to go to an adult unit (Table 2).
Differences Between Pediatric and Adult Consultations.
| Pediatric Consultation | Adult Consultation |
| Family orientedDevelopmental aspectsCoordination with colleges and social servicesHelp with treatmentGreater supervision and treatment Paternalistic care | Individually orientedHealth aspectsLess communication with social servicesGreater acceptance to treatment rejectionLess supervisionGreater participation by the patient in treatment decisions |
Although most rheumatologists support the development of transition programs, especially those that include a medical, psychosocial and educational27 approach, a 2006 study that included 10 centers showed that only 3.1% of English adolescents with JIA were included in these programs.8
Within the transition units there are two aspects that are of particular importance. The first is the information that must be transmitted to both the patient and his family, as this information is not always perceived as satisfactory.28 At a minimum, it should provide information on basic aspects of diagnosis, prognosis and management of the disease as well as risks and benefits of different therapies. Another important aspect is that the adolescent patient develops the skills necessary to become an active part in health care, in addition to the responsibility of parents and caregivers. It is therefore important that the adolescent patient gradually attends visits without parents, as this will improve communication skills, decision-making and negotiation. Monitoring adolescent independently of their parents was identified as a factor of improvement in the quality of life in patients with JIA.29 The main problem is that doctors believe that the young patient is ready to be seen independently from an earlier age than considered by the parents,30 so agreeing on this point is crucial.
Adults UnitThe transition unit should include both pediatric an adult rheumatologists; the connection between the two specialists guarantees the success of the transition unit. In several studies with different chronic diseases, including JIA, younger patients expressed a preference for meeting adult doctors before being transferred, which would be a first contact that facilitates a later relationship.28
ParentsParents play an important role in the lives of adolescents, primarily as support and protection. However, an important part of health professionals warn about conflicts with parents during the transition process and perceive parents and families as a highly influential factor in the success of the transition process. Discrepancies between both the adolescent and his parents and with a doctor, should be evaluated and negotiated to promote the success of the transition process.
In a study conducted in the United States among adolescents with sickle cell disease, 44% said that a transition program should include measures that would allow parents to let them “grow”,31 with growth understood as greater independence.
Multidisciplinary InvolvementBy definition, the transition unit should be involved, in addition to the patient and his family, medical specialists and family physicians, educators, social services and other people around the patient.
Qualified Personnel and Administrative SupportIt is important to have qualified personnel with experience in dealing with adolescents. The relevant data from medical records to be transferred effectively to the time change of physician and should have enough time to organize the various clinical activities.
Evaluation MechanismsIt is important to incorporate evaluation measures. There is some controversy about which outcome measures should be included to evaluate the proper functioning of these units. What defines a successful transition? Some authors define an effective transition process when the patient completes the first visit to an specialist,19 but other important aspects can be adherence to treatment, patient satisfaction, disease activity, rates of structural damage, etc.
Transition UnitsThe evidence at our disposal today highlights the need for transitional units where young patients with rheumatic diseases are transferred to specialized care units for adults. When assessing the expectations and concerns of adolescents with chronic diseases in the transition process, it is striking how the majority of respondents feel “forced” to perform this process, although benefits are identified after being trasferreds.32 On the other hand, many young patients feel that when diagnosed during childhood and followed through adolescence cannot be evaluated as young adults and professionals fail to recognize their new necessities.28
From the point of view of the patient and the family, the main problem is the perception of care in adult units as being of less quality.33 Changing the relationships with parents and health professionals is an important factor in the process, as it has to increase the responsibility for their own care. Clearly, a unit requires more independent adults and this can be a problem, especially for adolescents more dependent on their parents.
In 2002, a consensus document developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Academy of Family Physicians and the American Society of Internal Medicine set out the steps required to ensure a successful transition. According to this document, any young patient with rheumatic pathology should have a qualified professional with the necessary knowledge on the functioning of a transition process and should have a transition program that starts at 14 and includes regular updates of their health state and care based on prevention guidelines for the teen and has continuous health coverage.
Although there are several articles dealing with transition units, few programs are described in detail in the literature, and most of these units are developed in populations with JIA and, less frequently, in patients with SLE. In a small cohort of 23 patients described in Italy, the authors concluded that in the case of patients with SLE the primary objective for physicians should be monitoring adherence to treatment, especially in patients with active disease or risk of severe complications.34 Contraception is an important factor in these patients and pregnancy is a risk factor for severe complications that requires close monitoring.
In England, a Delphi study was conducted to develop a consensus on which aspects were necessary and feasible for a transition unit.27 There was agreement on the need to focus efforts on educational and psychosocial needs of adolescents, individualized transition programs, providing honest explanations about the state of health, provide opportunities for patients to express their opinions and being well informed decisions, continuity of staff and give the opportunity for the patient to be assessed without their parents. Other areas showed a limited viability: multidisciplinary teams, professionals trained in the care of adolescents, age-appropriate environment (waiting areas) and encounters with other teens in similar situations. These recommendations were used by the British Pediatric Society to develop a transition program for young people with arthritis (www.bspar.org.uk) and has shown a positive impact.29,35
A more recent study by Scala et al.,36 described how adolescents with arthritis received different care in the context of a transition unit in the U.S. About 75% were encouraged to take responsibility for their health and 50% had a discussion with their doctor about the need for change in their health care when moving to adulthood. Only 1 in 5 received advice on two aspects: (a) the need to go to a doctor for adults, and (b) how to get health insurance once in adulthood. Compared with the transition units for other chronic diseases such as diabetes, this study found a delay in the transition process.
Another study conducted in Germany picked up the perception of patients and their families on the transition units through surveys. It is striking how only 30% of respondents had discussed with their pediatrician the transition process and only 23% had visited the consultation of transition. The worst evaluations were on how to get an emergency appointment and to discuss personal issues.37
Although the transition unit should not focus only on medical aspects and control of disease, the transition should take place in periods of remission, as the adolescent patient will be more receptive to such interventions.
Models of TransitionSeveral models have been proposed transition. While et al. described 4 types: direct transition (only communication and information sharing), transition sequence (include the development of new services), transition from development (include training and support) and professional transition (with personnel qualified for the transfer). It is unclear which of these described models may be the most efficacious.38
Within the field of rheumatology there are 3 working groups that have published the details of the proposed transition programs.39–41
The transition program developed by McDonagh et al. has been shown to improve quality of life, vocational preparation and satisfaction with health status among adolescents aged between 11 and 17 years,29 although it is unknown whether these improvements are maintained at follow-up into adulthood and if they affect a positive and different long-term outcome.
Tucker et al. have described a model for young adults with rheumatic disease (YARD) that included patients 18–24 years.40 They proposed developing a clinic shared between pediatricians and rheumatologists, with a multidisciplinary team that includes nurses, physiotherapists, occupational therapy practitioners and social workers. The goal is that, when the patient turns 24 years of age, he or she is fully prepared to be transferred to an adult consultation. An interesting aspect of this program is that parents are invited to attend the first visit if the adolescent patient agrees.
The program described by Rettig et al., based on a population of 100 adolescents with JIA, SLE and dermatomyositis. In this program, the nurse coordinates the transition unit and consists of a pre-transitional phase, in which pediatrician teams assess whether the adolescents and their families are prepared for the transition process, and a transitional unit within adults.41
General RecommendationsSome recommendations that can be useful if there is the possibility of launching a transition unit are: to identify professionals who may be interested in their training and support, to identify other specialties that have this type of units in operation and which can provide support and experience, consider the integration of these units in routine clinical development to facilitate in-service support for the rest of the service, to become familiar with some of the websites that give recommendations on educational and psychosocial issues in these age groups (for example, arthritis guide for teens to be found in www.arc.org.uk)35 or other pages that provide different resources (Table 3).
Internet Resources on Transition Units.
| Web Page | Description |
| http://www.dreamteam-uk.org | Adolescent rheumatology team, Birmingham (Children's Hospital NHS Foundation Trust). Has different resources such as transition program information |
| http://www.transitioninfonetwork.org.uk | British organization that facilitates information for handicapped persons, their families and professionals |
| http://www.dh.gov.uk/transition | Official page of the British national health system for transition units |
| www.jong-en-reuma.nl | Page of the division of rheumatology and clinical immunology of the Medical school of the University of Utrecht. Practical information on JIA is available and patients may communicate with their physicians |
| http://www.rch.org.au/transition | Official page of the Royal Children's Melbourne Hospital (Australia) |
| http://www.sickkids.on.ca/good2go | Official page of the transition program of the Sick Kids Hospital, Toronto, Canada |
| http://www.hctransitions.ichp.edu | Initiative for transition care of the University of Florida. Includes downloadable didactic material |
| http://www.depts.washington.edu/healthtr/index.html | Official web page of the transition unit of the University of Washington, Seattle |
The implementation and improvement of transition units are a clear benefit in the care of rheumatic patients that has been documented by numerous authors, especially in patients with JIA.29,40,41
This review aims to summarize and evaluate the information available in the literature on the operation and the recommendations for the establishment of the transition units. The results of this review may serve as reference to generate recommendations regarding the operation of such units.
Although several authors have proposed different transition programs, it is unclear what advantages would be provided by each models and, therefore, what the ideal model would be is not defined. The transition in rheumatology units should be an integrated part of health systems where they coordinate teen musculoskeletal pathology patient care so that the transition occurs successfully.
From the patient's perspective, these units should not only include health and self-care recommendations but also help the patient to prepare for adult life taking into account their social, psychological and vocational experiences. Another aspect that needs to be focused on the transition agenda is the impact of arthritis on the emotional state and social opportunities.15
The limitations of this review are related to the lack of consensus on the operation of these units. Therefore, the literature is very heterogeneous and conclusions are based on expert opinions and recommendations. An important aspect is to define the quality criteria of a transition unit and then conduct research to assess which models more effectively reach these goals.
In conclusion, the goal of transition units is to guide patients and their families for the young patient to become an independent adult who participates actively in their health care and be a part of society. Most experts assume the need for transitional units, but it is necessary to determine what factors will define the proper functioning of a transition unit. Since there is no consensus on these units, it would be important to generate further research to develop universally accepted recommendations and studies designed specifically to assess the most appropriate strategies. The challenge for research in this area is to understand these units as a multidisciplinary process and therefore it is vital to involve all parties in developing them.
Conflict of InterestThis work was carried out with support from Abbott. Abbot did not participate either in the design of the study, literature search, data retrieval, interpretation or manuscript preparation.
| Population | Adolescents, young adults, infancy, children, pediatric or youngsters with the following diagnosis:Juvenile Idiopathic arthritisSystemic LupusErythematosusVasculitisOther Rheumatic Diseases |
| Intervention | Transition careTransference of careMedical treatmentTransition to adult care |
| Comparator | None |
| Outcome | Transition unit characteristics |
| P | (adolescent)) OR (children adolescents)) OR (young adults)) OR (young age)) OR (childhood)) OR (children)) OR (pediatric patients)) OR (youth)))AND(juvenile idiopathic arthritis)) OR (systemic lupus erythematosus)) OR (vasculitis) OR (rheumatology) | 2 380 56051 325 |
| I | (transition to adult health care) OR (transfer)) OR (transfer of care)) OR (transition counseling)) OR (transition care)) OR (health-care delivery)) OR (transition to adult care)) OR (transition to adulthood)) | 885 291 |
| O | Transition units characteristics | |
| Limits | Limits: Humans, English, Spanish, Child: 6-12 years, Adolescent: 13-18 years, Adult: 19-44 yrs | TOTAL 438 |
Please, cite this article as: Castrejón I. Unidades de transición para pacientes con patología reumática: revisión de la literatura. Reumatol Clin. 2012;8(1):20–26.