Carpal tunnel syndrome may present with skin lesions. This may lead to a differential diagnosis with vasculitis. Sympathetic nervous system perivascular involvement and recurrent injuries secondary to sensory loss are probably part of the mechanism of injury. In this case, we also comment on the pathogenic role of persistent median artery associated with a bifid median nerve.
El síndrome del túnel carpiano puede manifestarse con lesiones cutáneas. Estas pueden plantear el diagnóstico diferencial con una vasculitis. El compromiso del sistema nervioso simpático perivascular y los traumatismos a repetición secundarios a la hipoestesia son probablemente parte del mecanismo de daño. En este caso, se plantea además el papel patogénico de una arteria mediana remanente asociada a nervio mediano bífido.
Clinical manifestations of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) are known as subjective signs (paresthesia, proprioceptive alterations, paresis) and objective (alterations in sensitivity and motor function, positive Tinel and Phallen tests, and atrophy of the thenar eminence). Most of the patients are managed with medical or surgical treatment in relation to their clinical manifestations, the results of the electromyography in their progression. In some cases, presentation may be atypical and secondary atrophy may be present after severe compromise, which obliges the clinician to exclude other diagnoses.
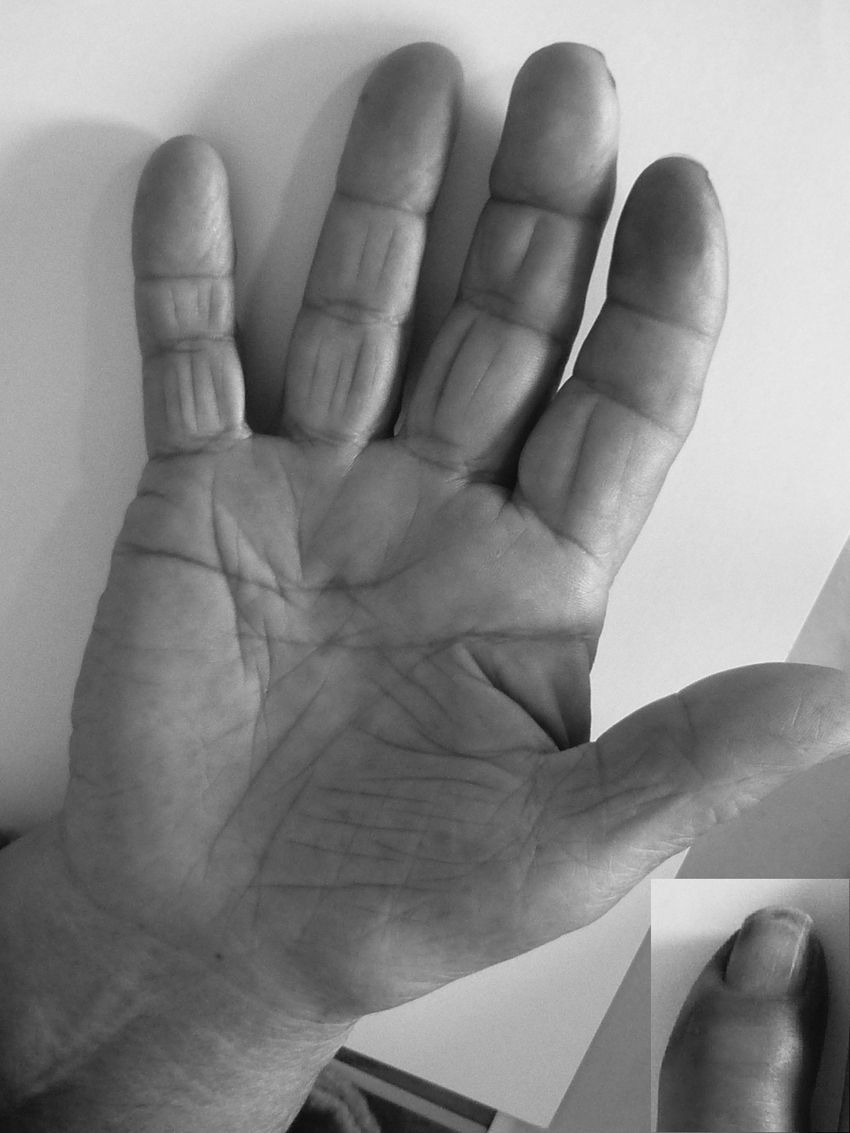
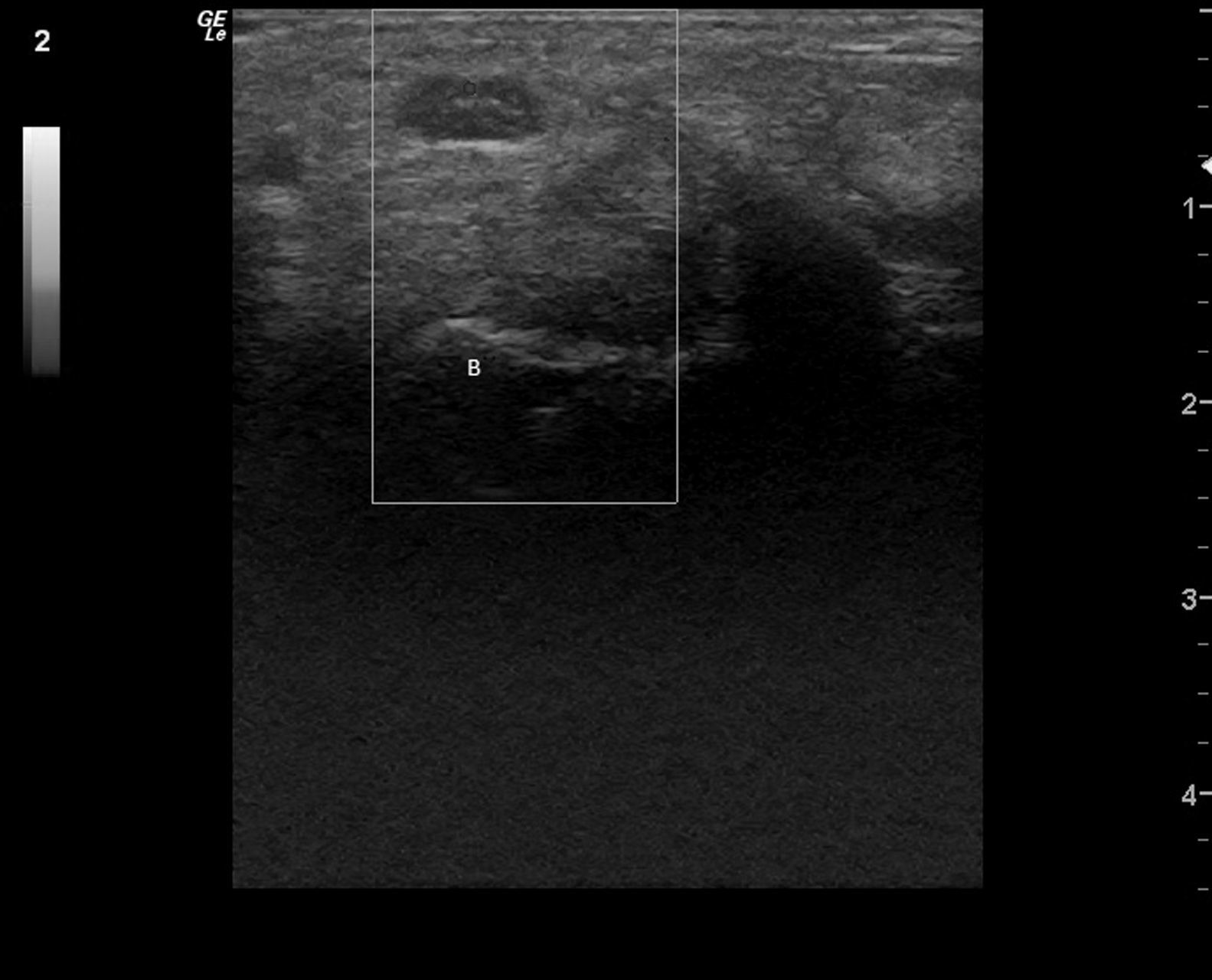
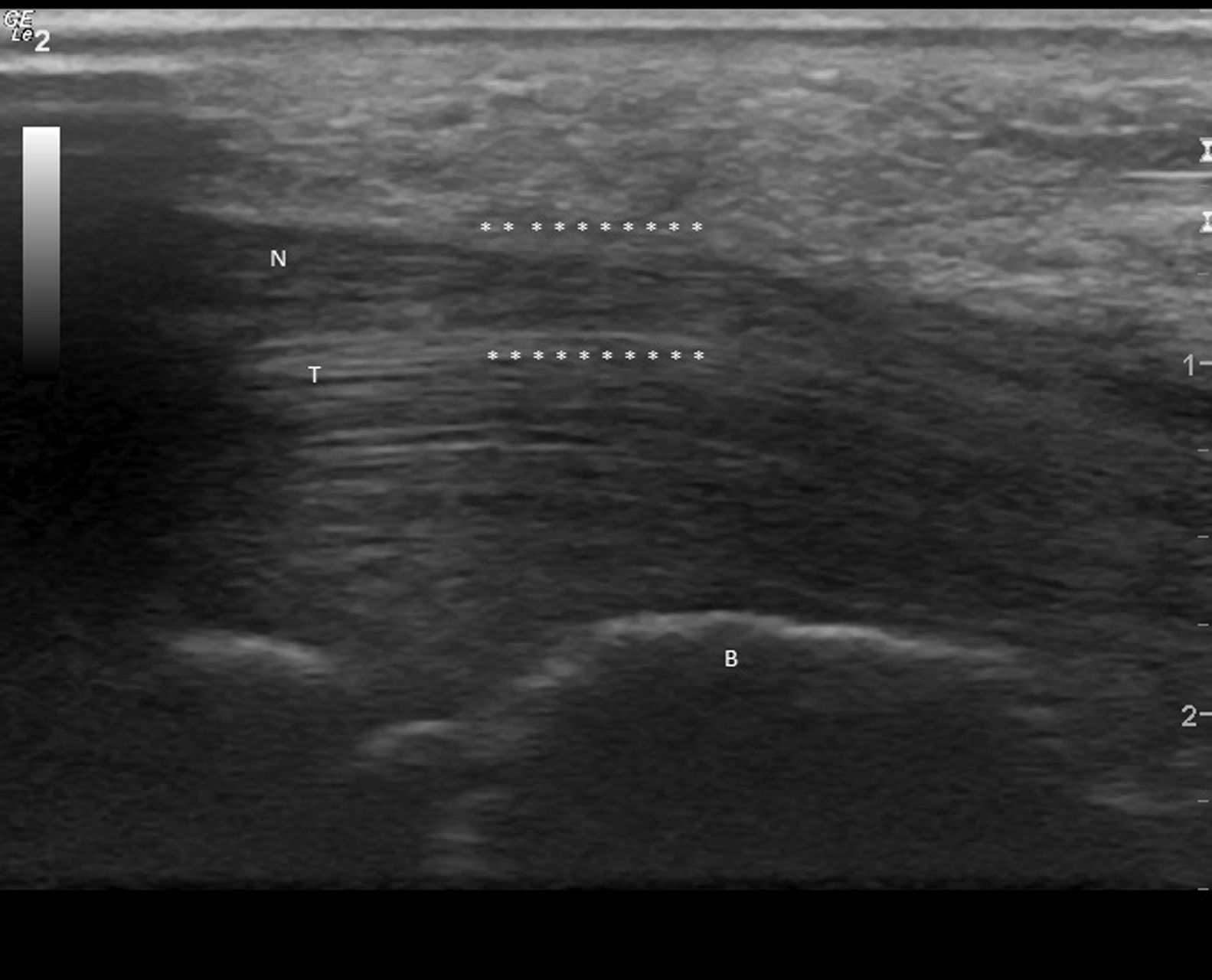
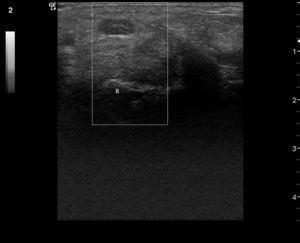
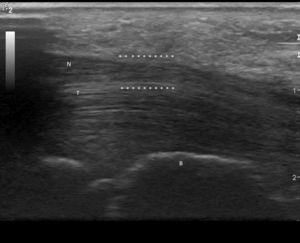
Clinical CaseWe present the case of an 84-year-old woman with a history of controlled hypertension and 2 months with skin lesions on both hands, classified as a type of vasculitis associated with cyanosis on the first, second and third fingers, and severe pain that led to emergency hospitalization for suspected systemic vasculitis. Upon directed interrogation, there was no evidence of connective tissue disease or drug use. She received enalapril to treat high blood pressure. Physical examination highlighted periungual lesions, indicative of vasculitis, but their distribution was dermatomal, associated with severe hypoesthesia in the same territory and significant atrophy of the thenar region, bilaterally (Fig. 1). The rest of the examination was normal, in particular, no skin lesions at other sites were seen and her blood pressure was normal. Laboratory studies were performed: blood count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and renal function as well as complete urine testing were normal, she had negative rheumatoid factor, negative antinuclear antibodies, ENA and negative C and P ANCA. The patient complained of abnormal sensitivity and nocturnal paresthesias and lack of strength in her hands for some time, so she had been seen by other physicians, leading to a diagnosis of CTS, undergoing an upper extremity electromyography a year earlier. This showed a severe entrapment of both median nerves at the carpal tunnel, with complete denervation of the thenar eminence. Ultrasonography was performed, showing the entrance to the tunnel at the pisiform, a right median nerve with a 17mm2 area (normal=±10mm2)1,2 (Fig. 2), with the central presence of a median artery remnant (Fig. 3). The left median nerve was also thickened, with an area at the pisiform level of 18mm2. Both nerves appeared trapped in the carpal tunnel in longitudinal sections (Fig. 4).
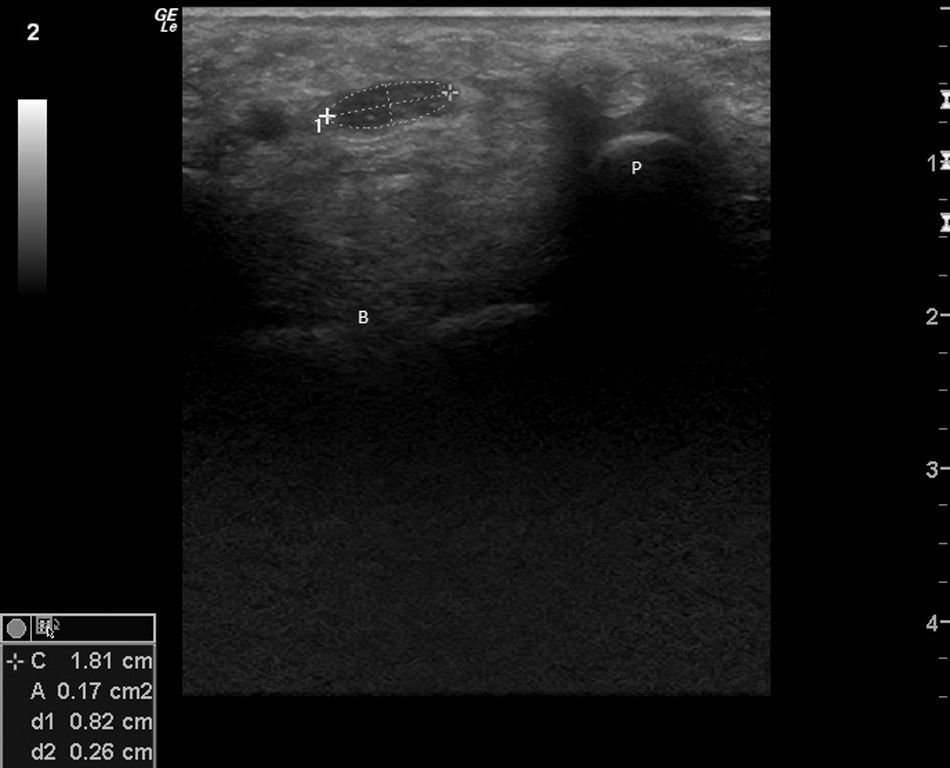
Transverse image of the right median nerve at the entrance of the carpal tunnel, with measurement of the nerve area with an ellipse (0.17cm2), at the pisiform level P (B: large bone). (Image obtained with a General Electrics LOGIC e ultrasound, with a lineal 8–12mHz transducer, using a frequency of 12mHz and maximal enlargement.)
Skin lesions are localized on the median nerve territory because, as reported in the literature, in severe CTS there may be perivascular sympathetic nervous system compromise in that distribution.3–5 This patient also presented a remnant of the median artery, an uncommon anatomical variant6 generally associated to a bifid median nerve, leading to a greater repercussion on the compression of structures in the tunnel, affecting tissue vascularization even further. Thrombotic phenomena and occlusion of the remnant artery may be triggered for CTS.7,8 The case presented had a unilateral remnant artery; we may suppose that if it had occurred bilaterally it may have occluded and increased symptoms. Severe hypoesthesia adds the possibility of presenting associated traumatic lesions.9,10 It is important to perform the diagnosis because a surgical option, through the liberation of the nerve at the retinaculum, could revert the lesions, impeding the appearance of severe complications. This clinical presentation with atrophy in severe, long-term CTS is currently infrequent because most of the patients have rapid access to specialized care.
ConclusionsFaced with a patient with possible systemic vasculitis but with limited hands, the clinician must make a differential diagnosis with severe CTS and secondary atrophy because the treatment is very different and the use of steroids and immunosuppresants will not benefit these patients.
Please, cite this article as: Areny-Micas R, et al. Alteraciones vasculares en síndrome del túnel carpiano severo: un diagnóstico diferencial de vasculitis. Reumatol Clin. 2012;8(1):36–38.