To describe the prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), the association between FIB4 and ultrasound findings, and the clinical characteristics of psoriatic arthritis patients.
Material and methodsWe carried out an observational cross-sectional study of patients seen in the outpatient clinic from January 1st, 2020, to November 30th, 2020, with psoriatic arthritis.
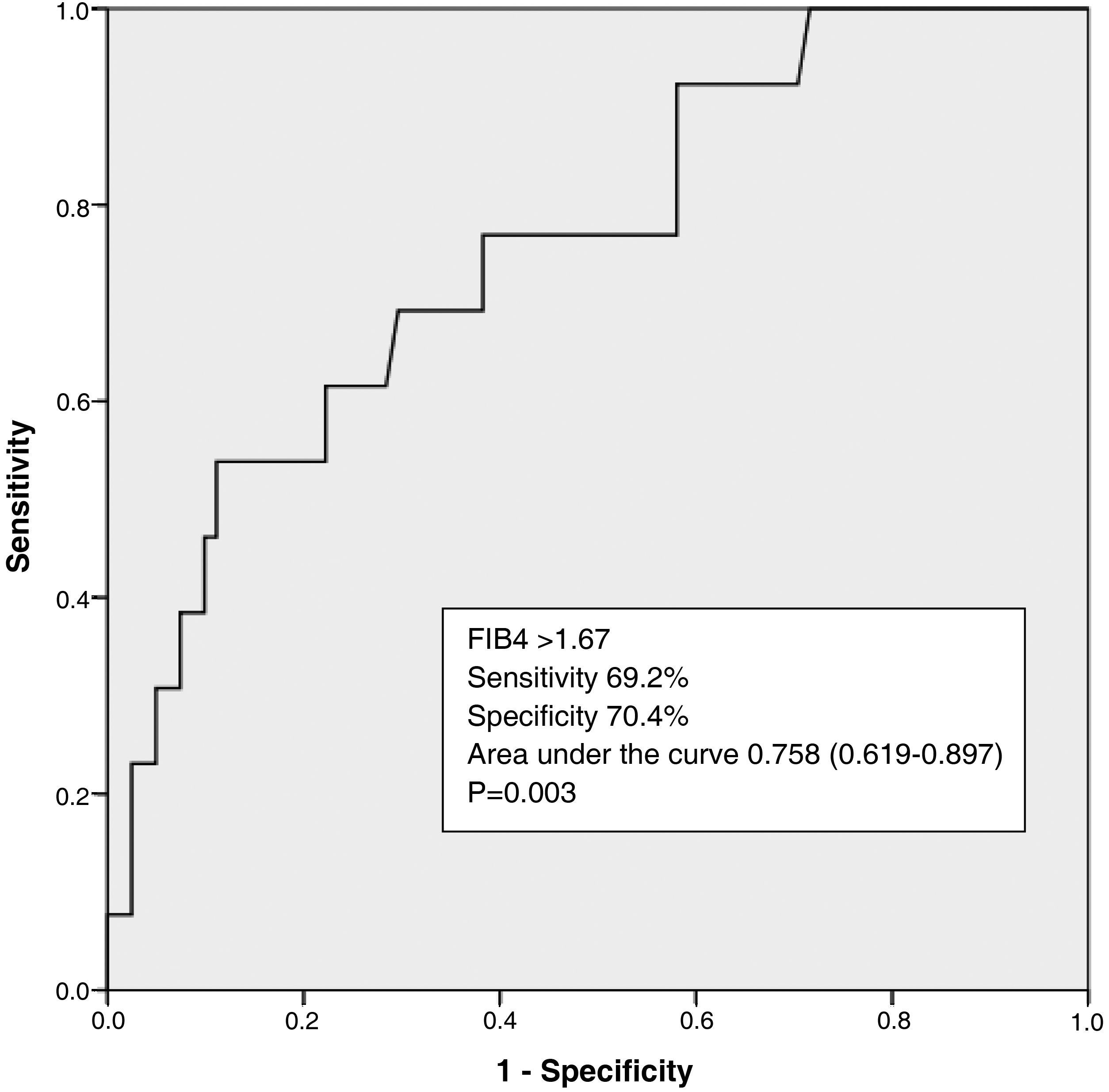
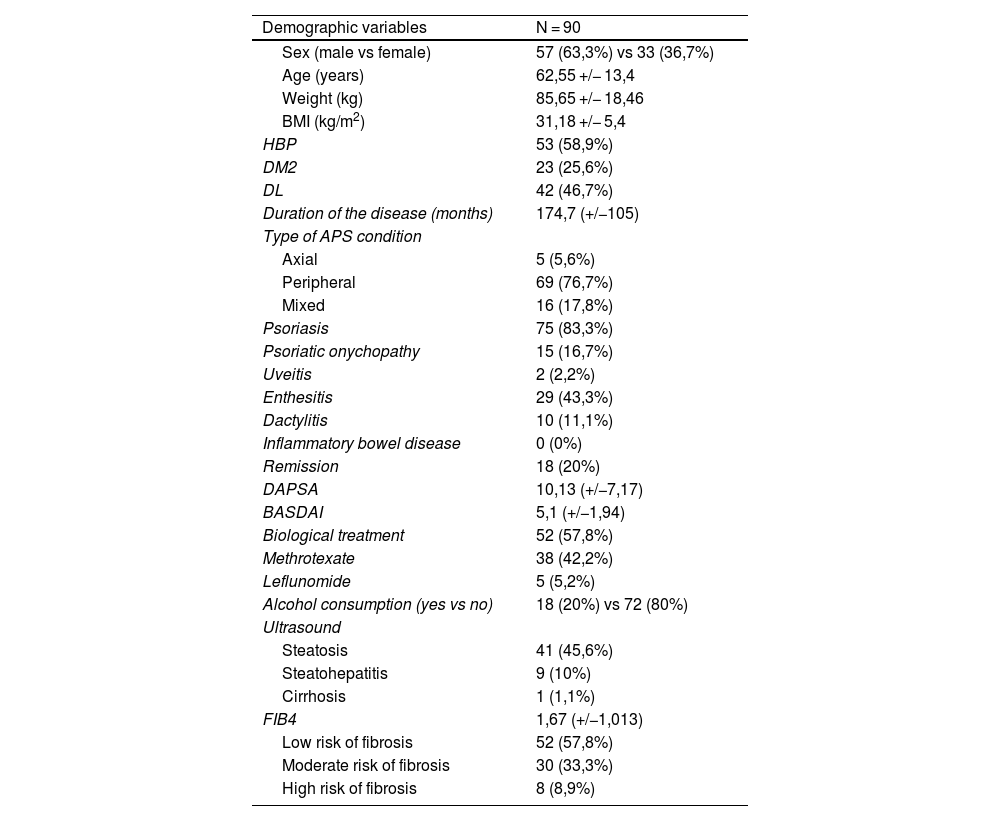
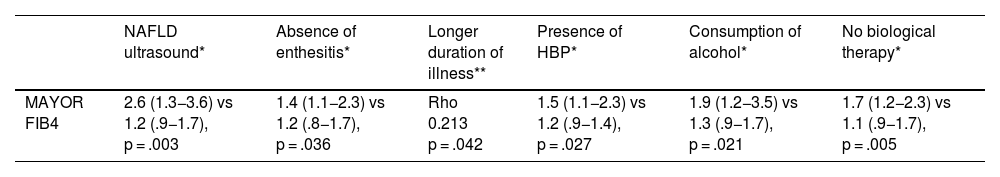
ResultsOf the 90 patients studied, the prevalence of NAFLD was 56.67%. FIB4 presents an association with ultrasound findings (p = .030), the absence of enthesitis (p = .036), and longer duration of disease (Rho .213 p = .042). It also presents an association with hypertension (p = .027) and alcohol consumption (p = .021). However, biological treatment can be considered as a protective factor (p = .005). FIB4 acts as a NAFLD predictor with 69.2% sensitivity and 70.4% specificity.
ConclusionsThe prevalence of NAFLD was higher in our sample than in the standard population. FIB4 index may be useful in screening for silent liver damage in psoriatic arthritis in clinical practice.
Describir la prevalencia de la enfermedad del hígado graso no alcohólico (EHGNA), la asociación entre FIB4 y los hallazgos en la ecografía y las características clínicas de los pacientes con artritis psoriásica.
Material y métodosEstudio transversal observacional de todos los pacientes con artritis psoriásica vistos de forma consecutiva en consulta desde 01/01/2020 hasta el 30/11/2020.
ResultadosDe los 90 pacientes estudiados la prevalencia de EHGNA fue de 56,67%. EL FIB4 presenta asociación con la ecografía (p = 0.030), la ausencia de entesitis (p = 0.036) y la mayor duración de la enfermedad (Rho 0.213 p = 0.042). También con la presencia de hipertensión (p = 0.027) y el consumo de alcohol (p = 0.021). Sin embargo, el tratamiento biológico puede considerarse como un factor protector (p = 0.005). El FIB4 actúa como predictor de EHGNA con una sensibilidad 69.2% y especificidad 70.4%.
ConclusionesLa prevalencia de EHGNA fue superior a la población general. El índice FIB4 puede ser una herramienta válida en el despistaje de EHGNA en nuestra práctica clínica diaria.