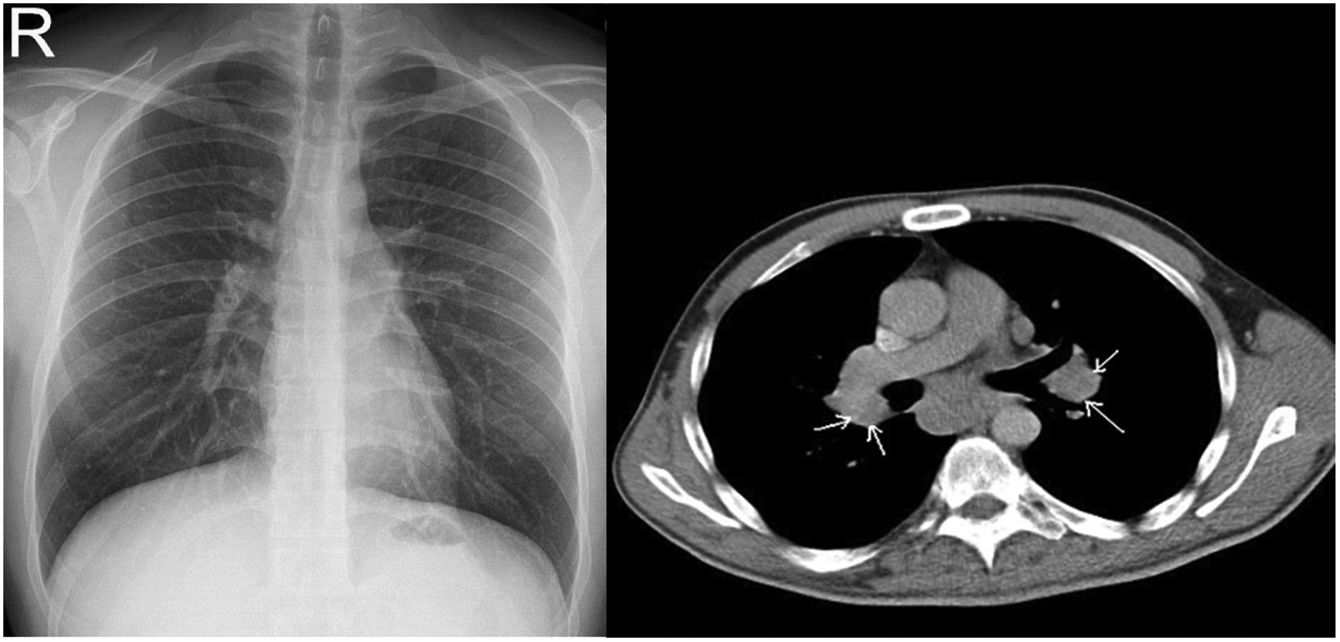
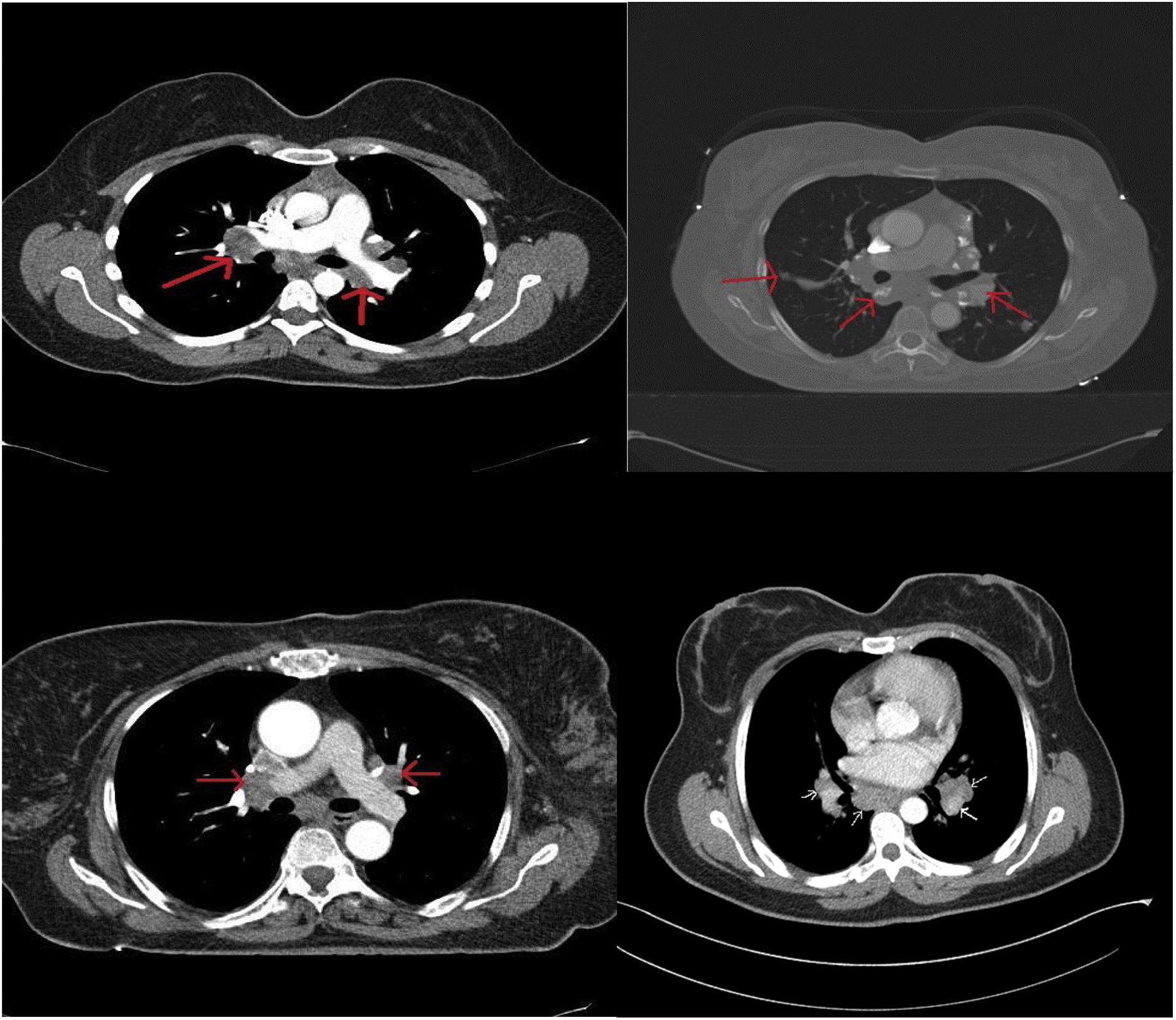
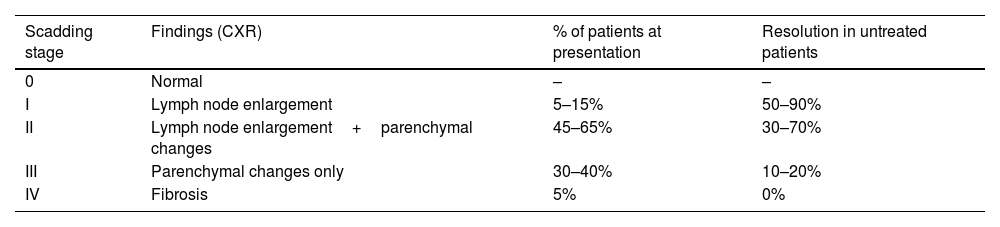
Sarcoidosis is a chronic granulomatous disease characterized by non-caseating granuloma. The conventional chest X-ray (CXR) has important role in the diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Computed tomography (CT) is a second-line imaging method used to determine the extent, complications and differential diagnosis of sarcoidosis.
ObjectivesTo determine the role of CXR in the early diagnosis and staging of sarcoidosis and to compare with CT imaging.
MethodsOne hundred and nine sarcoidosis patients followed at a single center were included in the study. Demographic, radiological, and clinical data of 81 patients were obtained from a total of 109 patients, and the record data of these 81 patients were evaluated. Patients who could not be reached for all tests were excluded from the study. CXR and CT imaging taken at diagnosis were evaluated retrospectively independently from two radiologists and one rheumatologist.
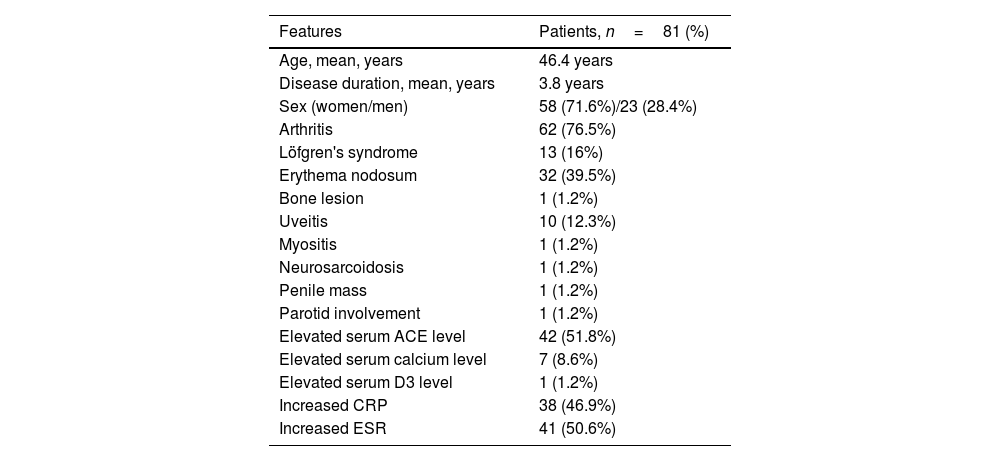
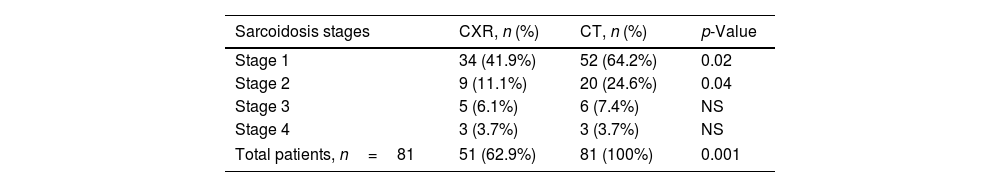
ResultsAmong 109 patients, eighty-one patients CXR and CT imaging taken at the same center has been reached. Among 81 sarcoidosis patients 23 (28.4%) were male, 58 (71.6%) were female. The mean patients age was 46.4 years and the mean disease duration was 3.8 years. CXR is regarded as normal at diagnosis in 30 patients (37%), while all of these patients had findings consistent with sarcoidosis on CT imaging. CT imaging are more superior than CXR in the early diagnosis and staging of sarcoidosis (p=0.001). Also CT imaging is more superior for detection of disease extent and complications.
ConclusionsIn this study, we observed that CT imaging outperforms CXR in terms of early detection and staging of sarcoidosis. The use of CT imaging is important for early diagnosis and staging of sarcoidosis. The low performance of CXR is a condition that requires the discussion of this method. Multicenter prospective study is needed in this regard.
La sarcoidosis es una enfermedad granulomatosa crónica caracterizada por un granuloma no caseificante. La radiografía de tórax convencional (CXR) tiene un papel importante en el diagnóstico, estadificación y seguimiento de la enfermedad. La tomografía computarizada (TC) es un método de imagen de segunda línea que se utiliza para determinar la extensión, las complicaciones y el diagnóstico diferencial de la sarcoidosis.
ObjetivosDeterminar el papel de la radiografía de tórax en el diagnóstico temprano y la estadificación de la sarcoidosis y compararlo con la tomografía computarizada.
MétodosSe incluyeron en el estudio 109 pacientes con sarcoidosis seguidos en un solo centro. Se obtuvieron datos demográficos, radiológicos y clínicos de 81 sujetos de un total de 109 pacientes, y se evaluaron los datos de registro de estos 81 individuos. Los pacientes que no pudieron ser contactados para todas las pruebas fueron excluidos del estudio. Las imágenes de CXR y CT tomadas en el momento del diagnóstico fueron evaluadas retrospectivamente de forma independiente por 2 radiólogos y un reumatólogo.
ResultadosDe un total de 109 pacientes se han obtenido imágenes de CXR y CT, tomadas en el mismo centro, de 81 individuos. De esos 81 pacientes con sarcoidosis 23 (28,4%) eran hombres y 58 (71,6%) eran mujeres. La edad media de los pacientes fue de 46,4 años y la duración media de la enfermedad fue de 3,8 años. La CXR se considera normal en el momento del diagnóstico en 30 pacientes (37%), mientras que todos estos pacientes tenían hallazgos consistentes con sarcoidosis en la TC. La TC es superior a la radiografía de tórax en el diagnóstico temprano y la estadificación de la sarcoidosis (p=0,001) y en la detección de la extensión de la enfermedad y las complicaciones.
ConclusionesEn este estudio observamos que la TC supera a la radiografía de tórax en términos de detección temprana y estadificación de la sarcoidosis. El uso de imágenes por TC es importante para el diagnóstico precoz y la estadificación de la sarcoidosis. El bajo rendimiento de CXR es una condición que requiere la discusión de este método. Son necesarios estudios prospectivos multicéntricos al respecto.