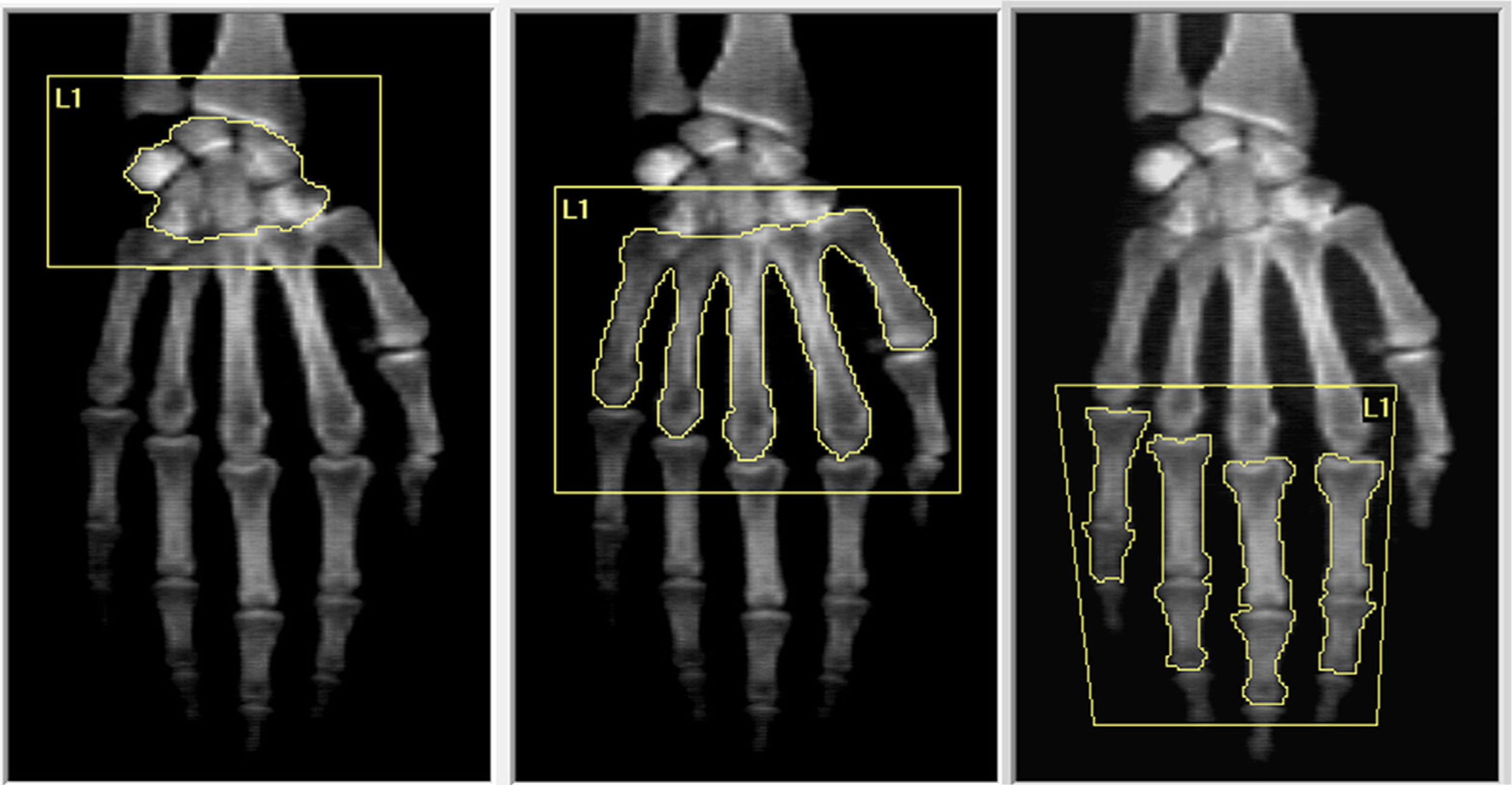
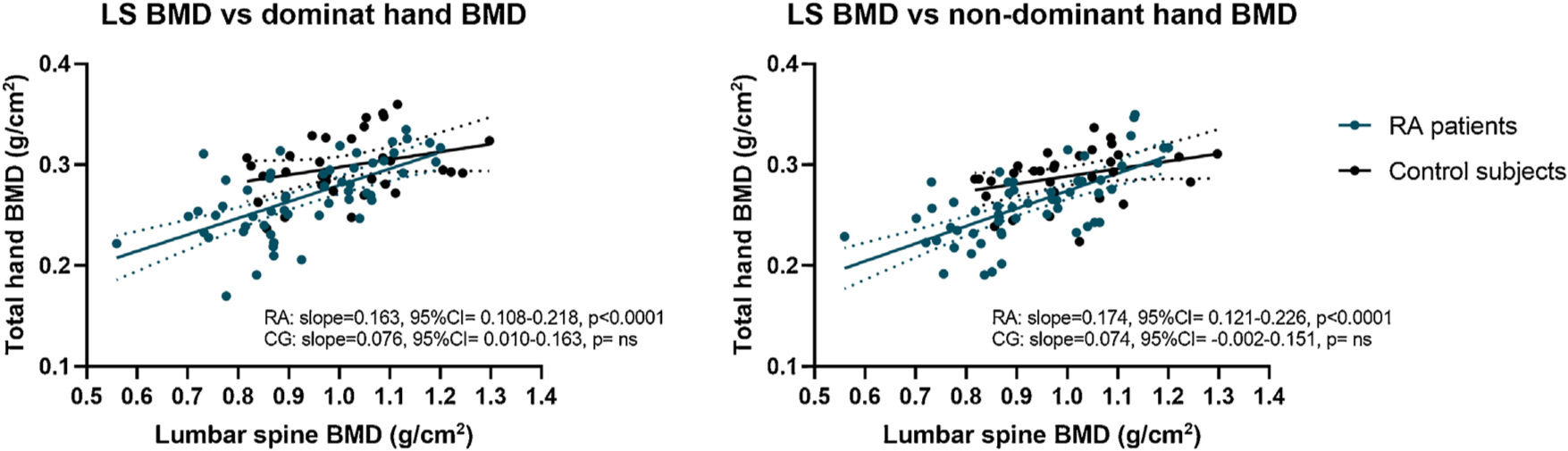
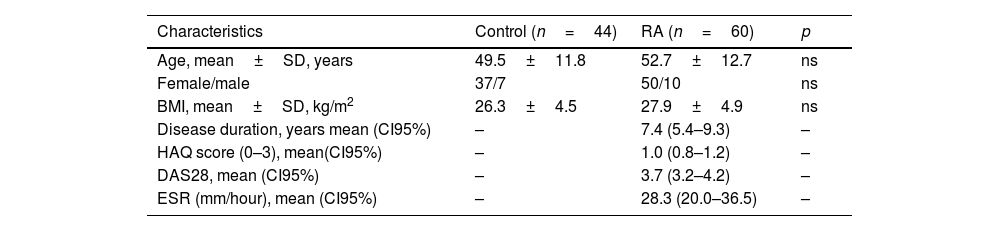
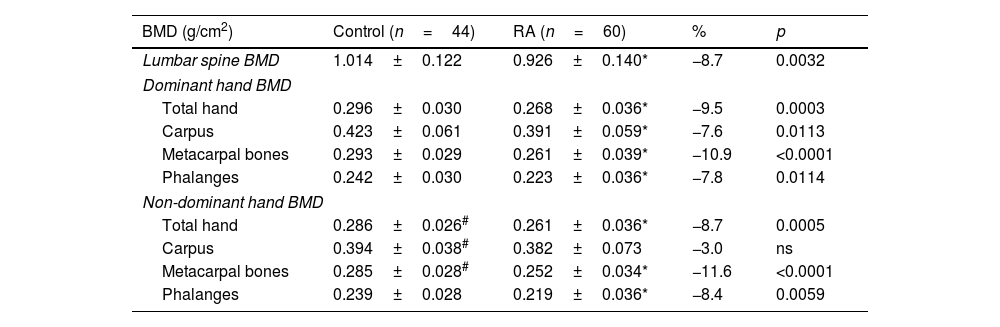
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by symmetric polyarthritis that can lead to joint deformity, disability, and osteoporosis. We aimed to evaluate whole hand and regional BMD in RA patients compared to controls. In addition, we evaluated the BMD of dominant versus non-dominant hands in healthy subjects. We included adult female and male RA patients and control subjects matched by age, sex, and BMI. BMD (g/cm2) was measured by DXA in lumbar spine (LS), whole hand, and three regions of interest: carpus, metacarpal bones, and phalanges. Results: 44 control subjects (49.5±11.8 y) and 60 with RA (52.7±12.7 y) were included. Significant lower BMD in RA patients was found in LS (−8.7%), dominant whole hand (−9.5%), carpus, metacarpal bones, and phalanges, and non-dominant whole hand (−8.7%), metacarpal bones, and phalanges compared to controls. A significant positive correlation was found between LS and whole-hand BMD (dominant r=.63, non-dominant r=.67). Finally, the whole hand, metacarpal bones, and carpus BMD measurements were significantly higher in the dominant hand compared to the non-dominant hand without differences in the phalangeal ROI. In conclusion, hand BMD was significantly lower in RA patients compared to control subjects and there was a significant correlation with LS BMD. We demonstrated that BMD measurements of the whole-hand, and different ROI (carpus, metacarpal bones, and phalanges) by DXA would be an easily reproducible technique to evaluate bone loss. In addition, the whole hand, metacarpal bones and carpus BMD measurements were significantly higher in the dominant hand compared to the non-dominant hand without differences in the phalanges.
La artritis reumatoide (AR) es una enfermedad autoinmune crónica caracterizada por poliartritis simétrica que puede provocar deformidad e incapacidad articular y osteoporosis. Nuestro objetivo fue evaluar la DMO de manos completa y por regiones en los pacientes con AR en comparación con los controles. Se incluyeron pacientes adultos de ambos sexos con AR, y sujetos controles de edad, sexo e IMC similar. La DMO se midió por DXA en columna lumbar (CL), manos completas y 3 regiones de interés: carpo, metacarpianos y falanges. Resultados: se incluyeron 44 sujetos control (49,5±11,8 años) y 60 con AR (52,7±12,7 años). Se encontró una DMO significativamente más baja en los pacientes con AR en CL (−8,7%), mano completa dominante (−9,5%) y mano completa no dominante (−8,7%) en comparación con los sujetos controles. Se encontró una correlación positiva significativa entre la CL y la DMO de la mano completa (dominante, r=0,63; no dominante, r=0,67). Finalmente, la DMO de la mano completa, los huesos metacarpianos y el carpo fueron significativamente más altos en la mano dominante en comparación con la mano no dominante sin diferencias en la región de las falanges. En conclusión, la DMO de la mano fue significativamente menor en los pacientes con AR en comparación con los sujetos controles, y hubo una correlación significativa con la DMO de la CL. Demostramos que las mediciones de la DMO de toda la mano y diferentes ROI (carpo, huesos metacarpianos y falanges) por DXA serían una técnica fácilmente reproducible para evaluar la pérdida ósea. Además, la DMO de la mano completa, los huesos metacarpianos y el carpo fueron significativamente más altos en la mano dominante en comparación con la mano no dominante.