To assess the bone mineral density (BMD) and the frequency of osteoporosis and clinical fractures in a large group of Spanish patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Patients and methodsBMD was determined by DXA in all the patients who were willing to participate and had peripheral PsA regularly evaluated in a tertiary university hospital. All patients underwent a physical examination and general laboratory analysis. We gathered demographic and clinical variables related with BMD and risk of fractures. We also recorded the history of clinical low impact fractures. The population of reference to calculate T-score and Z-score came from a Spanish database.
ResultsOne hundred and fifty-five patients were included (64 postmenopausal women, 26 premenopausal women and 65 men). The clinical forms of PsA were: 46% oligoarticular and 54% polyarticular. Mean disease duration was 13.7±9.4 years and mean ESR was 21.8±13.9mm/h; 66% of patients had received glucocorticoid treatment.
We found no differences in BMD status between the patients and the Spanish general population, neither in the whole series nor in each defined subgroup. Frequency of osteoporosis was 16%; it was higher in postmenopausal women (28%) than in men (9%) or premenopausal women (4%). Frequency of clinical fractures was 13%; it accounted specially in postmenopausal women.
ConclusionsThe magnitude of the problem of osteoporosis in PsA seems to be mild.
Analizar el estado de la densidad mineral ósea (DMO) así como la frecuencia de osteoporosis y de fracturas clínicas en una serie de pacientes con artritis psoriásica (APs).
Pacientes y MétodoSe determinó la DMO, mediante DXA, en todos los pacientes con APs periférica, evaluados de forma periódica en un hospital universitario, que aceptaron participar en el estudio. Se les practicó una exploración física y un estudio analítico y se recabó información acerca de variables clínicas relacionadas con la DMO y con el riesgo de fractura. Asimismo, se analizó si existía el antecedente de haber presentado una fractura de bajo impacto. El cálculo del T-score y del Z-score se realizó a partir de una base de datos de población española.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 155 pacientes (64 mujeres posmenopáusicas, 26 mujeres premenopáusicas y 65 varones). En el 46% de los casos la APS adoptó un patrón oligoarticular y en el 54% poliarticular. La duración media de la enfermedad fue 13.7±9.4 años, el valor medio de la VSG fue de 21.8±13.9mm/h; el 66% de los pacientes habían recibido tratamiento con glucocorticoides.
No se observaron diferencias entre la DMO de los pacientes y la de la población general, ni en la globalidad de la serie, ni en ninguno de los tres grupos. La frecuencia global de osteoporosis se situó en el 16%; fue más alta en las mujeres posmenopáusicas (28%) que en los varones (9%) y que en las mujeres premenopáusicas (4%). La frecuencia de fracturas clínicas fue del 13%; acontecieron fundamentalmente en las mujeres posmenopáusicas.
Chronic inflammation, including autoimmune disease, is a strong trigger for the development of osteoporosis1.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the paradigm of chronic inflammatory diseases that are frequently accompanied by bone loss. It has been long recognized that osteoporosis is a relevant co-morbid condition in both female2 and male3 patients with RA. Disease activity, decreased functional capacity, and corticosteroid use have been identified as the most important causative factors.4
Psoriasis5 and psoriatic arthritis (PsA)6,7 are chronic, immuno-mediated inflammatory diseases characterized by abnormal expressions of keratinocytes, as well as proliferation and neovascularization of the synovial.
Although patients with PsA seem to have local and systemic osteoporosis,8 little is known concerning the actual degree of bone loss. Nowadays, certain issues, specially related to the magnitude of the problem in practice, remain to be clarified.9
We report a cross-sectional study that used dual X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) to evaluate BMD at the lumbar spine and the hip and the frequency of osteoporosis and clinical fractures in 155 Spanish patients with peripheral PsA.
Patients and methodsStudy settingThe study was performed at the Rheumatology Department of the Hospital Universitari de Bellvitge. Our department has developed a standardized protocol to collect information on PsA patients. Collected data include medical history, physical, laboratory and imaging study findings, and management.
PatientsWe considered for the current study all PsA patients who had been attended within one-year period (n=202) in our outpatient clinics.
We excluded patients who met any of the following criteria: (a) disease duration <1 year (n=12), (b) evidence of ankylosing spondylitis (psoriatic spondyloarthropathy) (n=18) and (c) current clinical remission, defined as the absence of articular signs and symptoms for the last 6 months (n=14). Patients with axial involvement were excluded in order to avoid interferences in BMD measurement due to syndesmophytes.
One hundred and fifty-eight patients were invited to participate in the study; 155 gave their informed consent. All patients fulfilled the diagnostic criteria for PsA defined by the Classification of Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) study.10 None had received hormone replacement therapy or any drug for osteoporosis treatment other than calcium or vitamin D.
Outcome measureA full medical history was obtained and a complete physical examination was undergone. The following data were recorded: (1) gender, (2) menopausal status, (3) age, (4) body mass index (BMI), (5) duration of PsA, (6) type of PsA: oligoarticular (one to four swollen joints) or polyarticular (five or more swollen joints), (7) cutaneous involvement, (8) onychopathy, (9) uveitis, (10) glucocorticoid treatment, (11) disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARD) use, (12) biological therapy use, (13) erythrocyte sedimentation rate evaluated by the Westergren method (the value of the last routine determination was considered), (14) functional status; it was measured by the modified Health Assessment Questionnaire (mHAQ), and (15) personal history of low impact fractures. All patients were referred to the Bone Densitometry Unit of our department. BMD (g/cm2) was measured at the lumbar spine (L2–L4) and the hip by DXA (Hologic QDR 4500, Hologic Inc., Waltham, MA). The T-score (comparison with normal subjects of the same sex with peak bone mass) and the Z-score (comparison with age and sex matched normal controls) were established by comparison with data from the study of BMD at the lumbar spine and femoral neck in a Spanish population performed by the Multicentre Research Project on Osteoporosis (MRPO).11
Osteopenia (T-score between −1.0 and −2.5) and osteoporosis (T-score below −2.5) were defined according to the criteria of the World Health Organization.12 Additionally, according to the International Society of Clinical Densitometry,13 in premenopausal women and in male younger than 50 years, we calculated the percentage of patients that presented a BMD below the expected range for age (Z-score of −2 or lower).
In 2 patients with bilateral hip prosthesis, only lumbar BMD was available. In other 2 patients, lumbar BMD was not determined because of the antecedent of instrumented surgery of the spine.
Statistical analysisThe study variables were tabulated as means and standard deviations (SD), or proportions as applicable. Confidence interval (CI) was used to assess the difference between the mean Z-score at each site and the general population. Differences between groups of patients were assessed by ANOVA and chi squared tests. Statistical significance was set at p<0.05.
ResultsTable 1 shows the demographic and clinical characteristics of the patients included in the study.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients.
| Overall series (n=155) | Premenopausal women (n=26) | Postmenopausal women (n=64) | Male (n=65) | |
| Age, years | 55.51±13.53 | 39.35±6.74 | 62.63±8.03 | 55.06±14.18 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 27.20±4.86 | 25.67±6.12 | 28.25±5.02 | 26.88±3.92 |
| PsA duration, years | 13.65±9.37 | 9.12±6.95 | 15.60±8.57 | 13.57±10.41 |
| Type of PsA | ||||
| • Oligoarticular | 71 (46%) | 15 (58%) | 32 (50%) | 24 (37%) |
| • Polyarticular | 84 (54%) | 11 (42%) | 32 (50%) | 41 (63%) |
| Cutaneous involvement | 148 (96%) | 25 (96%) | 62 (97%) | 61 (94%) |
| Onychophathy | 91 (59%) | 13 (50%) | 35 (55%) | 43 (66%) |
| Uveitis | 3 (2%) | – | 2 (3%) | 1 (2%) |
| Glucocorticoids | ||||
| • Ever users | 102 (66%) | 13 (50%) | 45 (70%) | 44 (68%) |
| • Cumulative dose, g | 3.21±5.89 | 1.31±3.50 | 3.56±6.03 | 3.64±6.45 |
| DMARD | ||||
| Ever users | 131 (85%) | 21 (81%) | 63 (83%) | 57 (88%) |
| Biological therapy | ||||
| Ever users | 23 (15%) | 6 (23%) | 9 (14%) | 8 (12%) |
| ESR, mm/h | 21.84±13.85 | 21.40±12.72 | 25.37±15.04 | 18.31±12.26 |
| HAQ | 0.68±0.61 | 0.50±0.46 | 0.99±0.68 | 0.44±0.44 |
PsA: psoriatic arthritis; DMARD: disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs; ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; HAQ: Health Assessment Questionnaire.
Table 2 shows the densitometric status of the patients included in the study.
Densitometric status of the patients.
| Lumbar spine | Femoral neck | Total hip | |
| Overall series (n=155) | |||
| BMD, g/cm2 | 0.964±0.135 | 0.766±0.128 | 0.901±0.151 |
| T-score (95% CI) | −0.63±1.24(−3.6 to 2.8) | −0.80±1.13(−3.5 to 3.1) | −0.92±1.16(−3.2 to 2.9) |
| Z-score (95% CI) | 0.1±0.97(−2.1 to 3.0) | −0.01±1.11(−2.2 to 3.9) | −0.07±1.17(−2.7 to 3.6) |
| Female (n=90) | |||
| BMD, g/cm2 | 0.945±0.141 | 0.743±0.128 | 0.860±0.147 |
| T-score (95% CI) | −0.87±1.36(−1.2 to −0.6) | −0.79±1.25(−1.1 to −0.5) | −0.97±1.24(−1.2 to −0.7) |
| Z-score (95% CI) | 0.20±1.04(−0.1 to 0.4) | −0.10±1.15(−0.2 to 0.3) | −0.56±1.20(−0.3 to 0.2) |
| Premenopausal women (n=26) | |||
| BMD, g/cm2 | 1.033±0.108 | 0.807±0.103 | 0.906±0.134 |
| T-score (95% CI) | −0.02±1.03(−0.44 to 0.40) | −0.17±1.03(−0.5 to 0.24) | −0.60±1.15(−1.06 to −0.13) |
| Z-score (95% CI) | 0.07±1.01(−0.33 to 0.48) | −0.10±1.01(−0.51 to 0.31) | −0.40±1.19(−0.88 to 0.08) |
| Postmenopausal women (n=64) | |||
| BMD, g/cm2 | 0.909±0.138 | 0.717±0.128 | 0.840±0.149 |
| T-score (95% CI) | −1.22±1.33(−1.56 to–0.89) | −1.04±1.24(−1.36 to 0.73) | −1.12±1.25(−1.44 to −0.81) |
| Z-score (95% CI) | 0.26±1.06(−0.01 to 0.53) | 0.18±1.20(−0.13 to 0.48) | 0.08±1.19(−0.22 to 0.38) |
| Male (n=65) | |||
| BMD, g/cm2 | 0.991±0.121 | 0.797±0.122 | 0.957±0.138 |
| T-score (95% CI) | −0.31±0.96(−0.6 to −0.1) | −0.83±0.96(−1.1 to −0.6) | −0.86±1.06(−1.1 to −0.6) |
| Z-score (95% CI) | −0.03±0.86(−0.2 to 0.2) | −0.17±1.05(−0.4 to 0.1) | −0.09±1.12(−0.4 to 0.2) |
BMD: bone mineral density.
Table 3 shows the frequency of osteoporosis according to the WHO criteria in the whole series and in each defined subgroup.
Frequency of osteoporosis in the overall series and in each defined subgroup.
| Lumbar spine | Femoral neck | Total hip | Any site | |
| Overall series(n=155) (95%CI) | 7%(4%–12%) | 6%(3%–11%) | 11%(7%–17%) | 16%(11%–23%) |
| Premenopausal women(n=26) (95%CI) | – | – | 4%(1%–19%) | 4%(1%–19%) |
| Postmenopausal women (n=64) (95%CI) | 17%(10%–28%) | 13%(7%–23%) | 16%(9%–26%) | 28%(19%–40%) |
| Men(n=65) (95%CI) | – | 1%(0%–8%) | 9%(4%–19%) | 9%(4%–19%) |
In premenopausal women, the frequency of patients, that presented, in at least one of the evaluated sites, a BMD below the expected range for age was 15% (4/26); in males younger than 50, it was 19% (4/21).
Fifty-nine (38%) patients had a normal BMD (T-score≥−1 SD) both in the lumbar spine and hip (femoral neck and total hip). Patients with a normal BMD were younger (52.05±11.92 vs 57.59±14.07 years, p<0.05), had a shorter duration of PsA (11.00±7.39 vs 15.33±10.11 years, p<0.01), had a higher BMI (28.69±5.19 vs 26.28±4.43, p<0.01) and presented a better HAQ (0.51±0.46 vs 0.78±0.67, p<0.01).
No differences were found in BMD between patients with oligoarticular and polyarticular involvement.
Thirteen percent of the patients (19/155) had had a clinical low-trauma fracture. This complication accounted specially in postmenopausal women (16 cases, 84%). The most frequent localization was the forearm (10 cases); one case of vertebral fracture and another of hip fracture were found. Clinical and demographic data were similar in patients with and without fracture.
DiscussionWe have analyzed the BMD status, the frequency of osteoporosis and the clinical fractures in a large group of Spanish patients with PsA. We found no differences in BMD status between the patients and the Spanish general population. In the overall series, frequency of osteoporosis was 16% and frequency of clinical fractures, 13%. As expected, frequency of osteoporosis was clearly higher in postmenopausal women (28%) than in men (9%) or premenopausal women (4%); in this way, the majority of clinical fractures accounted in postmenopausal women.
To date, few studies are available in which BMD has been evaluated, using DXA, in patients with psoriasis and, more surprisingly, in patients with PsA.
In a recent study, Dreiher et al.14 analyzed the prevalence of osteoporosis in a large database of patients with psoriasis (7936 subjects). No difference was found among women, while among men, patients with psoriasis showed a higher prevalence than controls (14.835 subjects).
Unfortunately, the studies that identify patients with arthritis deal with smaller sample sizes. In the 1990s, our group15 measured BMD in 52 patients with PsA (14 premenopausal women, 19 postmenopausal women and 19 men); the only difference in densitometric data was at the femoral neck in the postmenopausal subgroup, with a BMD significantly lower than in controls. More recently, Borman et al.16 evaluated, by DXA, BMD at lumbar spine and total hip in a series of 47 patients (24 premenopausal women, 23 men) with psoriasis (18 with PsA). There was no significant difference between the BMD levels of psoriatic patients with and without arthropathy.
Only two studies17,18 on the prevalence of osteoporosis in patients with PsA include a substantial number of subjects.
Frediani et al.17 studied 186 patients with peripheral PsA and 100 healthy subjects, equally distributed in 3 groups: women of child-bearing age, women in menopause and men. No patient had received previously steroid treatment. BMD was significantly lower in the arthritic than in the healthy subjects regardless of gender, menopausal status, or age, as expressed in g/cm2 or by T and Z scores. Among PsA patients, osteoporosis in at least one skeletal region was observed in 11% of premenopausal women, 47% of postmenopausal women and 29% of men. In the whole series, age, BMI and HAQ were significant predictors of bone mass.
Hofbauer et al.18 studied 116 patients with peripheral PsA, 57 women (mean age 56±11yrs, 61% postmenopausal) and 59 men (mean age 49±13yrs). None of the patients had received glucocorticoids or DMARDs for the last 12 months and no patient had a history of long-term (>6 months) glucocorticoid therapy. Osteoporosis was detected in only one woman (1.75%), but in six men (10.2%).
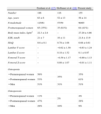
As Table 4 shows, the frequency of osteoporosis found in the present study is situated in an intermediate position with respect to the obtained by Frediani et al.17 and Hofbauer et al.18. The discrepancies between the results of these three studies probably may be ascribable to differences in the demographical, clinical and therapeutical variables with capacity to influence over bone mass.
| Frediani et al. (17) | Hofbauer et al. (18) | Present study | |
| Number | 186 | 116 | 155 |
| Age, years | 63±6 | 52±13 | 56±14 |
| Female/male | 125/61 | 57/59 | 90/65 |
| Postmenopausal women | 65 (35%) | 35 (61%) | 64 (41%) |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 22.3±2.8 | – | 27.20±4.86 |
| ESR, mm/h | 21±7 | 16±11 | 21.8±13.9 |
| HAQ | 0.6±0.1 | 0.78±1.08 | 0.68±0.61 |
| Lumbar T-score | – | −0.02±1.50 | −0.63±1.24 |
| Lumbar Z-score | – | 0.18±1.52 | 0.1±0.97 |
| Femoral T-score | – | −0.39±1.17 | −0.80±1.13 |
| Femoral Z-score | – | 0.08±1.07 | −0.01±1.11 |
| Osteopenia | |||
| • Premenopausal women | 56% | 35% | 35% |
| • Postmenopausal women | 53% | 61% | |
| • Men | 51% | 31% | 51% |
| Osteoporosis | |||
| • Premenopausal women | 11% | 2% | 4% |
| • Postmenopausal women | 47% | 28% | |
| • Men | 29% | 10% | 9% |
ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate. HAQ: Health Assessment Questionnaire.
In any case, it seems that it is possible to support that the intensity of bone loss in PsA is lower than the observed in RA, the major inflammatory arthropathy. PsA differs from RA in several ways, including more intermittent disease activity, milder inflammation, milder functional impairment, and less frequent use of glucocorticoids; these differences may result in a better bone mass preservation in PsA as compared to RA. Additionally, the difference in bone involvement between the two diseases could be largely determined by a different balance and expression of the factors controlling the coupling cycle of bone remodelling8.
There is a relevant absence of data on fracture in patients with PsA. Information is available only in one recent study, published by Pedreira et al.19 Data refer to a sample of 45 postmenopausal women with PsA (mean age: 60.5±8.7yrs), 52 patients with psoriasis (mean age: 61.4±9.1yrs) and 98 healthy controls. The prevalence of fragility fractures among patients with PsA (33%) was significantly greater than that observed in patients with psoriasis (28.8%). Both prevalence rates are reported as significantly greater compared to controls, but prevalence of fractures in controls is not provided. Interestingly, BMD data of lumbar spine and proximal femur are not significantly different in the 3 groups.
The frequency of fractures observed in the present study (13%) was clearly minor. Probably, this fact is consequence that, unlike Pedreira et al., we have not performed a thoracic and lumbar spine-X-ray analysis, in search of radiological vertebral fractures, a circumstance that constitutes a clear limitation of our study. However, every day clinical practice seems to suggest that osteoporotic fracture is not a prominent feature of the course PsA and the obtained data support this assumption. In fact, when we previously analyzed 669 patients with osteoporotic vertebral fracture diagnosed in our department over a 10-year period, only one case of PsA was observed.20
Our data, and the literature review, suggest that the magnitude of the problem of osteoporosis in PsA is mild. Nevertheless, it seems necessary to design large longitudinal prospective studies in order to characterize definitively the bone loss accounting in PsA patients. In addition, we need fracture studies than can define the risk of such an important complication, which may depend largely on factors other than BMD alone.
OpinionOsteoporosis does not appear to be a significant problem in patients with psoriatic arthritis.
Ethical responsibilitiesProtection of people and animalsThe authors declare that this research experiments have not been done in humans or animals.
Confidentiality of dataConfidentiality of data. The authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their workplace on the publication of data from patients and that all patients included in the study have received sufficient information and have given their informed consent to participate in the study.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.