A 47-year-old man presented with weight loss, bilateral calf pain, fever, hypertension, orchitis and oligoarthritis. Lab tests: anemia and elevated muscle enzymes. Resonance magnetic imaging: hyperintensity in gastrocnemius muscles (myositis). Histologic exam of the muscles: inflammatory infiltrate with atrophy and perifascicular regeneration. Treatment: methylprednisone (bolus) and cyclophosphamide. Muscle pain and swelling and difficulty in walking are common in panarteritis nodosa (PAN), whereas histologically demonstrated myositis is not. Even more rare is myositis as the initial presentation of this vasculitis.
Varón de 47 años que consulta por pérdida de peso, dolor con tumefacción en pantorrillas, fiebre, hipertensión arterial, orquitis y oligoartritis. Laboratorio: anemia y aumento de enzimas musculares. Resonancia magnética: hiperintensidad en gemelos (miositis). Histología de músculo: infiltrado inflamatorio con atrofia y regeneración perifascicular. Tratamiento: pulsos de metilprednisolona y ciclofosfamida. Mialgias, tumefacción muscular y deambulación dificultosa son hallazgos comunes en poliarteritis nodosa (PAN), no así la miositis demostrada histológicamente y más infrecuente aún como forma de inicio de esta vasculitis.
Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) is a necrosing arthritis of the small and medium-sized arteries, with no glomerulonephritis and not associated with ANCA.1 The organs most affected are the skin, gastrointestinal tract, kidney, peripheral nerves, heart, liver, pancreas, testicles, the nervous system and the muscles.2
Muscular manifestations are common (51%), consisting of muscular swelling, gait difficulty and myalgia, which might be due to compromised intramuscular arteries, neuropathy due to involvement of the peripheral nervous system or, more rarely, to myositis.3–8
We describe a case of PAN presenting with calf pain due to myositis as a form of onset of this vasculitis.
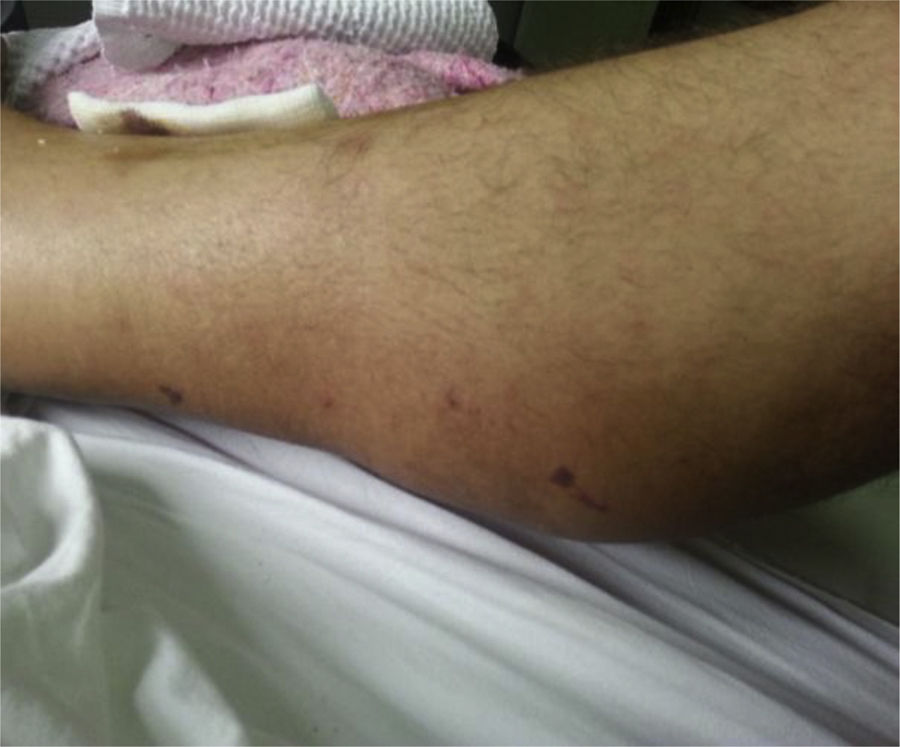
Clinical ObservationA 47-year-old male consulted with a one-month history of weight loss (10kg) and spontaneous, incapacitating calf pain. Physical examination: fever (38.5°C) predominantly in the evening, tachycardia, blood pressure 160/100mmHg, erythematous lumps in the twin muscles (approximately 6×10cm), of hard-elastic consistency and warm, and thermalgesic sensitivity was preserved (Fig. 1). Erythematous purpuric macules were also observed on the anterior and posterior surfaces of the legs, testicular pain on palpation, and arthritis in carpi, metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints.
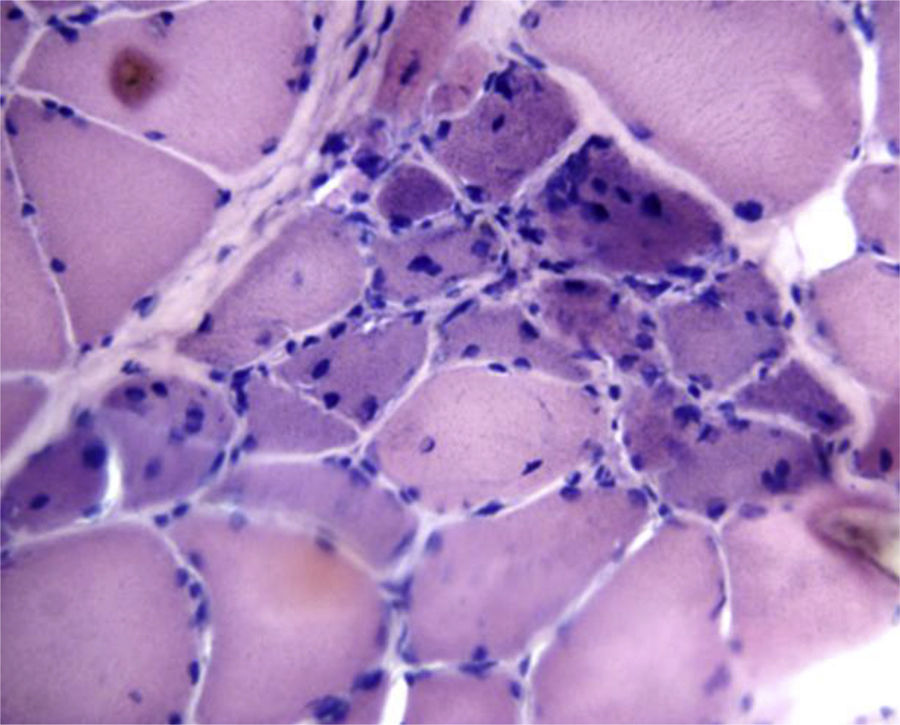
Laboratory tests: anaemia with haemoglobin: 10g/dl (11.9–15g/dl), white cells 25,160k/μl (4500–10,000), platelets 634,000k/μl (150,000–400,000), GTO: 144U/l (up to 38), TGP: 192U/l (up to 46), alkaline phosphatase 448U/l (35–105), direct bilirubin .31mg/dl (up to .20), CPK 1232IU/l (<135), LDH 233 (<460), aldolase 10U/l (<3), ESR 119mm/1h (up to 20), CRP 317mg/l (0–5). Renal function and serologies for hepatitis B and C; HIV, ANF (HeP-2), nDNA (Crithidia), ENA, p-ANCA and c-ANCA and complements: negative or normal. MRI showed hyperintensity in the twin muscles compatible with myositis, while electromyography of the upper and lower limbs showed a motor-sensitive polyneuropathy with decreased sural nerve conduction speed. Inflammatory infiltration, atrophy and focal perifascicular regeneration was found on muscle biography (Fig. 2). Biopsy of the sural nerve showed moderate myelinated fibre depletion and signs of axonal degeneration along with extensive lymphocytic infiltration around the small epineurial vessels and the wall of the median artery.
The skin biopsy showed acute and chronic inflammatory infiltration of septal distribution and medium-sized vessels with vasculitic phenomena and fibrinoid necrosis of the septal wall with erythrocyte extravasation in the hypodermis. Aortography and total bone scan were normal.
With a diagnosis of PAN (Chapell Hill and ACR criteria: weight loss of more than 4kg, testicular pain, myalgia, polyneuritis demonstrated by electromyography, diastolic blood pressure higher than 90mmHg and medium-sized artery biopsy compatible with vasculitis) 3 pulses of intravenous methylprednisolone 1g/day were given, continuing with 60mg/day of oral meprednisone and monthly intravenous cyclophosphamide. The patient made good progress.
DiscussionPAN is a vasculitis that predominantly affects the small and medium-sized arteries. It affects the skin (20%), gastrointestinal tract (50%), kidneys (40%–60%) and peripheral nerves (60%). Muscle compromise is not a feature of this disease. Although myalgia, swelling and impossibility of walking can present in 51% of patients,8 myositis is found in 19% of these diseases,3 and there are only 14 cases reporting this compromise as a form of onset of this vasculitis.2,6,7
The muscle enzymes are elevated in only 5% of cases, as occurred in the case we describe. The CPK enzymes (5%–25%) are the most altered, and elevated LDH and aldolase have been reported in some cases.
These cases must be differentiated from polymyositis and myositis of other origins, and therefore diagnosis relies on anatomical pathology. It is appropriate to choose the biopsy site by MRI, which shows increased signal intensity on the T2 and STIR sequences, indicating inflammatory changes.4–7 Almost all the patients reported underwent a muscular biopsy, compatible with vasculitis.3,9,10
This is the first described case with myositis demonstrated by histology. These histological signs might have gone unnoticed in previous cases.
ConclusionPerhaps we ought to broaden the spectrum when analysing muscle biopsies for PAN and look for signs of vasculitis as well as myositis.
Ethical DisclosuresProtection of people and animalsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflict of InterestThe authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Please cite this article as: Calvo R, Negri M, Ortiz A, Roverano S, Paira S. Miositis como forma de presentación de panarteritis nodosa. Reumatol Clin. 2019;15:e24–e26.