Paraneoplastic syndromes can be presented in multiple ways, which include endocrinological, hematologic, rheumatologic and nephrologic manifestations. While most of the publications described solid tumors as responsible for these manifestations, hematologic neoplasms are important cause to consider as part of the differential diagnosis. We report the case of a 46 year-old man with seronegative symmetric polyarthritis of large and small joints associated with membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis with deposits of immune complexes and acute impairment of renal function, as part of a paraneoplastic syndrome secondary of a classical Hodgkin lymphoma with bone marrow invasion, which reversed completely with chemotherapy treatment.
Los síndromes paraneoplásicos pueden presentarse de múltiples maneras, dentro de las cuales destacan las manifestaciones endocrinológicas, reumatológicas, hematológicas y nefrológicas. Si bien la mayoría de las publicaciones describen los tumores sólidos como responsables de dichos cuadros, las neoplasias hematológicas son causa importante a considerar como parte del diagnóstico diferencial. Se presenta el caso de un varón de 46 años con un cuadro de poliartritis simétrica seronegativa de grandes y pequeñas articulaciones, asociado a glomerulonefritis membranoproliferativa con depósitos de inmunocomplejos y deterioro agudo de la función renal, como parte de un síndrome paraneoplásico secundario a un linfoma de Hodgkin clásico con invasión medular, el cual revirtió completamente con el tratamiento de quimioterapia.
A paraneoplastic syndrome is characterized by its development prior to or concomitantly with a neoplasm, by the absence of tumor invasion as the cause and by its positive response to anticancer therapy.1 It can affect up to 10% of cancer patients, preceding the diagnosis of cancer by no more than 2 years, and can coexist with solid or hematologic neoplasms, with heterogeneous clinical pictures including endocrine, rheumatic, nephrological and hematological diseases, among others.2,3
Case ReportA 46-year-old man presented with a 3-month history of daily fever reaching 38.5°C, associated with profuse sweating, predominantly at night, and weight loss of 5kg. He also complained of symmetric polyarthritis in his hands (metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints), wrists and right ankle, together with 2 painless, rubbery, mobile lymph nodes measuring 2cm×2cm, 1 axillary and the other inguinal. He had normocytic, normochromic anemia with a hemoglobin level of 9g/dL, 2700×mm3 leukocytes (1210×mm3 neutrophils and 697×mm3 lymphocytes), 173,000×mm3 platelets, erythrocyte sedimentation rate 110mm/h, creatinine level of 1.85mg/dL, and urinalysis revealed abundant erythrocytes and proteinuria. Tests for antinuclear antibodies (ANA), anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies, anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies and rheumatoid factor (RF) were negative; cryoglobulins were weakly positive, complement C3 was normal and C4 was 1.3mg/dL (normal: 10–40). Serologic tests for human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis B and C were negative. His creatinine level rose to 3.36mg/dL, and he received three 500-mg doses of methylprednisolone for the treatment of glomerulonephritis with acute renal failure. This was followed by 60mg/day of prednisone, and his fever and polyarthritis remitted, and his creatinine level decreased to 0.77mg/dL. Computed tomography revealed supraclavicular and mediastinal lymph nodes measuring 2.5cm and mild splenomegaly. With this situation of renal failure and glomerulonephritis of unknown etiology, after the third dose of methylprednisolone, renal biopsy was performed. One week later, the axillary lymph node was biopsied. The first revealed glomerulonephritis with deposition of immune complexes and complement factors (Fig. 1b), with an acute diffuse proliferative pattern and membranoproliferative changes (Fig. 1a). In addition, the ultrastructural study showed glomerular electron dense deposits with substructural organization (Fig. 1d). Two weeks later, while the patient was still receiving steroid therapy, his fever, renal failure and progressive pancytopenia reappeared. Methylprednisolone was again administered but, this time, without response. Finally, the lymph node biopsy revealed the presence of mixed cellularity classical Hodgkin's lymphoma (Fig. 2a), with bone marrow infiltration (Fig. 2c). Chemotherapy was begun with doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine and dacarbazine. One month later, the patient's renal function was completely normal and, after 6 months of follow-up, he is in complete remission, with a normal blood cell count and a creatinine level of 1.12mg/dL.
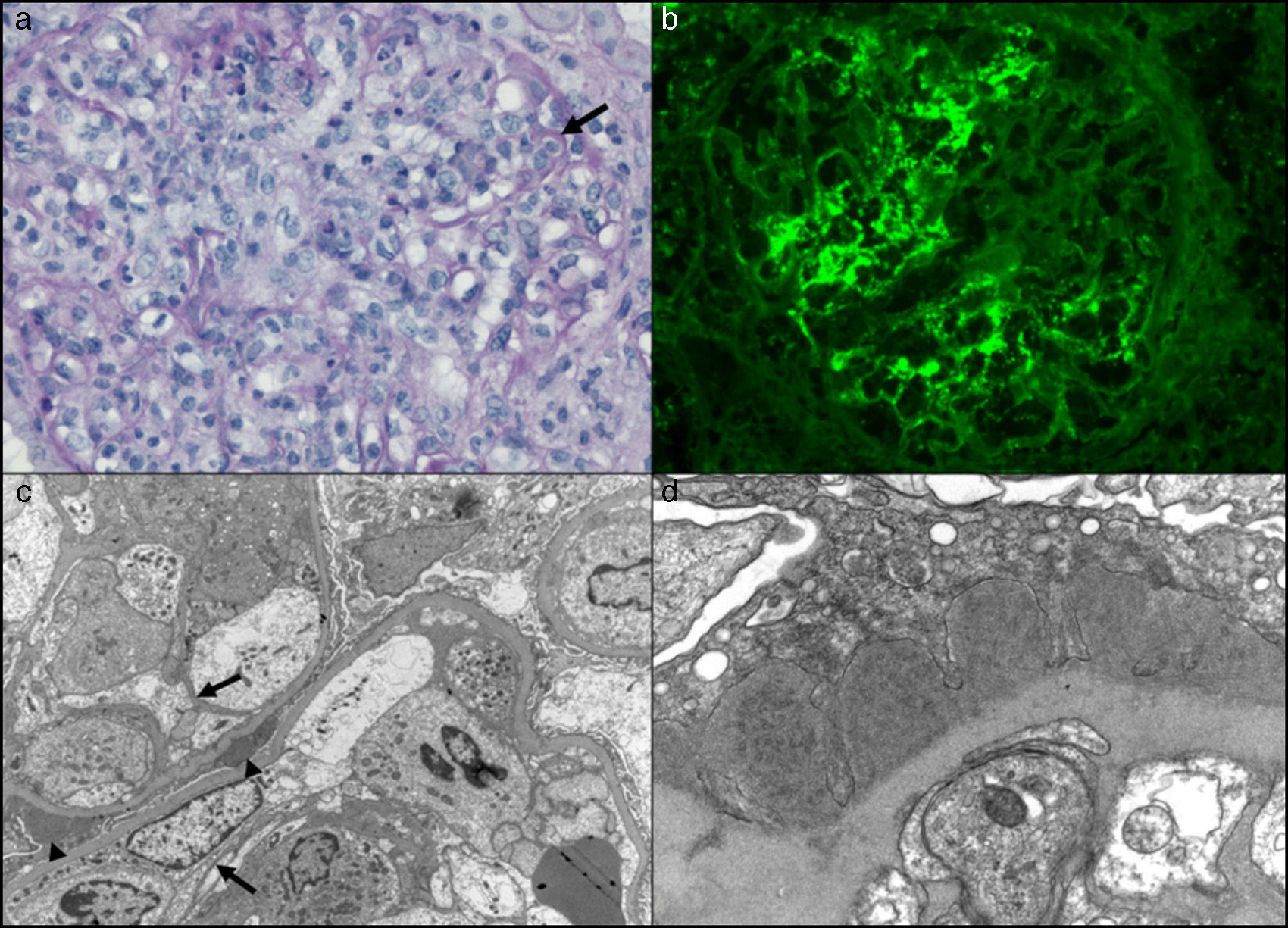
(a) Glomerulus of distorted architecture due to the marked mesangial and endocapillary hypercellularity with mononuclear and polymorphonuclear cells, characteristic of an acute diffuse proliferative pattern. There are images suggestive of subendothelial immune complexes (arrow) (PAS staining, 400×). (b) Direct immunofluorescence of a glomerulus with thick and thin granular deposits of IgG, both mesangial and in certain capillary loops (stained with fluoresceinated anti-IgG antibody; 400×). (c) Transmission electron microscopy showing a glomerulus with a distorted architecture and 2 adjacent capillary loops with marked intracapillary hypercellularity. The image shows focal dense subepithelial deposits (arrowheads). There is focal reduplication of basement membranes that characterize an incipient membranoproliferative lesion (arrows) (osmium tetroxide–uranyl citrate, 6000×). (d) Transmission electron microscopy showing a segment of a capillary loop, in which we see segmental and confluent dense subepithelial deposits that have substructures organized in microtubules measuring 40–50nm in diameter (osmium tetroxide–uranyl citrate, 16,000×).
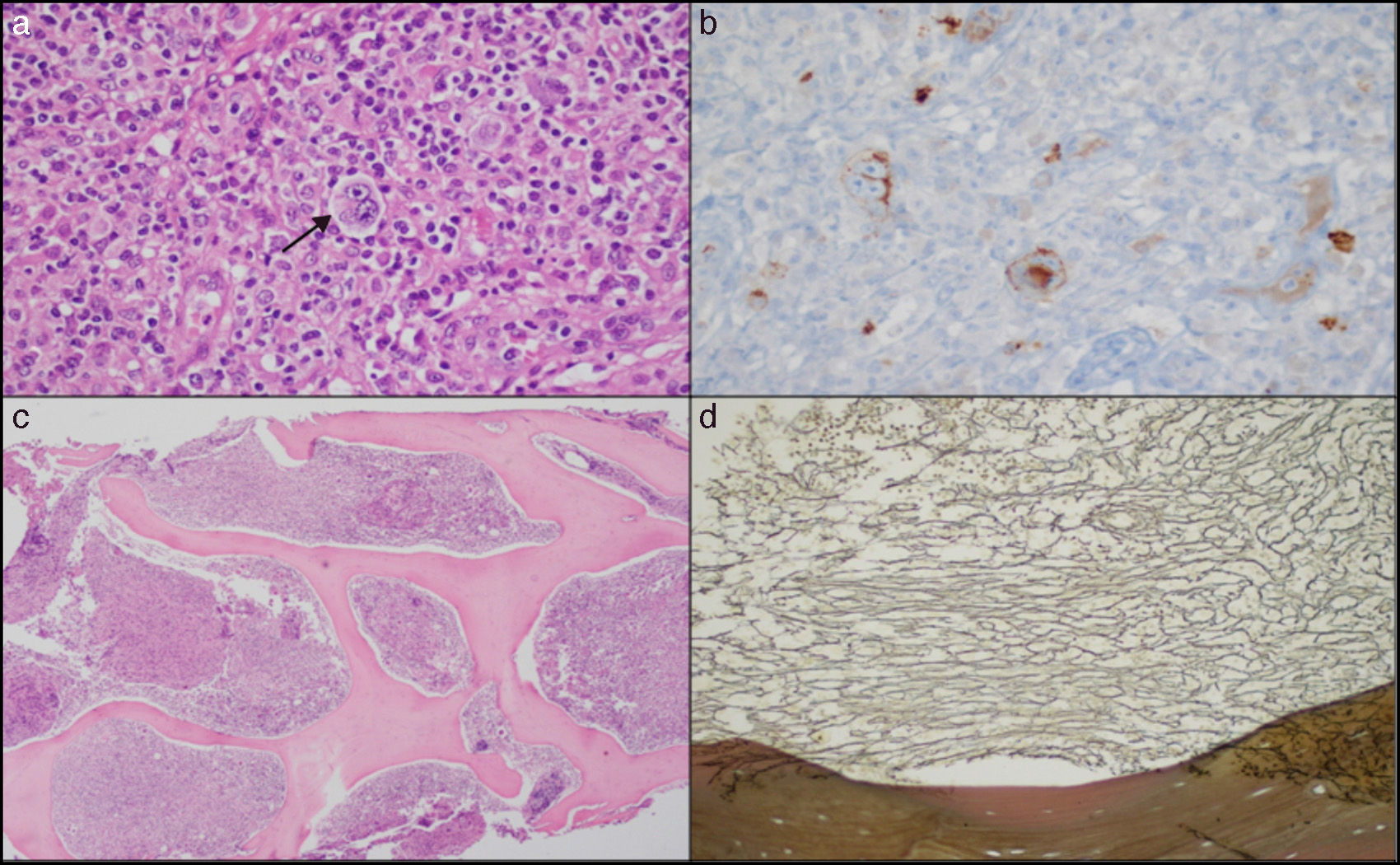
(a) A lymph node with a distortion of the architecture caused by a proliferation of large Reed Sternberg-like cells (arrow), with the presence of lymphocytes, eosinophils and plasma cells (hematoxylin–eosin [HE]). (b) Immunohistochemical staining showing membrane and paranuclear CD15-positivity in the neoplastic cells. (c) Bone marrow at a low magnification showing a marked increase in the cellularity of the medullary spaces, nearly 100% (HE). (d) Bone marrow showing a marked increase in the reticular network (reticulin stain).
Paraneoplastic syndromes have been reported in up to 23% of the patients hospitalized for rheumatic syndromes.3 Thus, any patient over the age of 50 years with polyarthritis, especially seronegative polyarthritis, should undergo studies for occult cancer.4
Paraneoplastic arthritis is associated with symmetric or asymmetric polyarticular or oligoarticular involvement. The pathogenesis has been attributed to the presence of circulating immune complexes and the cross-reaction between tumor antigens and the synovial membrane.5 It can be associated with solid and hematologic tumors, and with the presence of ANA and RF in up to 50% of the cases.1,2 Up to 90% of the patients have been reported to respond to steroid therapy.2
The prevalence of paraneoplastic glomerulopathies (PG) is variable, the membranoproliferative pattern being one of the most common forms.6 However, a study involving 1700 patients with Hodgkin's lymphoma reported that the most frequently detected PG was that in which the changes were minimal, with an incidence of 0.4%; the frequency of the remainder was negligible.7
In conclusion, this case of polyarthritis and glomerulonephritis is interesting in that it is an uncommon paraneoplastic manifestation of Hodgkin's lymphoma which, to the best of our knowledge, has not been reported previously. The existing publications refer to non-Hodgkin lymphomas and, if renal and joint manifestations are added to the search, the literature is considerably reduced, yielding only 1 case of arthritis associated with nephrotic syndrome.8 The excellent initial response to treatment with methylprednisolone is particularly noteworthy. In any case, the reappearance of said manifestations, even with high-dose steroids and, ultimately, the complete control of these signs with chemotherapy, underscores the essence of a paraneoplastic syndrome.
Ethical DisclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Please cite this article as: Erlij D, Calderón B, Rivera A, Mella C, Valladares X, Roessler E, et al. Poliartritis y glomerulonefritis membranoproliferativa como manifestaciones paraneoplásicas de linfoma de Hodgkin: presentación de un caso y revisión de literatura. Reumatol Clin. 2016;12:282–284.



![(a) A lymph node with a distortion of the architecture caused by a proliferation of large Reed Sternberg-like cells (arrow), with the presence of lymphocytes, eosinophils and plasma cells (hematoxylin–eosin [HE]). (b) Immunohistochemical staining showing membrane and paranuclear CD15-positivity in the neoplastic cells. (c) Bone marrow at a low magnification showing a marked increase in the cellularity of the medullary spaces, nearly 100% (HE). (d) Bone marrow showing a marked increase in the reticular network (reticulin stain). (a) A lymph node with a distortion of the architecture caused by a proliferation of large Reed Sternberg-like cells (arrow), with the presence of lymphocytes, eosinophils and plasma cells (hematoxylin–eosin [HE]). (b) Immunohistochemical staining showing membrane and paranuclear CD15-positivity in the neoplastic cells. (c) Bone marrow at a low magnification showing a marked increase in the cellularity of the medullary spaces, nearly 100% (HE). (d) Bone marrow showing a marked increase in the reticular network (reticulin stain).](https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/21735743/0000001200000005/v3_201704020032/S2173574316300570/v3_201704020032/en/main.assets/thumbnail/gr2.jpeg?xkr=ue/ImdikoIMrsJoerZ+w937trqSwLGgTrQM2QjUSRyU=)



