Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is frequent in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. The aim of this review was to identify the different screening methods for ILD in patients with RA.
MethodsWe ran a systematic search in Pubmed, Embase and Cochrane Library up to April 2020 and did a hand search of the references of the retrieved articles. The search was limited to humans and articles published in English, Spanish or French. We selected studies with any design where: (a) the population included adult patients with RA; (b) the intervention was any screening method for ILD; and (c) validity or reliability of the screening method were evaluated, or a screening method was described. Two reviewers independently screened the articles by title and abstract and subsequently extracted the information using a specific data extraction form.
Results25 studies were included with a total of 2593 patients. The most frequently used tool for ILD screening was high resolution computed tomography (HRCT) of the lung. Electronic auscultation, biochemical markers, bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), pulmonary function tests (PFTs) and lung ultrasonography were also evaluated. Across the different studies, electronic auscultation and lung ultrasonography achieved higher accuracy than PFTs, BAL and biochemical markers.
ConclusionsHRCT resulted as the most sensitive tool for ILD screening in patients with RA. Given its harmlessness and high sensitivity, lung ultrasonography may become the first-choice tool in the future.
La enfermedad pulmonar intersticial difusa (EPID) es una manifestación frecuente en pacientes con artritis reumatoide (AR) y asocia una gran morbimortalidad. El objetivo de esta revisión fue identificar los distintos métodos de cribado de EPID en pacientes con AR.
MétodosSe realizó una búsqueda sistemática en Pubmed, Embase y Cochrane Library hasta abril de 2020 y una búsqueda manual en la bibliografía de los artículos recuperados. Se limitó a estudios en humanos y artículos publicados en inglés, francés o español. Se seleccionaron estudios de cualquier diseño en los que: (a) la población a estudiar fuesen pacientes adultos con AR; (b) la intervención consistiese en cualquier método de cribado de EPID; y (c) se evaluase la validez o fiabilidad del método de cribado, o se describiesen criterios de cribado. Dos revisoras realizaron la selección por título y abstract de forma independiente y posteriormente extrajeron la información utilizando plantillas específicas.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 25 estudios con un total de 2.593 pacientes. La herramienta más frecuentemente utilizada para el cribado de EPID fue la tomografía computarizada de alta resolución (TCAR) pulmonar. También se evaluaron la auscultación electrónica, los marcadores bioquímicos, el lavado broncoalveolar (LBA), las pruebas de función respiratoria (PFR) y la ecografía pulmonar. En los diferentes estudios, la auscultación electrónica y la ecografía pulmonar alcanzaron mayor precisión que las PFR, el LBA y los marcadores bioquímicos.
ConclusionesLa TCAR ha demostrado ser la técnica más sensible para el cribado de EPID en pacientes con AR. Dada su inocuidad y su alta sensibilidad, es posible que la ecografía pulmonar se posicione como técnica de elección en un futuro.
Lung involvement is a common extra-articular manifestation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), which can occur in 60%–80% of patients.1 Different types of pulmonary involvement have been described, including interstitial lung disease (ILD), pleural disease, rheumatoid nodules, bronchiectasis and vasculitis.1 Different studies have estimated the prevalence of ILD in RA to be between 1% and 58% depending on the methodology used.2 The cumulative incidence of clinically significant ILD (abnormal pulmonary function tests [PFT]: decrease in forced vital capacity [FVC] or diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide [DLCO] of 15% of normal) in RA patients has been found to be 5% at 10 years3 and 6.8% after 30 years of follow-up.4 ILD is a major cause of morbidity and mortality. Mortality at 5 years after diagnosis was 35.9% in a US study.5
Underdiagnosis poses a major difficulty in determining the incidence and prevalence of ILD. A high prevalence of subclinical ILD (19%–57%) has been observed,6,7 defined as that incidentally detected on high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) and without symptoms. These radiological findings are progressive in half the patients8 and are associated with subsequent onset of respiratory symptoms and PFT abnormalities.9
The exact relationship between RA and ILD is not known, but genetic and environmental mechanisms are thought to be involved.2 Two pathways of connection between joint and lung disease have been proposed. On the one hand, it is possible that the disease starts in the synovial tissue following an immune response against citrullinated proteins, which would subsequently cross-react with tissue antigens in the lung.10 This theory is supported by the fact that joint disease appears before lung disease in most patients. Another possibility is that immune tolerance is initially lost in the lung, and that ILD generates an immune response against citrullinated proteins that secondarily spreads to the joints.11 This idea is supported by the observation that ILD may precede other extrapulmonary manifestations and by the existence of a high number of citrullinated peptides in the lung parenchyma of patients with RA-ILD.6,8
The temporal relationship between joint disease and ILD is therefore highly variable. Furthermore, the severity of lung involvement does not correlate with the severity of RA, although some features of RA, such as elevated rheumatoid factor, are risk factors for ILD. Some patients may be asymptomatic even though they show significant radiological involvement.12,13
Given the significant morbidity and mortality associated with RA-ILD, screening methods to diagnose asymptomatic cases and provide prompt treatment are essential. To help in the development of criteria for screening patients with RA-ILD, we conducted a systematic review to identify the different methods of screening for interstitial lung disease used in patients with RA.
MethodsThe recommendations of the PRISMA guidelines were followed for this review.
Search strategyA health sciences librarian (MGR) designed a systematic search strategy in the databases PubMed (Medline), Embase (Elsevier), and Cochrane Library (Wiley). The search included MeSH terms and free text with their different combinations referring to “rheumatoid arthritis”, “interstitial lung disease” and “screening” until April 2020 (Appendix B, Annex 1 of the supplementary material). The search was limited to human studies and articles published in English, French, or Spanish. A hand search of the references of the articles retrieved was also performed.
Selection of studiesThe Covidence systematic review tool (www.covidence.org) was used to screen studies. Studies of any design using screening methods for interstitial lung disease in patients with RA were selected. As per protocol, studies were included in which: (a) the study population was adult patients with RA; (b) the intervention consisted of any method of screening for ILD (questionnaire, examination, complementary tests…); and (c) the validity or reliability of the screening method was assessed, or screening criteria were described. Two reviewers (SGC and LSF) first independently screened by title and abstract. Any discrepancies were resolved by consensus. The selected articles were then evaluated in detail to select those for final inclusion based on the above criteria. A third reviewer (DSM) resolved any disagreement on inclusion between the two reviewers. The reason for excluding all the rejected studies was recorded.
Data extractionThe two reviewers extracted information from the articles independently using specific templates. The retrieved articles were classified according to the screening method studied (HRCT, PFT, ultrasound, etc). Study characteristics were extracted in terms of design, population included, screening method, gold standard used, and results of comparison. A synthesis of the collected information was made in a narrative form with tabulation of the characteristics and results of each included study. Study quality was assessed using the scale for levels of scientific evidence and formulating recommendations for diagnostic questions (NICE [National Institute for Health and Care Excellence]14 adaptation of the levels of evidence of the Oxford Centre for Evidence Based Medicine and Centre for Reviews and Dissemination15).
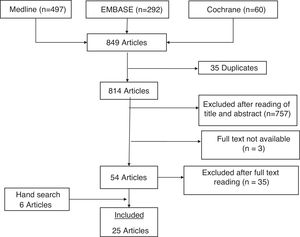
ResultsThe diagram in Fig. 1 details the results of the search. The search strategy identified 849 studies, of which 35 were duplicates. Initial screening by title and abstract discarded 757. Nineteen of the 54 articles reviewed in detail met the inclusion criteria. In addition, 6 articles found by hand search of the references of retrieved articles were selected. Table 1 shows the characteristics of the 25 included articles. The most relevant results of the studies are shown in Table 2. The excluded articles and the reasons for exclusion are detailed in Appendix B, Annex 2 of the supplementary material.
List of studies included in the systematic review.
| Study | Patients | Intervention | Links assessed | Quality of evidencea (NICE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pancaldi (2018)19 | n = 70 patients with RA (with and without respiratory symptoms for whom an HRCT was requested) | Auscultation with digital stethoscope (analysis with VECTOR algorithm) lung HRCT | Accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV of the VECTOR algorithm in the diagnosis of ILD | 2 |
| Cross-sectional | -RA-no ILD: 43, women 17, mean age: 66.8 ± 10.5 | |||
| -RA-ILD: 27, women 23, mean age: 69.8 ± 8.5 | ||||
| Manfredi (2019)24 | n = 137 consecutive patients with RA | Auscultation with digital stethoscope (analysis with VECTOR algorithm) lung HRCT | Accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV of the VECTOR algorithm for the diagnosis of ILD | 2 |
| Cross-sectional | for whom an HRCT was requested (respiratory symptoms, X-ray abnormalities, infection, monitoring of lung nodules) | |||
| -RA-no ILD: 78, women 31, mean age: 66.5 ± 10.3 | ||||
| -RA-ILD: 59, women 45, mean age: 69.8 ± 9.1 | ||||
| Abdel-Wahab (2016)18 | n = 50 patients with RA | Analysis of IL-33 | Correlation between IL-33 and ILD | 2 |
| Cross-sectional | Women: 41 | Lung HRCT | ||
| Mean age: 51.1 ± 9.6 | ||||
| n = 30 controls | ||||
| Women: 23 | ||||
| Mean age: 51 ± 9.4 | ||||
| Castellanos-Moreira (2020)28 | n = 179 patients with RA | Anti-CarP antibody test: anti-FCS, anti-Fib, anti-CFFHP and anti-FCS-IgA | Correlation between levels of Anti-carP antibodies and ILD | 3 |
| Cross-sectional | Previous diagnosis of ILD: 31 | HRCT patients with no previous diagnosis of ILD | ||
| -non-ILD RA: 142, women 116, mean age: 57.7 ± 12.9 | ||||
| -RA-ILD: 37, women 25, mean age: 67.3 ± 10.1 | ||||
| Chen (2015)22 | n = 133 consecutive patients with RA (identification cohort, China) regardless of respiratory symptoms | HRCT and PFT | Correlation between biomarkers (MMP-7 and IP-10) and ILD and its severity | 2 |
| Cross-sectional | RA-no ILD: 50, women 41, mean age: 43.4 ± 15.54 | Biomarker assay by ELISA MMP-7, IP-10, IFNγ, IL-8, IL-10, IL-15, IL-22, and α IL-2 receptor chain | ||
| RA-indeterminate ILD: 34, women 34, mean age: 57.07 ± 9.40 | ||||
| RA moderate-severe ILD: 41, women 29, mean age: 53.02 ± 14.20 | ||||
| n = 86 patients with RA (US replication cohort, previous diagnosis of ILD: 44%). | ||||
| RA-no ILD: 22, women 16, mean age: 50.32 ± 7.82 | ||||
| RA-indeterminate ILD: 15, women 15, mean age: 54.33 ± 12.24 | ||||
| RA moderate-severe ILD: 49, women 18, mean age: 65.27 ± 10.80 | ||||
| Wang (2015)26 | n = 41 patients with RA | HRCT, PFT | Correlation between lung function variables associated with ILD | 2 |
| Cross- sectional | irrespective of respiratory symptoms for whom an HRCT was requested | Blood test: tumour markers (CEA, CA125, CA19-9 and CA15-3) | Association between analytical variables and presence of ILD | |
| -RA without ILD: 16, women 10, mean age: 56.19 ± 12.11 | Anti-CCP, ESR, CRP | |||
| - RA-ILD: 25, women 11, mean age: 63.56 ± 11.90 | ||||
| Doyle (2015)29 | n = 113 patients with RA with HRCT performed for clinical reasons (BRASS cohort) | HRCT performed previously | Correlation between biomarkers and ILD | 3 |
| Cross-sectional | - RA without ILD: 29, women 28, mean age: 53 ± 12 | Serum biomarker assay (MMP-7, PARC, surfactant protein D) RF, anti-CCP | Development of an index to identify subclinical ILD in RA | |
| - Subclinical RA-ILD: 29, women 23, mean age: 68 ± 10 | ||||
| - Clinical RA-ILD: 17, women 13, mean age: 65 ± 10 | ||||
| - Indeterminate RA- ILD: 38 n = 76 patients with RA (ACR cohort) | ||||
| - RA without ILD: 22, women 16, mean age: 50 ± 8 | ||||
| - Subclinical RA-ILD: 18, women 13, mean age 65 ± 8 | ||||
| - Clinical RA-ILD: 21, women 12, mean age: 64 ± 14 | ||||
| - Indeterminate RA- ILD: 15 | ||||
| Tishlerb (1986)30 | n = 12 patients with RA | Chest X-ray | Cell distribution in patients with RA according to whether they had chest X-ray abnormalities | 3 |
| Cross-sectional | with no respiratory symptoms | PFT | ||
| -RA without ILD: 8, women 7, mean age: 52.5 ± 14.5 | BAL, cell count | |||
| -RA-ILD: 4, women 1, mean age: 53.5 ± 10.3 | ||||
| Gilliganb (1990)38 | n = 93 asymptomatic patients with RA | Chest X-ray | Neutrophil, N-terminal procollagen type III and fibronectin levels in patients with subclinical vs. established ILD | 3 |
| Cross sectional | -RA without ILD: 79, women 53, mean age: 51.2 ± 10.1 | PFT | ||
| -RA-ILD: 14, women 7, mean age: 53.6 ± 10.7 | BAL in patients with subclinical ILD | |||
| n = 11 patients with RA and known ILD = 15 healthy controls | ||||
| Gochuico (2008)8 | n = 74 asymptomatic patients with RA | Lung HRCT | Percentage of patients with subclinical ILD | 2 |
| Cohort | - RA without ILD: 43, women 36, mean age: 51.3 ± 1.3 | BAL | Percentage of patients with ILD who progressed | |
| -RA preclinical ILD: 31, women 14, mean age: 55.6 ± 2 | PFT | Quantification of cytokines and growth factors in BAL | ||
| n = 10 patients with RA and pulmonary fibrosis | ||||
| women 7, mean age: 53.7 ± 2.6 | ||||
| Mohd (2009)34 | n = 63 patients with RA of more than 5 years’ disease duration, recruited consecutively, regardless of respiratory symptoms | HRCT | To assess clinical and functional differences between patients with RA-ILD and RA without ILD | 3 |
| Transversal | -RA without ILD: 35 | PFT | ||
| -RA-ILD: 28 | ||||
| Zhang (2017)33 | n = 550 patients with RA regardless of respiratory symptoms | HRCT | Comparison of clinical data of patients with RA with ILD and RA without ILD | 3 |
| Transversal | -RA without ILD: 313, women 234, mean age: 47.7 ± 14.5 | PFT | Correlation between clinical/analytical characteristics and presence of ILD | |
| -RA-ILD: 237, women 151, mean age: 57.6 ± 13.2 | ||||
| Mori (2011)35 | n = 189 consecutive patients with RA, regardless of respiratory symptoms | HRCT | Correlation between clinical characteristics and PFT in patients with and without abnormal HRCT findings | 3 |
| Cross-sectional | -RA without ILD: 155, women 130, mean age: 60 | PFT | ||
| -RA-ILD: 19, women 13, mean age: 72 | ||||
| -RA bronchiolitis pattern: 15, women 15, mean age: 63 | ||||
| Yilmazer (2016)36 | n = 130 patients with RA regardless of respiratory symptoms | HRCT(performed for any reason) | Damage and radiological extent correlated with Warrick score and clinical variables, PFT | 3 |
| Transversal | -RA without ILD: 70, women 55, mean age: 54.2 ± 10.7 | PFT | ||
| -RA-ILD: 60, women 36, mean age: 64.5 ± 9.8 | ||||
| Leonel (2012)37 | n = 36 consecutive patients with RA, regardless of respiratory symptoms | HRCT | Correlation of PFT with lung HRCT in RA patients | 3 |
| Transversal | Women: 36 | PFT | ||
| Mean age: 46.7 ± 10.9 | ||||
| Cogliati (2014)16 | n = 39 patients with RA | Transthoracic lung ultrasound | Validity of ultrasound in the diagnosis of ILD | 1 |
| Transversal | with known or suspected ILD | HRCT | ||
| -RA without ILD: 26, women 21, mean age: 64.65 ± 10 | PFT | |||
| -RA-ILD: 13, women 8, mean age: 65.31 ± 10 | ||||
| Moazedi-Fuerst (2014)17 | n = 64 patients with RA | Transthoracic lung ultrasound | Diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of ultrasound in the diagnosis of ILD | 1 |
| Cross-sectional | with no respiratory symptoms | Lung HRCT | ||
| Women 54, mean age 59 ± 12 | PFT | |||
| -RA without ILD: 46 | ||||
| -RA-ILD: 18 | ||||
| n = 40 controls | ||||
| Women 25, mean age 52 ± 22 | ||||
| Moazedi-Fuerst (2015)20 | n = 45 patients with rheumatic disease, without respiratory symptoms, including 25 patients with RA | Transthoracic lung ultrasound | Validity of ultrasound in the diagnosis of ILD | 2 |
| Cross-sectional | -RA without ILD: 18 | PFR | ||
| - RA-ILD: 7 | ||||
| n = 40 healthy controls | ||||
| Hassan (1995)25 | n = 20 patients with RA with no respiratory symptoms and normal chest X-ray | HRCT PFT Chest X-ray | Frequency of findings on HRCT in patients with RA | |
| Cross-sectional | Women 18, mean age 59 | |||
| Gabbay (1997)6 | n = 36 consecutive patients with RA (<2 years’ disease duration) | TCAR, Chest X-ray | Prevalence of ILD in patients with RA of <2 years’ duration; to compare characteristics between patients with RA and ILD and RA without ILD | 2 |
| Cross-sectional | -RA without ILD: 15, women 11, mean age: 49.4 ± 3.3 | 99mTc-DTPA nuclear scan BAL | ||
| -RA subclinical ILD: 16, women 13, mean age: 52.4 ± 3.3 | PFT | |||
| -RA clinically significant ILD: 5, women 1, mean age: 54.4 ± 2.1 | Modified American Thoracic Society Respiratory Questionnaire | |||
| Dawson (2001)27 | n = 150 consecutive patients with RA regardless of respiratory symptoms | HRCT PFT | Prevalence of fibrosing alveolitis in patients with RA diagnosed with HRCT | 2 |
| Cross-sectional | -RA without ILD: 122, women 81, mean age: 58.3 ± 10.6 | Chest X-ray | ||
| -RA ILD: 28, women 19, mean age: 61.2 ± 8.7 | ||||
| Raniga (2006)31 | n = 30 patients with RA, regardless of pulmonary symptoms or changes or chest X-ray changes | HRCT PFT chest X-ray | Prevalence of ILD in RA patients and description of findings in complementary tests | 3 |
| Transversal | Women 23 | |||
| -RA without ILD: 19 | ||||
| -RA ILD: 11 | ||||
| Zayeni (2016)32 | n = 44 consecutive RA patients | HRCT chest X-ray | Prevalence of ILD in patients with RA, description of clinical characteristics | 3 |
| Cross-sectional | Women 35, mean age: 49 ± 13 | |||
| Affara (2014)21 | n = 50 asymptomatic patients with RA | HRCT PFT | Prevalence of subclinical ILD in patients with RA | 2 |
| Cross-sectional | Women 40 | |||
| Chen (2013)23 | n = 103 consecutive patients with RA | HRCT PFT | Comparison of clinical and demographic characteristics of patients with RA and ILD vs. RA-no ILD diagnosed by HRCT and PFT | 2 |
| Cross-sectional | regardless of respiratory symptoms | |||
| -RA-no ILD: 40, women 30, mean age: 42.9 ± 12.4 | ||||
| -RA-ILD: 63, women 46, mean age: 53.0 ± 14.8 |
Anti-CFFHP: antibodies against fibrin/filaggrin homocitrullinated peptide; Anti-FCS: antibodies against foetal calf serum; Anti-Fib: anti-fibrinogen antibodies; AUC: area under the curve; BAL: Bronchoalveolar lavage; CA125: Carbohydrate antigen 125; CA19-9: Carbohydrate antigen 19-9; CA15-3: Carbohydrate antigen 15-3; CEA: carcinoembryonic antigen; DLCO: diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide; DLCO/VA: DLCO corrected for alveolar volume; FVC: forced vital capacity; HRCT: high-resolution computed tomography; IFN: interferon; IL: interleukin; ILD: interstitial lung disease; IP-10: interferon-gamma-inducible protein 10; MMP-7: matrix metalloproteinase-7; NPV: negative predictive value; PPV: positive predictive value; PFT: pulmonary function tests; RA: rheumatoid arthritis; TLC: total lung capacity; VC: vital capacity.
Results of the studies included in the systematic review.
| Studies | Results |
|---|---|
| Pancaldi (2018)19 | Digital auscultation (VECTOR): |
| Cross-sectional | Accuracy: 90%; specificity: 88.4%; sensitivity: 92.6%; PPV: 83.3%; NPV: 95% |
| Manfredi (2019)24 | Digital auscultation (VECTOR): |
| Cross-sectional | Accuracy: 83.9%; specificity: 76.9%; sensitivity: 93.2%; PPV: 75.3%; NPV: 93.75% |
| Abdel-Wahab (2016)18 | There is a correlation between IL-33 levels and ILD (r = 0.3; P = .04) |
| Cross-sectional | |
| Castellanos-Moreira (2020)28 | -Anti-CarP ILD vs. non-ILD RA: |
| Cross-sectional | anti-FCS: 70% vs. 43% |
| anti-Fib: 73% vs. 51% | |
| anti-CFFHP: 38% vs. 19% | |
| anti-FCS- IgA: 51% vs. 20%, P < .05 for all comparisons | |
| -Mean antibody titres were significantly higher in the ILD group | |
| -Adjusted logistic regression anti-FCS (OR: 3.42; 95% CI: 1.13–10.40), anti-CFFHP (OR: 3.11; 95% CI: 1.06–9.14) and anti-FCS- IgA (OR: 4.30; 95% CI: 1.41–13.04) independent association with ILD | |
| Chen (2015)22 | - Mean MMP-7 levels, subclinical ILD 5.94 ± 3.46 ng/mL and RA-clinically evident ILD 6.24 ± 3.38 ng/mL (P = .0006 and P < .0001, respectively vs. RA-no ILD) |
| Cross-sectional | - In both cohorts MMP-7 and IP-10 correlated with the presence and severity of ILD, after adjusting for age and DAS28 |
| Wang (2015)26 | - Higher CA15-3 and CA125 levels in RA-ILD (P = .01 and 0.03, respectively), CEA and CA19-9 did not differ significantly (P = .47 and 0.19, respectively) |
| Cross-sectional | - Logistic regression model: only DLCO (beta –0.06) retained statistically significant association with RA-ILD. ROC curves for DLCO: AUC: 0.87 (95% CI 0.76–0.98) (P < .001). For a cut-off point DLCO 52.95% sensitivity: 100%, specificity: 60.87% |
| Doyle (2015)29 | - BRASS cohort: MMP-7, RA without ILD: 5.7 ± 2.5 and RA-subclinical ILD 9.1 ± 3.3 (P< .05). PARC, AR without ILD 132 ± 63 and subclinical ILD 277 ± 187 (P < .05). Surfactant protein D, RA without ILD 11.9 ± 7.9 and subclinical RA-ILD 20.6 ± 12 (P < .05) |
| Cross-sectional | - ACR cohort: MMP-7, RA without ILD 4.8 ± 2 and subclinical RA-ILD 10.0 ± 5.4 (P < .05). PARC, RA without ILD 129 ± 49 and subclinical RA-ILD 217 ± 141 (P < .05). Surfactant protein D, RA without ILD 7.1 ± 3.1 and subclinical RA-ILD 18.4 ± 13.7 (P < .05) |
| Tishler (1986)30 | BAL: elevated lymphocyte counts 30.7 ± 8.3% in groups with X-ray changes compared with 7.2 ± 1.7% normal X-ray group (P < .001) |
| Cross-sectional | PFT within normal limits in both groups |
| Gilligan (1990)38 | - BAL: 11 patients with established ILD had increased neutrophils, collagenase (P < .01) and type III procollagen N terminal peptide levels (P < .02). Of the patients with subclinical ILD, 1 had increased neutrophils and 2 increased collagenase levels |
| Cross-sectional | |
| Gochuico (2008)8 | - Follow-up HRCT (mean 1.5 years): Disease progression in 57% patients with preclinical RA-ILD (7 already identified at baseline and 5 de novo) |
| Cohort | - Higher concentrations of IFN gamma and TGF-β1 in BAL in the subjects who progressed compared to those who did not (P = .04 and P = .03, respectively) |
| - FEV1, FVC, TLC were normal in patients with preclinical ILD in RA | |
| DLCO normal in preclinical RA-ILD, but % DLCO was les and the alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient was statistically significantly higher in subjects with preclinical RA-ILD vs. RA subjects without ILD (P = .01 and P = .004, respectively) | |
| Mohd (2009)34 | Clinic: 46/63 (73%) without respiratory symptoms |
| Cross-sectional | PFT: 60 (95.2%) had abnormalities: 42 (66.7%) restrictive pattern, 12 (19%) mixed characteristics and 6 (9.5%) obstructive pattern |
| 100% reduced DLCO. Mean with ILD 50.89 ± 13.58% and without ILD 48.31 ± 10.22%, P = .393; DLCO/VA with ILD 70.14 ± 12.49% and without ILD 69.11 ± 13.57%, P = .758 | |
| Zhang (2017)33 | - RA-ILD: 59% asymptomatic ILD |
| Cross-sectional | - RA-ILD group: 98% abnormalities on PFT: 28.3% restrictive pattern, DLCO abnormalities 91.9% |
| - RA without ILD group: 88.7% abnormality on PFT: 4.8% restrictive pattern, DLCO abnormalities 75.8%. –Frequency significantly greater in RA-ILD vs. RA without ILD of restrictive and diffusion abnormalities | |
| Mori (2011)35 | In patients with ILD, the median values of % predicted for DLCO and DLCO/VA were significantly decreased. RA without ILD: DLCO 103% (91.5, 116.5); RA-ILD, DLCO 82.3% (72.6, 97.0); P < .001. RA without ILD DLCO/VA, 82.3% (72.6, 93.7); RA-ILD DLCO/VA 71.8% (57.4, 80.6); P < .01 |
| Cross-sectional | |
| Yilmazer (2016)36 | FEV1, DLCO and TLC levels in patients with normal HRCT versus in pat en pacientes con TCAR normal versus abnormal TCAR (FEV1% predicted 92 ± 22.7 and 80.8 ± 20.2 P = .017; DLCO% predicted 79.5 ± 25.3 and 66 ± 241 P= .016; TLC% predicted 87.3 ± 14.8 and 78.2 ± 18.2, P = .043, respectively) |
| Cross-sectional | DLCO values <75% (OR = 4.29, P = .01) and respiratory symptoms (cough and/or dyspnoea) (OR = 5.51, P = .02) contribute to pulmonary damage after adjusting for gender, RF positivity and FEV1% |
| Leonel (2012)37 | Patients with abnormal PFT: 12 |
| Cross-sectional | Patients with abnormalities on HRCT: 20 |
| ROC curve analysis showed that the FEV1 cut-off of 81.7% has a better sensitivity (59%) – specificity (83%) balance for detecting HRCT abnormalities | |
| Cogliati (2014)16 | Lung ultrasound |
| Cross-sectional | -Sensitivity 92% (95% CI 78–100) |
| -Specificity 56% (95% CI 38–75) | |
| -Cut-off of 17 B-lines on ultrasound: sensitivity 92% (95% CI 78-100) and specificity 72% (95% CI 54–90) | |
| Moazedi-Fuerst (2014)17 | Normal PFT in all cases |
| Cross-sectional | Ultrasound: |
| -Sensitivity 97.1% | |
| -Specificity 97.3% | |
| -PPV 94.3%, NPV 98.6% (P < .001) | |
| Moazedi-Fuerst (2015)20 | Pathological ultrasound patterns were more frequent in the ILD group than the non-ILD group (B lines: 100% vs. 12%, P < .001; subpleural nodules: 55% vs. 17%, P = .006; pleural thickening: 95% vs. 12.5%, P < .001) |
| Cross-sectional | Subpleural nodules were present in 100% of RA patients |
| Hassan (1995)25 | 1 patient showed signs of ILD (ground-glass opacity) |
| Cross-sectional | |
| Gabbay (1997)6 | Subclinical RA-ILD: Abnormal PFT 4, (DLCO < 75%) on HRCT 7, and one alveolitis on BAL in 10, 11 had an abnormality on 1 test, 4 on 2 tests, and 1 in 3 tests |
| Cross-sectional | Abnormalities on DLCO significantly more in the clinically significant RA-ILD group, DLCO 69% ± 5.7, subclinical RA-ILD 87% ± 3.7, RA without ILD 86% ± 3.5 P < .05 |
| FVC clinical ILD 91% ± 8.1; subclinical ILD 111% ± 3.8; without ILD 113% ± 4.2; P < .05) | |
| Dawson (2001)27 | X-ray was not very sensitive for the diagnosis of ILD |
| Cross-sectional | On the univariate analysis, bilateral basal chest crackles (P < .0001) FEV1/FVC (P = .03) and DLCO (P = .009) (OR .0875, 95% CI 0.0332–0.2301) were associated with fibrosing alveolitis on HRCT |
| Raniga (2006)31 | 6/30 (20%) had respiratory symptoms, 3/30 (10%) had suggestive physical examination, 8/30 (26,6%) had spirometric abnormalities, 4/30 (13.3%) X-ray abnormalities |
| Cross-sectional | - 2/30 (6.66%) ILD on HRCT with no clinical, spirometric or chest X-ray changes |
| - 3/30 (10%) ILD on HRCT with no clinical or radiographic changes | |
| - 6/30 (20%) ILD on HRCT with no clinical findings | |
| Zayeni (2016)32 | Chest X-ray: 1/44 (2.9%) abnormal findings |
| Cross-sectional | HRCT: fibrosis 19 (44%) |
| Asymptomatic patients: 15 (71.4%) abnormal HRCT and 7 (33.3%) abnormal PFT | |
| No relationship between respiratory symptoms and HRCT findings | |
| There was a relationship between PFT and respiratory symptoms (P = .659 and .016, respectively) | |
| There was no relationship between clinical respiratory examinations and HRCT findings (P = .578). PFT did have a relationship with physical examinations (P = .009) | |
| Affara (2014)21 | 46% (23/50) diagnosed with subclinical ILD |
| Cross-sectional | |
| Chen (2013)23 | - 63/103 (61%) ILD according to HRCT and PFT |
| Cross-sectional | - 57/63 (90%) subclinical ILD |
| - FEV1, FVC, DLCO levels reduced in patients with ILD, correlated with HRCT | |
| - PFT RA-ILD (47) and RA-no ILD (36): FEV1 74.1 ± 14.6 and 88 ± 12.9 (P < .001), respectively; FVC 74.9 ± 12.2 and 86.9 ± 11.3 (P < .001), respectively, and DLCO 68.1 ± 19.5 and 96.2 ± 17.7 (P < .001, respectively) TLC 87.7 ± 15.7 and 98.4 ± 11.3 (P = .001) |
Anti-CFFHP: antibodies against fibrin/filaggrin homocitrullinated peptide; Anti-FCS: antibodies against foetal calf serum; Anti-Fib: anti-fibrinogen antibodies; AUC: area under the curve; BAL: Bronchoalveolar lavage; CA125: Carbohydrate antigen 125; CA19-9: Carbohydrate antigen 19-9; CA15-3: Carbohydrate antigen 15-3; CEA: carcinoembryonic antigen; DLCO: diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide; DLCO/VA: DLCO corrected for alveolar volume; FEV1: forced expiratory volume in 1 s; FVC: forced vital capacity; HRCT: high-resolution computed tomography; IFN: interferon; IL: interleukin; ILD: interstitial lung disease; IP-10: interferon-gamma-inducible protein 10; MMP-7: matrix metalloproteinase-7; NPV: negative predictive value; PPV: positive predictive value; PFT: pulmonary function tests; RA: rheumatoid arthritis; TGF-β1: transforming growth factor beta 1; TLC: total lung capacity; VC: vital capacity.
A total of 2593 RA patients without a known diagnosis of ILD were included. The included population was mainly female (70%), with a mean age of 46–68 years, and a mean disease duration of between 1 and 12 years.
Most of the included studies were of cross-sectional design, except for the study by Gochuico et al.,8 which is a prospective cohort. After quality assessment, 2 studies were of high quality,16,17 12 of medium quality,6,8,18–27 and 11 of low quality.28–38
Apart from 2 studies,30,38 lung HRCT was the most frequently used tool for screening for ILD. Some studies also used other tools such as digital auscultation, biochemical markers, bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), pulmonary function tests (PFTs), or lung ultrasound, as detailed below.
Digital auscultationStudies by Pancaldi et al.19 and Manfredi et al.24 compare the use of a digital stethoscope to automatically detect velcro-type lung crackles with HRCT findings. The digital audio collected was analysed using an algorithm for the binary classification of the findings (VECTOR). The target population comprised patients diagnosed with RA who had undergone HRCT for respiratory symptoms, velcro crackles, pathological lung function, or lung nodule study. Digital auscultation achieved diagnostic accuracy of 84%–90%, specificity of 77%–88%, sensitivity of 93%, positive predictive value (PPV) 75%–83%, and negative predictive value (NPV) 94%–95% in detecting ILD, and the accuracy obtained by auscultation by a rheumatologist was 67.2%.
Biochemical markersThe study by Abdel-Wahab et al. established a significant association between serum levels of interleukin-33 (IL-33) and the presence of DIDP in patients with RA.18 Castellanos-Moreira et al.28 assessed the presence of autoantibodies against 3 carbamylated antigens: foetal calf serum (FCS), fibrinogen (Fib), and chimeric fibrin/filaggrin homocitrullinated peptide (CFFHP) in RA patients. Included patients without a previous diagnosis of ILD were screened with HRCT. It was found that all anti-carbamylated protein antibodies studied were more frequent and with higher mean titres in the ILD group. In addition, logistic regression adjusted for age, RA duration, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies (anti-CCP), rheumatoid factor (RF), sex and cumulative tobacco dose showed that anti-FCS, anti-CFFHP and anti-FCS-IgA were independently associated with ILD. Another study22 that evaluated different serum biomarkers in a Chinese cohort (later confirmed in a US cohort) showed an association between levels of extracellular matrix metalloproteinases 7 (MMP-7) and IFNγ-inducible protein-10 (IP-10) and the presence of (HRCT-diagnosed) ILD in RA patients. This finding was confirmed in patients with clinical and subclinical ILD. Biomarker levels were correlated with the severity of the ILD. The area under the ROC curve (Receiver Operating Characteristic curve) of these markers for the diagnosis of ILD reached values between 0.68 and 0.86. In a study26 with fewer RA patients who underwent lung HRCT, higher levels of CA15-3 and CA125 were laboratory determined in patients with ILD than in those without ILD. Finally, the study by Doyle et al.29 showed a significant increase in MMP-7, PARC, and surfactant protein D in patients with subclinical ILD in two different cohorts.
Bronchoalveolar lavageThe search yielded 2 studies conducted in the late 1980s30,38 in which BAL was used to screen for ILD in RA patients. The diagnosis of ILD was established by plain chest X-ray and patients underwent BAL for cellular and biochemical analysis. The study by Tishler et al.30 showed that patients with radiological abnormalities had a higher percentage of lymphocytes in the BAL than patients with normal X-rays. Gilligan et al.38 detected subclinical ILD in 15% of patients by chest X-ray and PFT. In the BAL of patients with established ILD, there was a significant difference in the number of neutrophils compared to controls, as well as an increase in collagenase and N-terminal procollagen type III. Gochuico et al.8 compared BAL findings between RA patients with biopsy-confirmed pulmonary fibrosis, RA and subclinical ILD diagnosed by HRCT and RA patients without lung disease. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-AB and PDGF-BB levels were higher in patients with ILD versus those with RA without ILD. Moreover, significantly higher levels of interferon gamma and transforming growth factor beta 1 (TFG-β1) were detected in patients with ILD with progression of lung damage versus those without.
Pulmonary function testPFTs have been assessed in several studies for the diagnosis of ILD. The study by Mohd Noor et al.34 estimated that PFT abnormalities exist in 95% of patients with RA of more than 5 years’ disease duration, 66.6% of them with restrictive pattern. Zhang et al.33 observed that patients with ILD had significantly more PFT abnormalities consisting of restrictive pattern and decreased diffusion. Mori et al.35 found that patients with ILD had significantly lower DLCO and DLCO/VA (DLCO corrected for alveolar volume) values than patients without ILD. Wang et al.26 proposed a DLCO cut-off point of less than 52.95% for the detection of HRCT-confirmed ILD. This DLCO screening method achieved sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 61%. Yilmazer et al.36 found a significant association between DLCO values <75% and respiratory symptoms with the presence of ILD in multivariate analysis. In the study by Leonel et al.,37 PFT was statistically significant as a predictor of HRCT abnormalities in patients with RA. Manfredi et al.24 studied the accuracy of PFT for the diagnosis of ILD with FVC cut-off points below 70% and DLCO below 47%. They reported an accuracy of 52.8% and 54.9%, sensitivity of 20% and 30.8%, and specificity of 82.1% and 80%, respectively.
Lung ultrasoundThree studies assessed the usefulness of transthoracic lung ultrasound in screening for ILD.16,17,20 Cogliati et al.16 evaluated the presence of B-lines in 72 lung segments (28 anterior and 44 posterior) following anatomical lines. The presence of more than 10 B-lines in a single segment was considered diagnostic of ILD. In this study, the sensitivity of ultrasound compared to HRCT was 92% and specificity 56% in a population of RA patients with suspected ILD. The group of Moazedi-Fuerst et al.,17,20 in addition to B-lines (pathological if more than two lines), considered pleural thickening (pathological if more than 3 mm), and the presence of subpleural nodules (pathological if at least one nodule). Ultrasound was estimated to have a sensitivity of 92%–97%, specificity of 56%–97%, PPV of 94%, and NPV of 99% for the diagnosis of HRCT-confirmed ILD in consecutive RA patients without respiratory symptoms.17,20
High-resolution computed tomographyHRCT was the most sensitive technique for the diagnosis of ILD compared to chest X-ray or PFT in several studies, although a relationship between HRCT findings and respiratory symptoms could not be established.31,32 In the series of Hassan et al.,25 HRCT detected 5% of ILD in respiratory asymptomatic RA patients. In the study by Gabbay et al.,6 33% of RA patients with RA of less than 2 years' duration had ILD on HRCT, clinically insignificant in 3 out of 4 patients. In the paper by Gochuico et al.,8 33% of patients had subclinical ILD on inclusion in the study. After a mean follow-up of 1.5 years, 57% of these patients were found to have progression of lung damage as assessed by HRCT.
Combination of several testsThe combination of HRCT and PFT detected subclinical ILD in 17%–55% of RA patients in the different studies.6,8,21,23,27,33 Gabbay et al.6 found that 58% of patients with RA of less than 2 years’ duration had some abnormality suggestive of ILD in the tests performed (HRCT, chest X-ray,PFT, BAL, scintigraphy). Forty-four percent had subclinical ILD (mild abnormalities on HRCT, FFP and BAL).
The studies by Gabbay et al.6 and Dawson et al.27 concluded that plain X-ray is not a highly sensitive technique for the diagnosis of ILD in RA.
DiscussionILD is a common extra-articular manifestation in patients with RA. It accounts for 7%–20% of deaths, making it the second leading cause of death after cardiovascular disease.39,40 The prevalence varies depending on the cohort studied and method used, ranging from 5%-61%. Between 5% and 55% of patients are thought to be asymptomatic.6,8,21,23,25,27,33
The temporal relationship between joint involvement and ILD is variable, although the diagnosis of RA usually precedes the diagnosis of lung involvement. Several risk factors have been described in patients with RA for the development of ILD. The main associations have been found to be with older age, male sex, smoking history, and the presence of RF and anti-CCP2 antibodies. The importance of screening for ILD in RA patients lies in the morbidity and mortality associated with it. However, the presence of ILD influences treatments for control of joint activity and progression of radiological damage.
The studies included in this review evaluated the use of different diagnostic techniques to screen for ILD in patients with RA.
Digital auscultation is one of the most recently developed techniques. Considering that lung auscultation, together with specific history taking, is the most useful clinical tool to establish a suspicion of ILD, the INSPIRATE study19,24 explored the usefulness of a digital stethoscope to detect velcro-like crackles. Digital auscultation achieved an accuracy of 84%–90% in the diagnosis of ILD compared to HRCT. As it is a non-invasive technique, these results could make it a useful tool in screening for ILD.
Regarding the use of serum biochemical markers, an association between the presence of subclinical ILD in RA patients has been observed with markers such as IL-33,18 MMP-7,22,29 IP-10,22 PARC, surfactant protein D,29 and antibodies to the carbamylated antigens FCS, Fib and CFFHP28; however, cut-off points for the application of these markers in clinical practice have not yet been established. Apart from their use as a screening technique, biomarkers could be of interest to assess the progression and prognosis of patients already diagnosed with ILD.
Two low-quality studies have failed to demonstrate the usefulness of BAL in screening for ILD.30,38 Since the widespread use of HRCT, BAL has fallen into disuse for the diagnosis of ILD and is now reserved for excluding other diseases (cancer, infections, etc.). Several studies have explored the usefulness of PFT in screening for ILD with very different results. The most frequent abnormalities were decreased DLCO and restrictive pattern.26,33–35 An association has been found between decreased DLCO and the presence of ILD on HRCT. The sensitivity of PFT for diagnosing ILD was between 59% and 100%, and the specificity between 61% and 83%. Decreased DLCO was found to be the most sensitive abnormality.26,36,37 As a non-invasive technique, PFT is useful for complementary screening.
Three studies on the use of transthoracic lung ultrasound for screening for ILD were included.16,17,20 A good association was found between ultrasound and HRCT findings, with ultrasound achieving sensitivities of over 90%.16,17 Given that ultrasound is a fast, non-invasive technique that costs less than HRCT and avoids subjecting the patient to additional radiation, it can be considered a key tool in screening for ILD during follow-up of RA patients.41 However, the need for specialist training may limit its accessibility.
Lung HRCT was found to be the most sensitive technique for early detection in asymptomatic patients.31,32 It is currently considered the gold standard test for the diagnosis and classification of the type of ILD in RA patients and is the gold standard used in most validity studies of other techniques. A single study prospectively followed up patients with ILD diagnosed by HRCT.8 Radiological progression was found in 57% of patients with ILD after a mean follow-up of one and a half years.
One of the limitations of this review is that most of the studies included were not specifically designed for screening for ILD and the methodological quality was generally poor. The populations were also very heterogeneous, as they included both respiratory asymptomatic and highly symptomatic patients in the same cohorts. This heterogeneity in both the populations included and the methodology of the studies did not allow for a meta-analysis.
In conclusion, ILD is a common manifestation in patients with RA. Given the high morbidity and mortality associated with the condition, techniques that allow early detection are important. In our review, HRCT proved the most sensitive technique and plain X-ray the least sensitive. In PFT, decreased DLCO was the most sensitive parameter for detecting ILD. Other methods such as digital auscultation, biomarkers, and lung ultrasound could be emerging methods for screening for ILD, but more studies are needed to establish their real value in larger and unselected RA patient populations.
FundingThis review was funded by the Spanish Society of Rheumatology.
Conflict of interestsThe authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Please cite this article as: Garrote-Corral S, Silva-Fernández L, Seoane-Mato D, Guerra-Rodríguez M, Aburto M, Castañeda S, et al. Cribado de enfermedad pulmonar intersticial difusa en pacientes con artritis reumatoide: una revisión sistemática. Reumatol Clín. 2022;18:587–596.