In this article, we present a case of resistant chondrocalcinosis who had a good response with 40mg subcutaneous adalimumab. To our knowledge, this is the first report using adalimumab successfully in severe CPDD. Anti-TNF therapy can be a good therapeutic option for second line therapy in CPPD.
En este artículo, presentamos un caso de condrocalcinosis resistente que tuvo una buena respuesta con 40mg de adalimumab subcutáneo. Hasta donde sabemos, este es el primer informe en el que se utiliza adalimumab con éxito en la enfermedad por depósitos de cristales de pirofosfato de calcio dihidratado (CPPD) grave. El tratamiento anti-TNF puede ser una buena opción terapéutica de segunda línea en la CPPD.
Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition (CPPD) is an inflammatory disease caused by the deposition of calcium pyrophosphate crystals in the joints. Although CPPD can stay mostly asymptomatic, it can present as acute or chronic arthritis.1,2 Intra-articular corticosteroids injection, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, colchicine, methotrexate and hydroxychloroquine can be used for CPPD. In resistant cases, biological treatments can also be used. IL-1 inhibitor anakinra is the most widely used biological agent for chondrocalcinosis.3–5 Since TNF is also involved in the pathophysiology, anti-TNF drugs are also considered to be used in treatment.
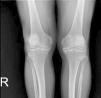
Case presentationForty-six years old male patient presented with history of hip and joint pain for 2 years. His pains were resistant to analgesics. He does not have any comorbidities. He does not have any family history of CPPD or CPPD like symptoms. On laboratory examination C-reactive protein was 2.35mg/L (0–5), serum calcium was 9.2mg/dL (8.6–10.2), magnesium was 1.81mg/dL (1.5–2.6), uric acid was 4.1mg/dL (3.5–7.2), ferritin was 23.5μg/L (30–400), erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 2mm/h (<15), parathormone was 56.82ng/L (15–65), thyroid releasing hormone was: 0.953mU/L (0.27–4.2) and vitamin D was 48ng/mL (20–50). Rheumatoid factor and antinuclear antibodies were negative. HLA-B27, HLA B-51, HLA B52 were negative. There was no history of inflammatory bowel disease and psoriasis. X-rays revealed chondrocalcinosis of the glenohumoral joints, intervertebral disks, acetabular joints, iliac crests, femoral trochanters, iliopubic tuberosities, symphisis pubis, meniscuses, knee joint cartilages, ankles, tarsal joints and heels (Fig. 1). In his magnetic resonance imagining chondrocalcinosis and early coxarthrosis was seen in bilateral hip joints. There was not any sign of sacroiliac inflammation. He was refractory to multiple NSAIDs, colchicine, sulfasalazine, methotrexate and low-middle dose corticosteroid. Subcutaneous adalimumab 40mg was started each 2 weeks. Methotrexate and 2mg dexamethasone treatments continued. A major reduction of pain was observed in his 3 months follow-up. No side effects of adalimumab were observed. The patient's follow-up continues stably under anti-TNF therapy.
DiscussionIn the literature, successfully treated cases with IL-1R antagonist anakinra are published.4–6 One of the cases treated with anakinra was resistant to adalimumab treatment.4 Patients that successfully managed with the IL-6 receptor inhibitor tocilizumab that resistant to anakinra was also reported.7,8 In a report infliximab was used for treatment of two resistant chondrocalcinosis and results has been shown to be effective.9 Although several reports exist of monosodium urate crystals deposition being successfully treated with anti-TNFα drugs, published cases of CPPD successfully treated with these agents are lacking.10 Due to various roles of TNF in inflammatory processes we decided to use anti-TNF blocking agent adalimumab in therapy of resistant chondrocalcinosis patient. In the follow-up periods the patient had really good answer to our therapy and there were no major side effects. To our knowledge, this is the first report using adalimumab successfully in severe CPDD.
FundingThis research received no financial support from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Informed consentInformed consent was taken from patient.
Conflict of interestsAll other authors declare no competing interests.