Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is often accompanied by musculoskeletal (MS) symptoms, which can hinder the diagnosis of concurrent conditions like rotator cuff tendinopathy (RCT), the most common cause of shoulder pain. Undiagnosed RCT in patients with RA may be associated with higher disease activity scores. This study aimed to assess the difference in these scores between RA patients with and without RCT, considering ultrasound pathological findings.
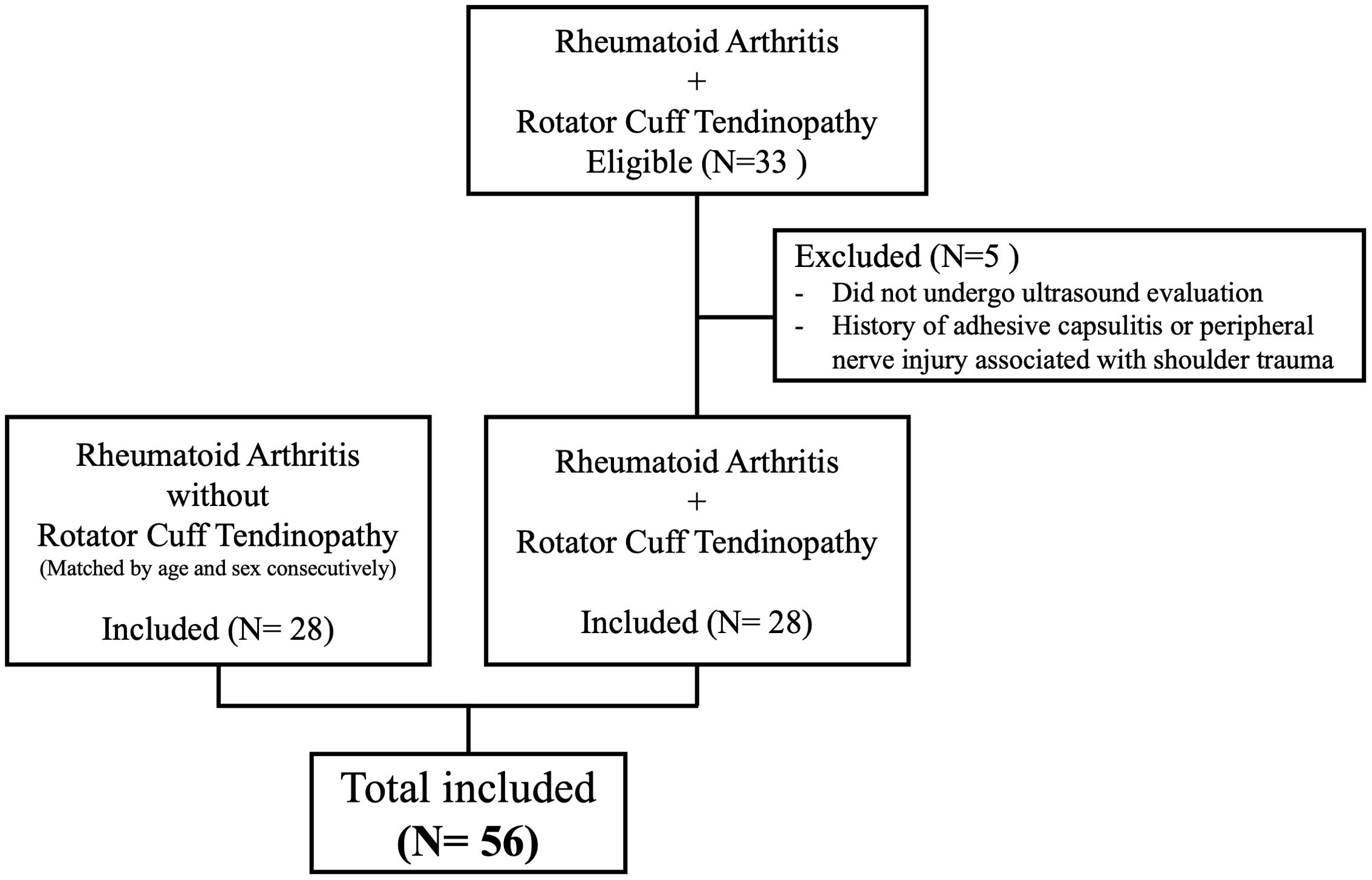
MethodsWe conducted a cross-sectional, observational, comparative study in patients with shoulder pain who met the 2010 ACR-EULAR classification criteria for RA between January 2022 and January 2023. The measurements of Disease Activity Score based on 28 joints using C-Reactive Protein (DAS28-CRP), Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (DAS28-ESR), and the Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) were used to evaluate RA activity, while functional capacity was assessed using the Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI). The Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand questionnaire (DASHe) and shoulder ultrasound examination was performed to detect the presence or absence of RCT.
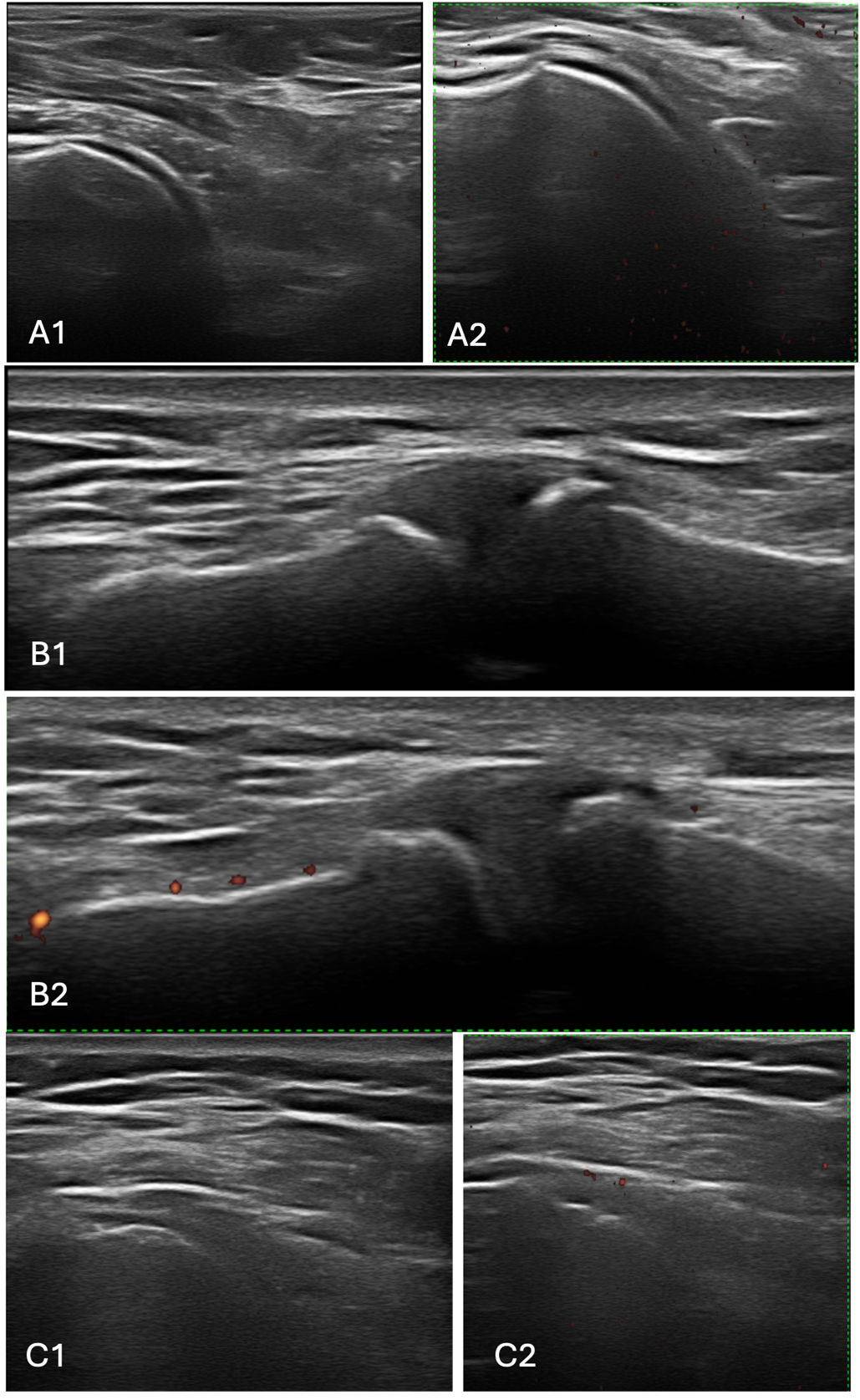
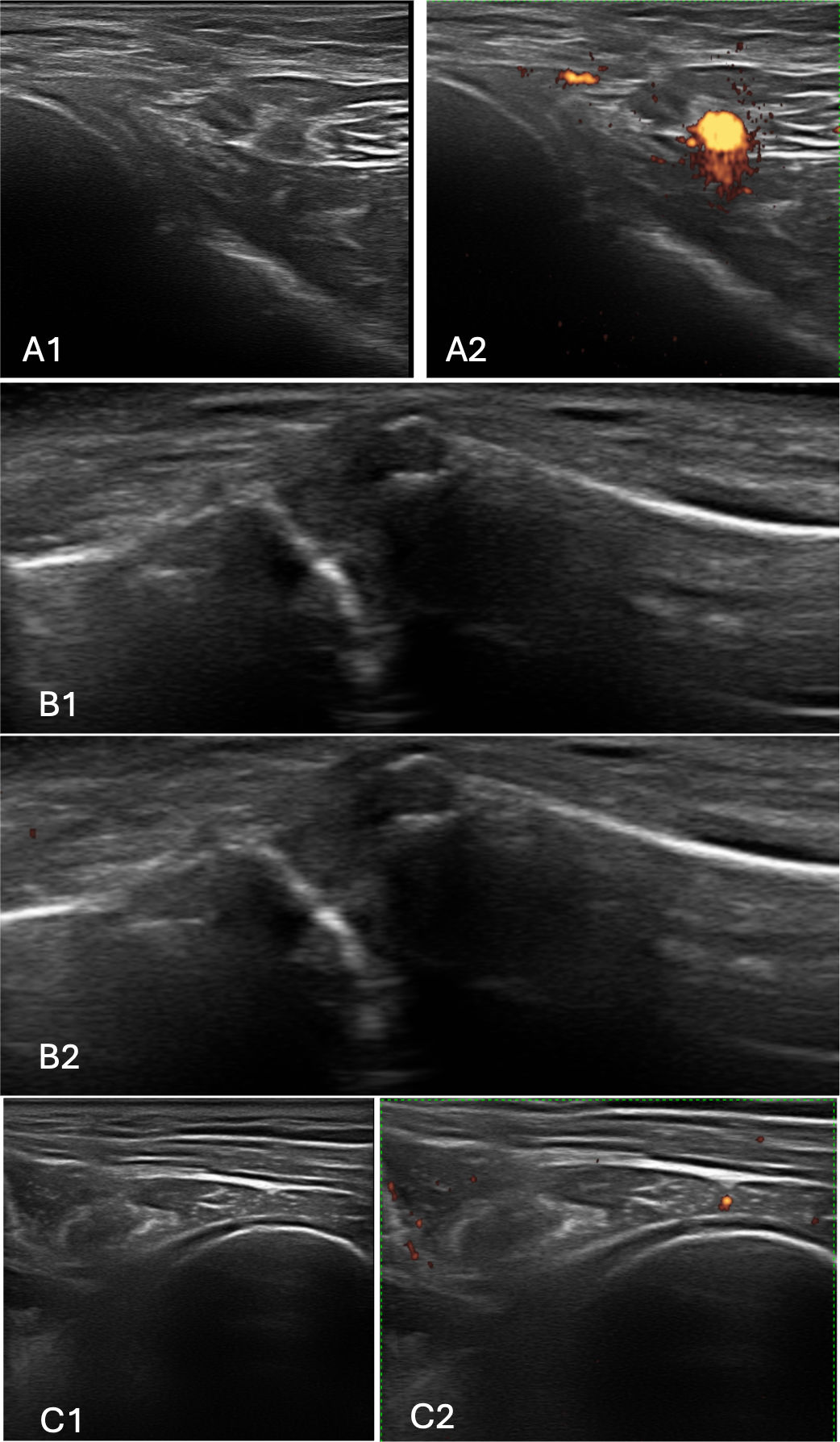
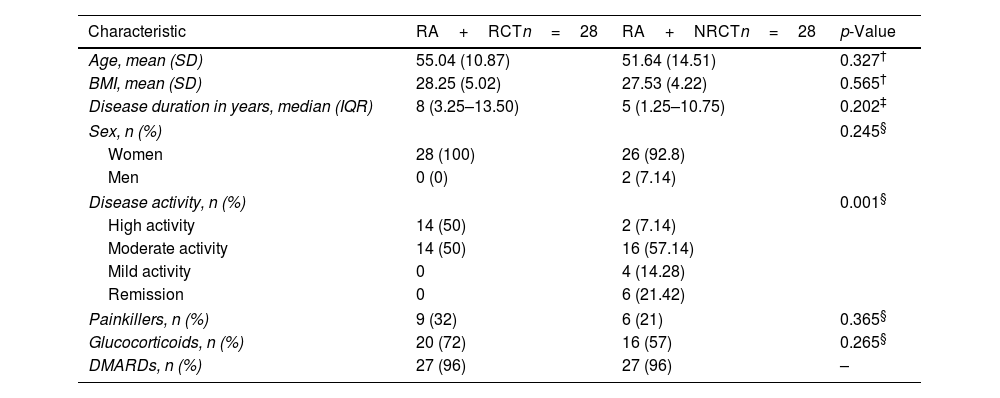
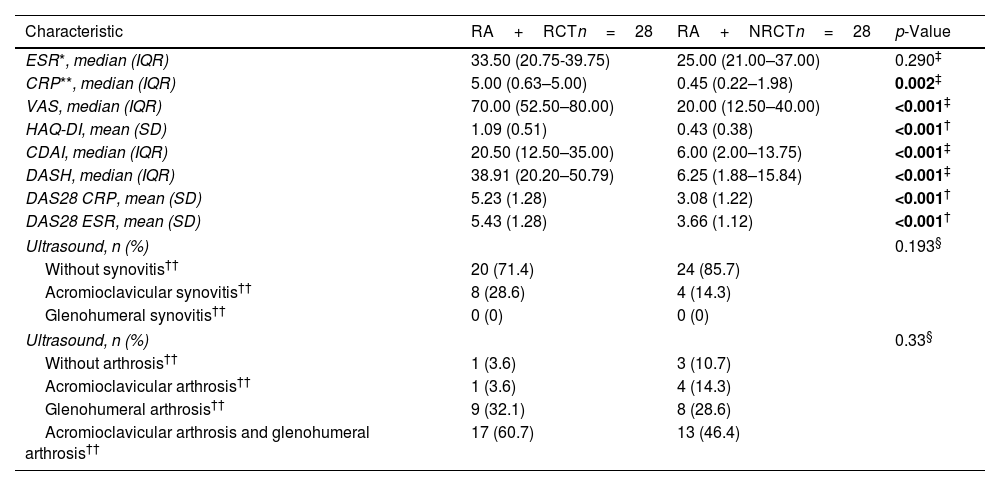
ResultsPatients with RCT had greater mean scores on DAS28-CRP (5.23, 1.28 vs. 3.08, p<0.001), and DAS 28-ESR (5.43, SD=1.28 vs. 3.66, p<0.001). VAS median scores were higher in the RCT group (70.00 vs. 2.00, p<0.001). By ultrasound 12 patients (21%) had acromioclavicular synovitis. Glenohumeral and acromioclavicular arthrosis was found in both groups. No patients had arthritis in the glenohumeral joint.
ConclusionRA patients with RCT have higher composite index and disease activity scores than those without RCT. An intentional RCT screening should be recommended for those with shoulder pain and elevated disease activity.
La artritis reumatoide (AR) puede acompañarse de síntomas musculoesqueléticos, lo que enmascara el diagnóstico de condiciones concurrentes como la tendinopatía del manguito rotador (TMR). La TMR en pacientes con AR puede asociarse con puntajes más altos de actividad de la enfermedad. El objetivo es evaluar la diferencia de estas puntuaciones en pacientes con AR con y sin TMR.
MetodologíaSe realizó un estudio observacional, transversal y comparativo en pacientes con dolor de hombro que cumplían los criterios de clasificación ACR-EULAR 2010 para AR entre enero de 2022 y enero de 2023. Se utilizaron el Índice de Actividad de Enfermedad basado en 28 articulaciones usando la proteína C reactiva (DAS28-PCR), la velocidad de sedimentación globular (DAS28-VSG) y el Índice de Actividad de la Enfermedad Clínica (CDAI) para evaluar la actividad de la AR. La capacidad funcional se evaluó utilizando el Índice de Discapacidad del Cuestionario de Evaluación de la Salud (HAQ-DI). Se aplicó el cuestionario de Discapacidades de Brazo, Hombro y Mano (DASHe) y se realizó un ultrasonido del hombro para detectar TMR.
ResultadosLos pacientes con TMR tuvieron promedios mayores en DAS-PCR (5,23, 1,28 vs. 3,08, p<0,001) y DAS28- VSG (5,43, DE=1,28 vs. 3,66, p<0,001). Las medianas de la escala visual análoga fueron mayores en TMR (70,00 vs. 2,00, p<0,001). Por ultrasonido, 12 pacientes (21%) tenían sinovitis acromioclavicular. En ambos grupos se encontró artrosis glenohumeral y acromioclavicular. Ningún paciente tenía artritis en la articulación glenohumeral.
ConclusiónLos pacientes con AR y TMR presentan puntajes de actividad más altos que aquellos sin TMR. Se recomienda un cribado en pacientes con dolor de hombro y alta actividad de enfermedad.