Behcet's disease (BD) is an autoimmune systemic inflammatory disease, and its exact pathogenesis is unknown. There are currently no specific tests to evaluate the disease activity of BD, making its management more difficult. This study aims to determine the neutrophil/albumin ratio (NAR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) to albumin ratio (CAR) and investigate their associations with clinical findings in patients with BD and to determine optimum cutoff levels of CAR and NAR.
MethodsThe study included 75 consecutively recruited patients with BD with a mean age of 33.29±6.23 years and disease duration of 7.21±4.64 years, as well as 75 healthy participants. Clinical characteristics and laboratory data were obtained. Disease activity was assessed using the BD current activity form score (BDCAF).
ResultsNAR and CAR were elevated in patients with BD compared with those of healthy controls (NAR: 1.08±0.34 vs. 0.607±0.06, CAR: 2.49±1.73 vs. 0.39±0.142; p<0.0001), as well as in active BD versus inactive BD. Both NAR and CAR were significantly correlated with CRP, active uveitis, and BDCAF score (p≤0.05). In patients with active BD, the cutoff value of NAR was >0.9744 (sensitivity: 89.74%, specificity: 80.56%), while that of CAR was >2.04 (sensitivity: 74.36%, specificity: 83.33%).
ConclusionsNAR and CAR are both elevated in patients with BD and may contribute to its active state. NAR and CAR can be feasible and inexpensive markers for predicting BD activity.
La enfermedad de Behçet (EB) es una enfermedad inflamatoria sistémica autoinmune y se desconoce su patogenia exacta. Actualmente no existen pruebas específicas para evaluar la actividad de la EB, lo que dificulta su manejo. El objetivo de este estudio es determinar la proporción neutrófilos/albúmina (NAR) y de proteína C reactiva (CRP)/albúmina (CAR) e investigar sus asociaciones con los hallazgos clínicos en pacientes con EB y determinar los niveles de corte óptimos de CAR y NAR.
MétodosEl estudio incluyó a 75 pacientes con EB reclutados consecutivamente con una edad media de 33,29±6,23 años y una duración de la enfermedad de 7,21±4,64 años, así como a 75 participantes sanos. Se obtuvieron características clínicas y datos de laboratorio. La actividad de la enfermedad se evaluó utilizando la puntuación del formulario de actividad actual de la EB (BD Current Activity Form [BDCAF]).
ResultadosNAR y CAR estaban elevados en pacientes con EB en comparación con controles sanos (NAR: 1,08±0,34 vs. 0,607±0,06, CAR: 2,49±1,73 vs. 0,39±0,142; p<0,0001), así como en pacientes EB activos versus EB inactivos. Tanto la NAR como la CAR se correlacionaron significativamente con la PCR, la uveítis activa y la puntuación BDCAF (p≤0,05). En pacientes con EB activa, el valor de corte de NAR fue>0,9744 (sensibilidad: 89,74%, especificidad: 80,56%), mientras que el de CAR fue>2,04 (sensibilidad: 74,36%, especificidad: 83,33%).
ConclusionesNAR y CAR están elevados en pacientes con EB y pueden contribuir a su estado activo. NAR y CAR pueden ser marcadores factibles y económicos para predecir la actividad de EB.
Behcet's disease (BD) is a chronic multisystemic disease of unknown etiology. It can affect a variety of organs and can go into remission and relapse. Characteristic BD features include recurrent oral, genital, and mucosal ulceration, uveitis, and cutaneous lesions. The neurological, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and musculoskeletal systems may also be involved.1–3 Neutrophil hyperfunction, vasculitis, and autoimmune reactions appear to be responsible for the disease.4,5
Several laboratory tests have been studied for their ability to reflect disease activity, evaluate treatment efficacy, or predict future complications of BD, but no particular test has been found to detect disease activity.6–9 Nevertheless, the C-reactive protein (CRP) to albumin ratio (CAR) has been proposed as a better indicator of inflammatory response compared with CRP or albumin alone.10,11 CAR is a well-established predictor of a variety of diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, BD uveitis, heart disease, and various cancers.12–14 Furthermore, higher levels of CAR are also associated with poor prognosis and worse treatment outcomes in systemic diseases.15,16
The neutrophil/albumin ratio (NAR) has been reported as a new inflammatory indicator in severe infection, cancer, and schizophrenia. In patients with cancer, a higher level of NAR was found to represent an increased inflammatory state, which poorly affects prognosis and treatment response.17 Neutrophils, the key components of the innate immune system, are activated and recruited to the target tissue by inflammatory mediators due to the chronic inflammatory status of BD, causing damage and organ dysfunction.18 Hypoalbuminemia in BD reflects the underlying active inflammatory state; the decrease in hepatic albumin production (a negative acute-phase reactant) may be caused by increased inflammatory mediators.19 However, NAR has not been studied in BD.
Thus, we aim to examine the value of the CAR and NAR in patients with BD in terms of their associations with clinical characteristics, as well as to determine their optimum cut-off levels. In this study, we hypothesized that CAR and NAR are associated with disease activity and can serve as novel inflammatory markers in BD.
MethodsStudy designThis case-control study was conducted in the Rheumatology & Rehabilitation Departments, Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University.
Study populationThe study included 75 patients with BD who were routinely followed up at the Department of Rheumatology, Rehabilitation, and Physical Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, from January 2021 to May 2021. BD diagnosis was made according to the revised International Criteria for Behcet's Disease 2010 criteria.20 The study also included a control group of 75 healthy adults of the same age and gender. We excluded patients with other autoimmune diseases or systemic disorders (i.e., malignancy, diabetes mellitus, heart failure, hepatic dysfunction, renal dysfunction, acute infection, and chronic infection). Informed consent was obtained from each subject before their participation in the study. Approval was obtained from the ethics committee of the university (registration number: ZU-IRB 6614/19-9-2019). The study was conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Data collectionPatient data were gathered from their medical records, including demographic data, such as name, age, sex, and disease duration. Furthermore, the same rheumatologist carried out a comprehensive history and clinical examination in all patients.
Determination of disease activityDisease activity during the past 4 weeks was evaluated using the validated Turkish version of the BD Current Activity Form (BDCAF). The presence of active disease was defined as having a BDCAF score of ≥2 out of 12.21
Laboratory investigationsA complete blood count including the differential count, erythrocytes sedimentation rate (ESR), CRP, and serum albumin were obtained from patients with BD and healthy controls. The white blood cell (WBC), neutrophil, lymphocyte, and platelet counts were recorded. The neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet/lymphocyte ratio (PLR), NAR, and CAR were calculated from these parameters.
In our hospital, complete blood counts were determined using the Sysmex KX-21 hematology analyzer (Sysmex Corporation, America), and albumin was measured using the automated clinical chemistry analyzer Cobas Integra 400 plus (Roche Diagnostics, Deutschland). CRP levels were measured using automated nephelometry BN Prospec (Siemens, UK), and ESR was analyzed in the 1st hour using Westergren's method.
Statistical analysisAll data were collected, tabulated, and statistically analyzed using SPSS 20.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA 2011). Quantitative data were expressed as the mean±standard deviation and median (range), and qualitative data were expressed as absolute frequencies (number) and relative frequencies (percentage). Comparisons of normally distributed continuous variables were carried out using independent samples Student's t-test, while the Mann–Whitney U test was used for non-normally distributed data. Percent of categorical variables were compared using Chi-square test or Fisher's exact test when appropriate. Relationships of the NAR and CAR ratio with various parameters of BD were assessed by calculating Pearson's and Spearman's correlation coefficients. To differentiate between patients with active and inactive BD, the optimal cut-off values of the NAR, CAR, CRP, ESR, NLR, and PLR with the maximum sensitivity and specificity were calculated via receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. The -statistic was used to compare the areas under the ROC curves (AUCs). p-Values of ≤0.05 were statistically significant, whereas p-values of >0.05 were considered statistically insignificant.
ResultsThe main clinical characteristics of the 75 patients with BD are summarized in Table 1. Oral ulceration (77.3%) and genital ulceration (69.3%) were the most common clinical features of patients with BD, whereas pulmonary and arterial involvement was the least common (1.33%). The mean duration of BD was 7.21±4.64 years. The median disease activity score assessed via BDCAF was 2 (range: 1–4). Accordingly, 39 patients were considered to have active BD.
Clinical characteristics of patients with BD.
| Variables | Behcet patients (n=75) |
|---|---|
| Disease duration (year) | 7.21±4.64, 7 (1–24) |
| Oral ulcer | 58 (77.3%) |
| Genital ulcers | 52 (69.3%) |
| Papulopustular lesions | 3 (4%) |
| Erythema nodosum | 2 (2.6%) |
| Pathergy test | 4 (5.3%) |
| Articular manifestations | 22 (29.3%) |
| Ocular affection | 38 (50.6%) |
| Active Uveitis | 29 (38.6%) |
| Anterior uveitis | 4 (5.3%) |
| Posterior uveitis | 34 (45.3%) |
| Pan uveitis | 3 (4%) |
| Arterial involvement | 1 (1.33%) |
| Venous involvement | 34 (45.3%) |
| Deep venous thrombosis | 6 (8%) |
| Superficial thrombophlebitis | 7 (9.33%) |
| Neurological involvement | 5 (6.6%) |
| Pulmonary involvement | 1 (1.33%) |
| Cardiovascular involvement | 11 (14.7%) |
| BDCAF score, median (range) | 1.94±1.005, 2 (1–4) |
| Active disease, n (%) | 39 (52%) |
| Treatment | |
| Colchicine | 28 (37.3%) |
| Dapsone | 3 (4%) |
| Corticosteroids | 53 (70.6%) |
| Azathioprine | 35 (46.7%) |
| Cyclophosphamide | 6 (8%) |
| Cyclosporine | 4 (5.3%) |
| Chlorambucil | 1 (1.33%) |
| Methotrexate | 5 (6.7%) |
| Infliximab | 17 (22.6%) |
| Adalimumab | 22 (29.3%) |
| Anticoagulants | 6 (8%) |
Values are stated as number and percentage n (%), mean±Sd or median (range), BDCAF: Bechet's disease current activity form.
Our study included 75 patients with BD with a mean age of 34.29±6.23 years (24 females, 51 males) and 75 healthy controls matched for age and sex (p>0.05). Patients with BD had significantly increased levels of ESR, CRP, albumin, WBCs, neutrophil, NLR, and PLR compared with those of controls (p≤0.05). Furthermore, patients with BD also had significantly increased NAR (1.08±0.34; p<0.0001) and CAR (2.49±1.73; p<0.0001) compared with those of controls. However, the two groups did not differ significantly in the other parameters, such as body mass index, hemoglobin level, and platelet and lymphocyte counts (p>0.05) (Table 2).
Demographic and laboratory results of Behcet patients and controls.
| Variables | Behcet patients (n= 75) | Control (n =75) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 33.29±6.23 | 32.96 ± 5.33 | 0.16a |
| 34 (22-57) | 33 (24-54) | ||
| Gender | |||
| Female | 24 (32%) | 27 (36%) | 0.61c |
| Male | 51 (68%) | 48 (64%) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.47 ± 2.43 | 24.62 ± 2.05 | 0.68a |
| 24.2 (21.4-31.8) | 24.5 (21.4-32.2) | ||
| ESR, mm/h | 28 (3-130) | 18 (10-28) | 0.001b* |
| CRP, mg/ dL | 10.3 ± 7.2 | 1.71 ± 0.63 | |
| 10 (0.12 - 33.6) | 1.6 (0.3 -3.5) | 0.0001a* | |
| Albumin (g/dl) | 4.22 ± 0.34 | 4.46 ± 0.19 | |
| 4.2 (3.49-4.81) | 4.39 (3.64-4.8) | 0.001a* | |
| HGB | 12.84 ± 0.65 | 12.88 ± 0.65 | 0.68a |
| 12.7 (11.9-15) | 12.9 (12.3-14.7) | ||
| WBCS, (x103/mm3) | 8.16 ± 1.704 | 5.89 ± 1.17 | < 0.0001a* |
| 7.9 (4.2-15.4) | 5.6 (4.2-8.8) | ||
| Platelets, (x103/mm3) | 272 (201 -402) | 265 (228-320) | 0.13b |
| Neutrophil, × (x103/mm3) | 4.551 ± 1.36 | 2.725 ± 0.30 | < 0.0001a* |
| 4.4 (2.5-7.6) | 2.7 (2.2-3.4) | ||
| Lymphocyte, × (x103/mm3) | 2.23 ± 0.531 | 2.15 ± 0.34 | 0.289a |
| 2.2 (1.4-3.2) | 2.1 (1.3-2.9) | ||
| NLR | 2.109 ± 0.67 | 1.31 ± 0.28 | 0.0001a* |
| 2.04 (0.8-5.2) | 1.27 (0.16-2) | ||
| PLR | 122.17 (52.64-202.66) | 116.1 (79.31-168.8) | 0.0397b* |
| CAR | 2.49 ± 1.73 | 0.39 ± 0.142 | |
| 2.4 (0.02-7.3) | 0.37 (0.074-0.755) | 0.0001a* | |
| NAR | 1.08 ± 0.34 | 0.607 ± 0.06 | |
| 1.1 (0.31-3.2) | 0.6 (0.33-0.48) | 0.0001a* |
All values are presented a number and percentage n (%), mean±Sd or median (range), number (%) or mean±SD.
When we compared patients in the active (n=39) and inactive BD (n=36) state, significant differences were found in the ESR, CRP, WBC count, neutrophil count, serum albumin, and NLR (p=0.004, p<0.001, p=0.0039, p=0.001, p=0.002, and p=0.0008, respectively). Patients with active BD (n=39) had a significantly higher NAR compared with those with inactive BD (n=6, p<0.0001). Furthermore, patients with active BD had a significantly increased CAR compared with those with inactive BD (p<0.0001) (Table 3).
Comparison of parameters according to disease activity in BD.
| Variables | Active | Inactive | T test | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n=39 | n=36 | |||
| Age | 34.82±8.85 | 34.44±5.72 | ||
| 35 (22-57) | 34.5 (26-48) | t = 0.21 | 0.82a | |
| Gender (female/male) | 11/28 | 13/23 | 0.537 | 0.46c |
| Disease duration | 6.46±4.24 | 8.36±4.72 | ||
| 6 (1-14) | 8 (2-24) | t = 1.836 | 0.0704a | |
| ESR (mm/hour) | 31 (5-130) | 20 (3-65) | u=3.48 | .004b* |
| CRP (mg/L) | 14.19±6.97 | 6.231±4.92 | ||
| 14.2 (0.2-33.6) | 6.1 (0.12-26.8) | t = 5.66 | < .0001a* | |
| WBCS, (x103/mm3) | 8.68±1.95 | 7.58±1.088 | ||
| 8.5 (5-15.4) | 7.5 (4.2-10) | t = 2.9822 | 0.003a* | |
| Neutrophil, × (x103/mm3) | 5.21±1.45 | 3.83±0.7 | ||
| 5.1 (3-7.6) | 3.7 (2.5-5.8) | t = 5.149 | 0. 001a* | |
| HGB | 12.856±0.609 | 12.85±0.682 | ||
| 12.7 (11.9-14.6) | 12.7 (12-15) | t = 0.04 | 0.96a | |
| Lymphocyte, × (x103/mm3) | 2.31±0.61 | 2.13±0.387 | ||
| 2.3 (1.5-3.2) | 2.1 (1.4-2.8) | t = 1.511 | .135a | |
| Platelets, (x103/mm3) | 268 (201-402) | 248.5 (201-316) | u=1.67 | 0.094b |
| Albumin (g/dl) | 4.16±0.28 | 4.38±0.31 | ||
| 4.1 (3.49-4.6) | 4.2 (3.7.4.81) | t=3.18 | 0.002a* | |
| NLR | 2.349±0.734 | 1.847±0.475 | ||
| 2.2 (1.6-5.2) | 1.7 (0.8-2.9) | t = 3.484 | 0.0008a | |
| PLR | 123.63 (52.641-202.66) | 116.84 (80-158.64) | u= 1.33 | 0.18b |
| CAR | 3.26±1.56 | 1.4659±1.182 | ||
| 3.2 (0.04-7.3) | 1.3 (0.02-6.3) | t = 5.6 | <0.00001a* | |
| NAR | 1.236±0.3149 | 0.882±0.2028 | ||
| 1.2 (0.65-3.2) | 0.86 (0.31-1.26) | t = 5.73 | <0.0001a* |
All values are presented a number and percentage n (%), mean±Sd or median (range), number (%) or mean±SD.
Gender and smoking habits were not significantly associated with either NAR or CAR among patients with BD (p>0.05). However, NAR levels tended to be higher in patients with BD with oral ulceration, articular involvement, and ocular involvement (i.e., active uveitis) (p=0.0416, p=0.0493, and p=0.0108, respectively) compared with those without involvement. Similarly, a significant difference regarding CAR was found in patients with BD with ocular involvement (active uveitis) (p=0.0349) compared with those without active uveitis. Thus, NAR was closely linked to the presence of oral ulcerations and articular manifestations, whereas CAR was not. Otherwise, neither NAR nor CAR levels were affected by the presence of vascular, pulmonary, cardiovascular, or neurological involvements in BD (p>0.05) (Table 4).
Comparison of CAR and NAR according to BD characteristics.
| Variables | CAR, mean±SD | p value | NAR, mean±SD | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||||
| Female (24) | 2.628±1.85 | p=0.60 | 0.998±0.248 | p=0.16 |
| Male (51) | 2.401±1.758 | 1.117±0.376 | ||
| Smoking | ||||
| Yes (22) | 2.156±1.56 | p=0.2922 | 1.076±0.3752 | p=0.93 |
| No (53) | 2.623±1.87 | 1.083±0.2703 | ||
| Oral ulcer | ||||
| Present (58) | 2.628±1.79 | p=0.17 | 1.120±0.351 | p=0.0416* |
| Absent (17) | 1.947±1.67 | 0.936±0.182 | ||
| Genital ulcers | ||||
| Present (52) | 2.298±1.78 | p=0.204 | 2.156±1.5625 | p=0.26 |
| Absent (23) | 2.871±1.75 | 2.623±1.8716 | ||
| Rash | ||||
| Present (5) | 1.858±1.59 | p=0.21 | 1.085±0.3127 | p=0.94 |
| Absent (70) | 2.580±1.80 | 1.077±0.3506 | ||
| Articular manifestations | ||||
| Present (22) | 2.854±1.84 | p=0.28 | 1.209±0.5081 | p=0.049* |
| Absent (53) | 2.345±1.759 | 1.034±0.2573 | ||
| Active uveitis | ||||
| Present (29) | 2.905±1.617 | p=0.0349* | 1.183±0.239 | p=0.0108* |
| Absent (46) | 2.007±1.855 | 0.966±0.402 | ||
| Venous involvement | ||||
| Present (28) | 2.723±1.694 | p=0.31 | 1.087±0.281 | p=0.85 |
| Absent (47) | 2.298±1.84 | 1.072±0.384 | ||
| Superficial thrombophlebitis | ||||
| Present (7) | 2.397±1.6626 | p=0.841 | 0.967±0.222 | p=0.123 |
| Absent (68) | 2.496±1.8282 | 1.111±0.366 | ||
| Cardiovascular involvement | ||||
| Present (11) | 2.489±1.776 | p=0.976 | 1.115±0.396 | p=0.69 |
| Absent (64) | 2.471±1.796 | 1.072±0.337 | ||
| Neuro–Bechet | ||||
| Present (5) | 2.068±1.634 | p=0.441 | 1.012±0.324 | p=0.504 |
| Absent (70) | 2.536±1.806 | 1.089±0.347 | ||
All values are stated as mean and SD, CAR: C-reactive protein/albumin ratio, NAR: neutrophil/albumin ratio, NLR: neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio.
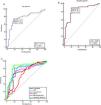
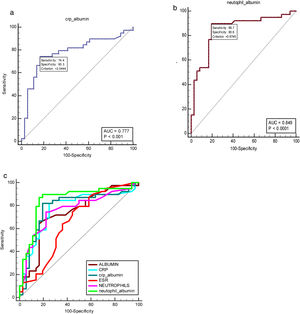
The ROC curve analyses for CAR and NAR as well as other inflammatory markers were performed to evaluate the disease activity in patients with BD included in the study. Specifically, CAR was compared with the CRP and albumin levels as presented in Table 5. The AUC of the NAR (0.849, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.747–0.921, p<0.0001) and CAR (0.777, 95% CI: 0.666–0.865, p<0.001) in patients with BD were higher than those of albumin, neutrophil count, CRP, and ESR. Fig. 1 depicts the discriminatory value of these indicators in relation to the BDCAF score.
ROC curve analysis of NAR and CAR and other inflammatory markers to differentiate between active and inactive Behcet disease.
| Variable | Cut-off value | Sensitivity | Specificity | AUCs | 95% CI | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neutrophils | >4.5 | 74.36 | 77.78 | 0.762 | 0.650–0.853 | <0.001* |
| Albumin | ≤4.16 | 64.10 | 86.11 | 0.733 | 0.618–0.829 | <0.002* |
| CAR | >2.0444 | 74.36 | 83.33 | 0.777 | 0.666–0.865 | <0.001* |
| NAR | >0.9744 | 89.74 | 80.56 | 0.849 | 0.747–0.921 | <0.0001* |
| CRP (mg/dl) | >9.3 | 71.79 | 86.11 | 0.759 | 0.647–0.851 | <0.001* |
| ESR (mm/hr.) | >29 | 61.54 | 72.22 | 0.679 | 0.562–0.783 | 0.0045* |
CAR: C-reactive protein/albumin ratio, NAR: neutrophil/albumin Ratio, CR: C-reactive protein, ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
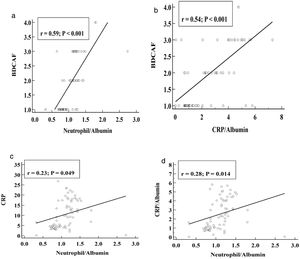
In patients with BD, NAR had significant positive correlations with the presence of active uveitis (r=0.31, p<0.006), oral ulcerations (r=0.244, p=0.034), joint involvement (0.236, p=0.041), BDCAF score (r=0.59, p<0.001), ESR (r=0.153, p=0.028), CRP (r=0.230, p=0.04), neutrophil count (r=0.69, p<0.001), NLR (r=0.67, p<0.0001), and CAR (r=0.28, p=0.014). Moreover, CAR also had significant positive correlations with the presence of active uveitis (r=0.25, p=0.03), BDCAF score (r=0.541, p<0.001), CRP (r=0.49, p<0.0001), and NAR (r=0.28, p=0.014). Furthermore, both CAR (r=−0.369, p=0.011) and NAR (r=−0.451, p=0.0004) had significant negative correlations with serum albumin. Other parameters such as age, disease duration, mucocutaneus involvement, vascular involvement, and PLR were not correlated with either NAR or CAR (p>0.05) (Table 6, Fig. 2).
Correlations of CAR and NAR with patients’ characteristics in BD.
| Variable | CAR(n=75) | NAR(n=75) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p value | r | p value | |
| Age | 0.19 | 0.102 | 0.18 | 0.12 |
| Disease duration | 0.22 | 0.0578 | 0.11 | 0.34 |
| Mucocutaneous manifestations | 0.161 | 0.173 | 0.201 | 0.083 |
| Oral ulceration | 0.049 | 0.67 | 0.244 | 0.034* |
| Articular manifestations | 0.109 | 0.35 | 0.236 | 0.041* |
| Active uveitis | 0.25 | 0.03* | 0.31 | 0.006* |
| Vascular involvement | 0.11 | 0.34 | 0.03 | 0.79 |
| BDCAF score | 0.541 | <0.001* | 0.59 | <0.001* |
| CRP (mg/dl) | 0.49 | <0.0001* | 0.230 | 0.04* |
| ESR (mm/h) | 0.22 | 0.057 | 0.153 | 0.028* |
| Albumin (g/dl) | −0.369 | .0011* | −0.451 | .0004* |
| WBCS, (×103/mm3) | 0.096 | 0.442 | 0.192 | .098 |
| Neutrophil, (×103/mm3) | 0.19 | 0.102 | 0.69 | <0.001* |
| Lymphocyte, (×103/mm3) | 0.21 | .0705 | 0.133 | 0.255 |
| Platelets, (×103/mm3) | 0.10 | 0.36 | 0.145 | 0.214 |
| NLR | 0.020 | 0.86 | 0.67 | <0.0001* |
| PLR | 0.12 | 0.305 | 0.004 | 0.970 |
| NAR | 0.28 | 0.014* | – | – |
| CAR | – | – | 0.28 | 0.014* |
BDCAF: Bechet's disease current activity form; ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CR: C-reactive protein; CAR: C-reactive protein/albumin ratio, NAR: neutrophil/albumin ratio, PLR: platelet to lymphocyte ratio, NLR: neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio.
The principal finding of the present study was that patients with BD had higher NAR and CAR values than healthy controls especially during the active stage of the disease, even in those of treated patients with BD. Moreover, comparisons showed that these two parameters were positively correlated with CRP, active uveitis, and BDCAF score. Previous studies have shown that CAR levels correlated with the activity of different autoimmune and rheumatic diseases.22 However, no studies have associated CAR and NAR with the different clinical manifestations and disease activity in patients with BD.
Although acute-phase protein, immunoglobulin, complement, autoantibody, lymphocyte, surface indicator, and cytokine levels are used as indicators of BD activity, there is no specific indicator for disease activation.6 Previously, the total BDCAF score was found to correlate well with both ESR and CRP levels, but there are still conflicting findings regarding the relationship between these parameters and clinical disease activity in BD.23 Recently, studies have suggested that CAR and NAR are reliable biomarkers of inflammation, and a combination of inflammatory markers including CAR and NAR can be used to indicate increased inflammatory status.24 Besides CAR and NAR, we also evaluated ESR, CRP, NLR, and PLR, all of which have been investigated in several studies.
Similarly, in a study comparing the inflammatory markers between patients with acutely exacerbated and remitted schizophrenia and healthy controls,24 CAR and NAR levels were found to be significantly higher in patients with schizophrenia than in control subjects. The authors proposed that a combination of inflammatory markers including CAR and NAR could be used to reflect the increased inflammatory status in schizophrenia. In accordance with this, a retrospective study of 32 patients with and 32 healthy controls found that CAR had the highest correlation with disease activity in patients with Takayasu arteritis.22
In our study, serum NAR was significantly increased in patients with active BD (n=39) compared with those with inactive BD (n=36, p<0.0001). Furthermore, patients with active BD had a significantly increased CAR compared with those with inactive BD (p<0.0001). Both CAR and NAR also had significant positive correlations with the BDCAF score.
Interestingly, NAR was significantly correlated with NLR (p≤0.05), whereas PLR was not correlated with either NAR or CAR (p>0.05). Significant differences in NLR values were also found in patients with active BD versus those with inactive BD; this is consistent with a previous Egyptian study, which concluded that NLR was higher in patients with active BD than in those with inactive BD (p<0.01). Although both NLR and PLR were correlated with BDCAF, the correlation of NLR with BDCAF was significantly stronger than that of PLR.25
Moreover, a recent study revealed that active BD was associated with higher NLR and PLR, but only a slight correlation between NLR and BD activity. Those authors recommended further separate investigations of PLR and NLR and their relationship with various manifestations of the disease, since NLR and PLR seem to have specific associations with BD activity.26
Similarly, two studies have found CAR to be a useful biomarker in describing the activity of inflammatory bowel diseases, including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.26,27 This finding is consistent with other studies investigating the correlation of CAR and NAR with other inflammatory mediators in various diseases.24 On the other hand, in a cross-sectional study of 121 patients with rheumatoid arthritis assessing the relationship of CAR with disease activity, quality of life, and physical function, a significant but weak correlation between CAR and disease activity was found among the enrolled patients.11
Patients with BD with oral ulcerations had significantly higher articular involvement, ocular involvement (active uveitis), and NAR than in those without involvement. Similarly, patients with BD with active uveitis had a considerable difference in CAR value compared with those without active uveitis. Thus, NAR was closely associated with the presence of oral ulcerations and articular manifestations, whereas CAR was not. However, no studies have been conducted to compare CAR and NAR based on BD characteristics.
In our study, ROC interpretation revealed that the NAR and CAR values in patients with active BD had an AUC of 0.849 and 0.777, respectively, which are higher than those of albumin, neutrophil count, CRP, and ESR. The cut-off value of NAR in our study was >0.9744, and this had a sensitivity of 89.74% (the highest sensitivity percentage among patients with active BD) and a specificity of 80.56%. On the other hand, CAR had a cut-off value of >2.0444, with a sensitivity and specificity of 74.36% and 83.33%, respectively. To date, no studies have previously provided cut-off values or AUC for BD activity.
However, it was previously reported that the AUC of CAR was 0.801 when used to predict the existence of uveitis among patients with BD; this was remarkably high compared with the AUCs of other inflammatory biomarkers.28 In line with this, another study in patients with systemic sclerosis identified the AUC of CAR to be 0.788 (p=0.000), which was significant with a 95% CI of 0.651–0.925.29
Notably, CAR is accepted as an important parameter in the prognosis and follow-up of many diseases. It is used as a prognostic marker for disease activity and mortality, especially in inflammatory conditions, such as sepsis and septic shock.15 The novelty of this study lies in the comparison of CAR and NAR in patients with BD with different clinical and laboratory findings as well as disease activity.
BD is characterized by chronic relapsing episodes and may cause significant morbidity and mortality due to ocular, vascular, and neurological involvements. Early prediction of disease activity may enable clinicians to aggressively manage the disease to prevent the occurrence of complications.30 However, further research is still required to establish the optimal laboratory tests for predicting BD activity.
LimitationsOur study had some limitations. First, this study was a single-center case–control study. Furthermore, the duration of the treatment in each patient could have changed CAR and NAR levels; this should be investigated in future studies to confirm their diagnostic potential. Nevertheless, large multicenter prospective studies are needed to verify our findings.
ConclusionsNAR and CAR are elevated in patients with BD and may contribute to the active disease state. Our results suggested that NAR and CAR are feasible and inexpensive tools for predicting BD activity.
Authors’ contributionsAll authors have contributed to designing the study, collecting and analyzing, interpretation of data, and preparing and revising the manuscript. Design of the study: DK, RZ, MH and WM. Recruitment of patients: DK, RZ, MH and WM. Data collection: DK, RZ, MH and WM. Manuscript preparation and revision: DK, RZ, MH and WM. All co-authors have approved the final version.
Each author made significant individual contributions to the following: the conception and design of the study, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the article, critical revisions for important intellectual content, and approval of the final manuscript. Each author believes that the manuscript represents honest work. All authors contributed actively to the study.
Ethical statementInformed consents were obtained from all patients. An approval was obtained from the ethics committee of Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, and the approval number was ZU-IRB 6614/19-9-2019 and the study was conducted in conformity with Declaration of Helsinki.
FundingThe authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interestThere is no conflict of interest to the author's knowledge.
None declared.