The aim of this study is to examine how gene mutation diversity and disease severity affect physical capacity and quality of life in children/adolescents with Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF).
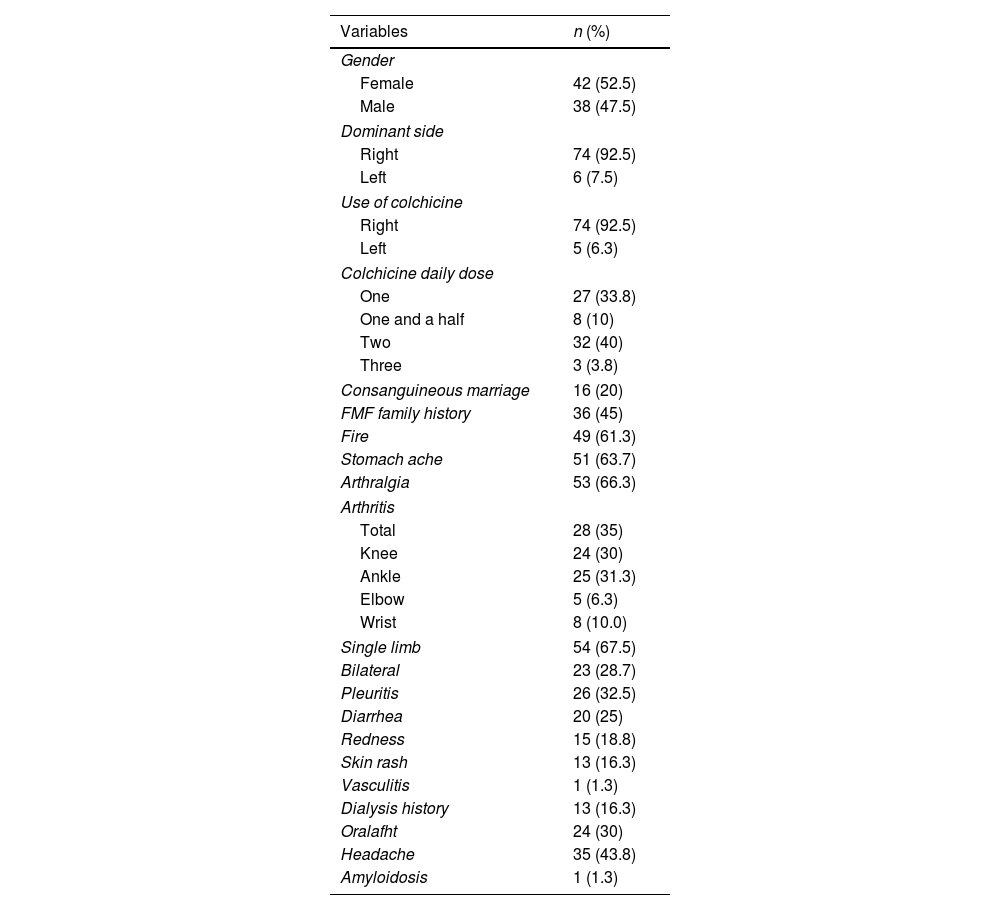
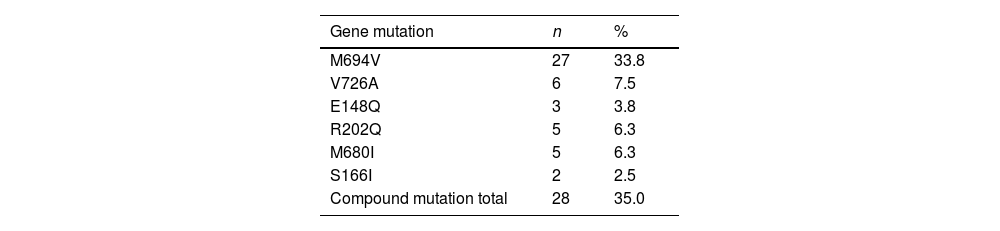
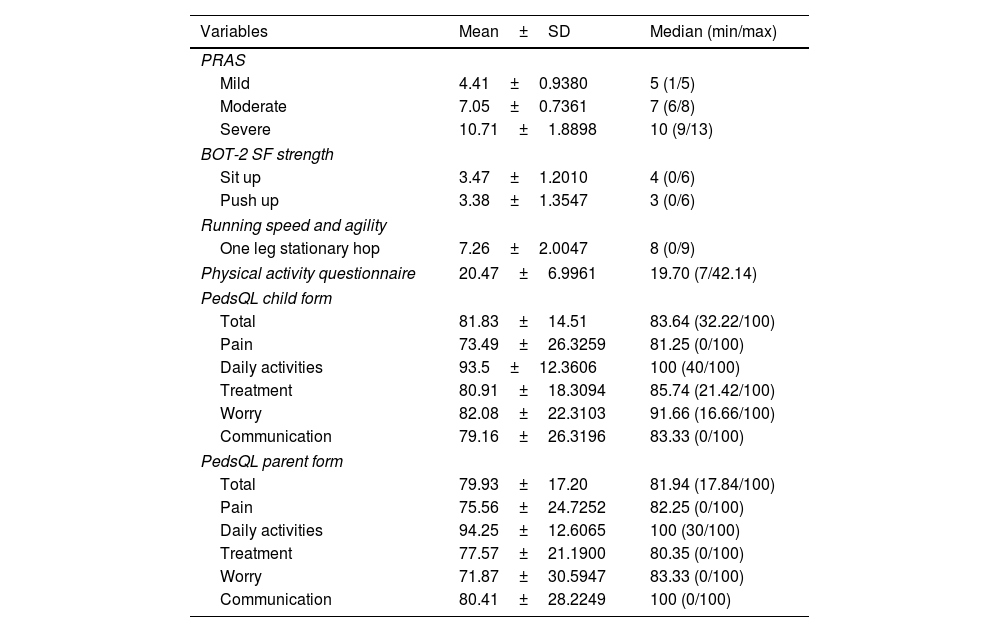
MethodsEighty children/adolescents (42 female, 38 male) diagnosed with FMF according to Tell-Hashomer diagnostic criteria were included in this study. Disease severity score (PRAS), running speed and agility and strength subtests of Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency Second Edition Short Form (BOT-2 SF), Physical Activity Questionnaire, Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory 3.0 Arthritis Module (PedsQL) was used for evaluation. Participants were divided into 2 groups as M694V and other mutations according to MEFV gene mutation and were divided into 3 groups as mild, moderate and severe according to PRAS.
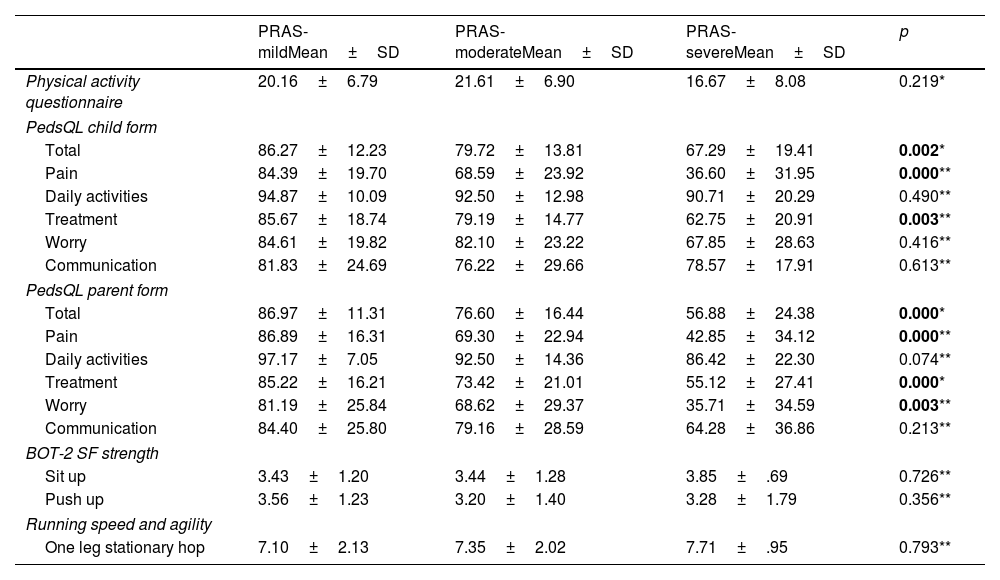
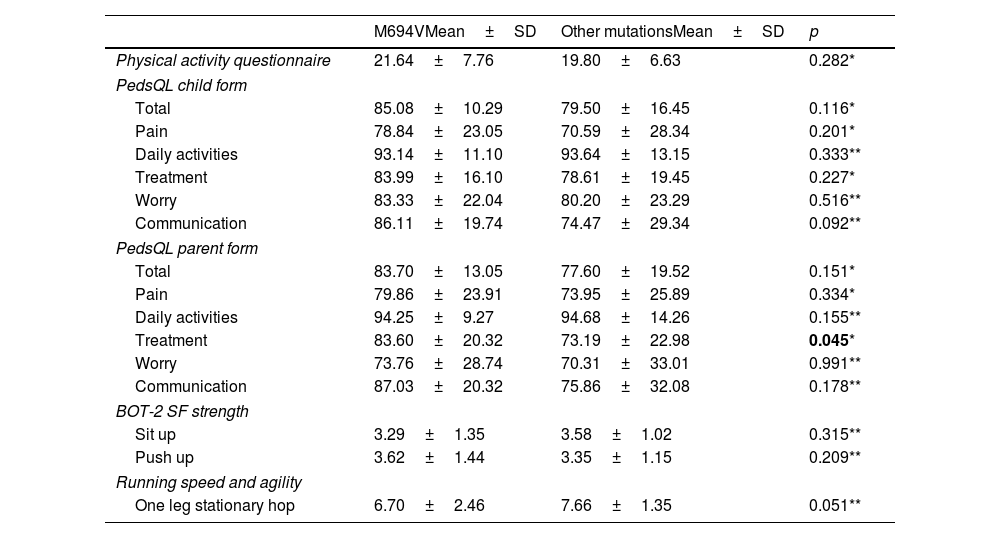
ResultsWhen the data were compared between groups; in terms of gene mutation, a significant difference was observed in treatment subtest of PedsQL-parent form in favor of the M694V gene mutation group (p<0.05). In terms of PRAS, significant difference was seen in the pain, treatment subtests and total score of the PedsQL-child form, and in the pain, treatment, worry subtests and total score of the PedsQL-parent form in favor of the mild group (p<0.05).
ConclusionsMEFV gene mutations in children and adolescents with FMF did not differ on physical capacity and quality of life. PRAS was not effective on physical parameters, but quality of life decreased as the severity score increased. Encouraging children/adolescents with FMF to participate in physical activity and to support them psychosocially can be important to improve their quality of life.
El objetivo de este estudio es examinar cómo la diversidad de mutaciones genéticas y la gravedad de la enfermedad afectan la capacidad física y la calidad de vida en niños/adolescentes con fiebre mediterránea familiar (FMF).
MétodosSe incluyeron en este estudio 80 niños/adolescentes (42 niñas y 36 niños) diagnosticados con FMF según los criterios diagnósticos de Tell-Hashomer. Disease Severity Score (PRAS), running speed and agility and strength subtests of Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency Second Edition Short Form (BOT-2 SF), Physical Activity Questionnaire, Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory 3.0 Arthritis Module (PedsQL) se utilizó para la evaluación. Los participantes se dividieron en 2 grupos como M694V y otras mutaciones según la mutación del gen MEFV y se dividieron en 3 grupos como leve, moderado y grave según PRAS.
ResultadosCuando se compararon los datos entre grupos; en términos de mutación genética, se observó una diferencia significativa en la subprueba de tratamiento de la forma parental PedsQL a favor del grupo de mutación genética M694V (p<0,05). En términos de PRAS, se observaron diferencias significativas en las subpruebas de dolor, tratamiento y puntuación total del formulario PedsQL-niño, y en las subpruebas de dolor, tratamiento, preocupación y puntuación total del formulario PedsQL-padre a favor del grupo leve (p<0,05).
ConclusionesLas mutaciones del gen MEFV en niños y adolescentes con FMF no difirieron en la capacidad física y la calidad de vida. PRAS no fue eficaz en los parámetros físicos, pero la calidad de vida disminuyó a medida que aumentó la puntuación de gravedad. Animar a los niños/adolescentes con FMF a participar en actividades físicas y apoyarlos psicosocialmente puede ser importante para mejorar su calidad de vida.