Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is characterized by progressive fibrosis of the skin and internal organs, microvascular damage and cellular and humoral immunity abnormalities. Microvascular damage can be easily detected through nailfold videocapillaroscopy (NVC).
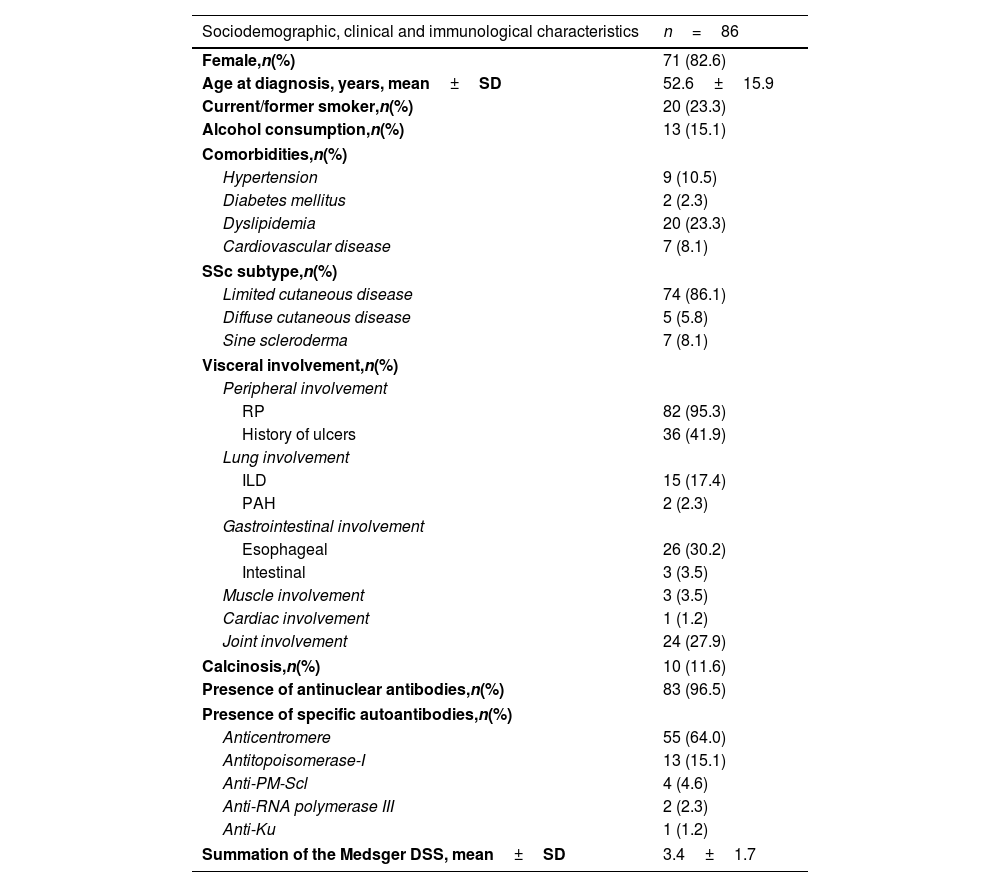
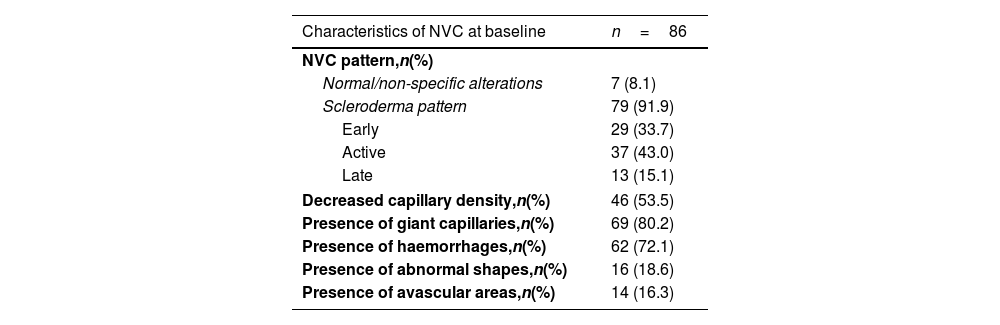
Materials and methodsA retrospective study of patients with SSc and a NVC performed within the first 6 months after diagnosis was conducted. Visceral involvement in the first 3 years of the disease and NVC findings were collected. The severity of microvascular damage was classified into four categories, according to the worsening of the NVC patterns. The severity of organ involvement was assessed by the disease severity scale of Medsger for each organ and as a global measure of disease severity, the simple summation was used.
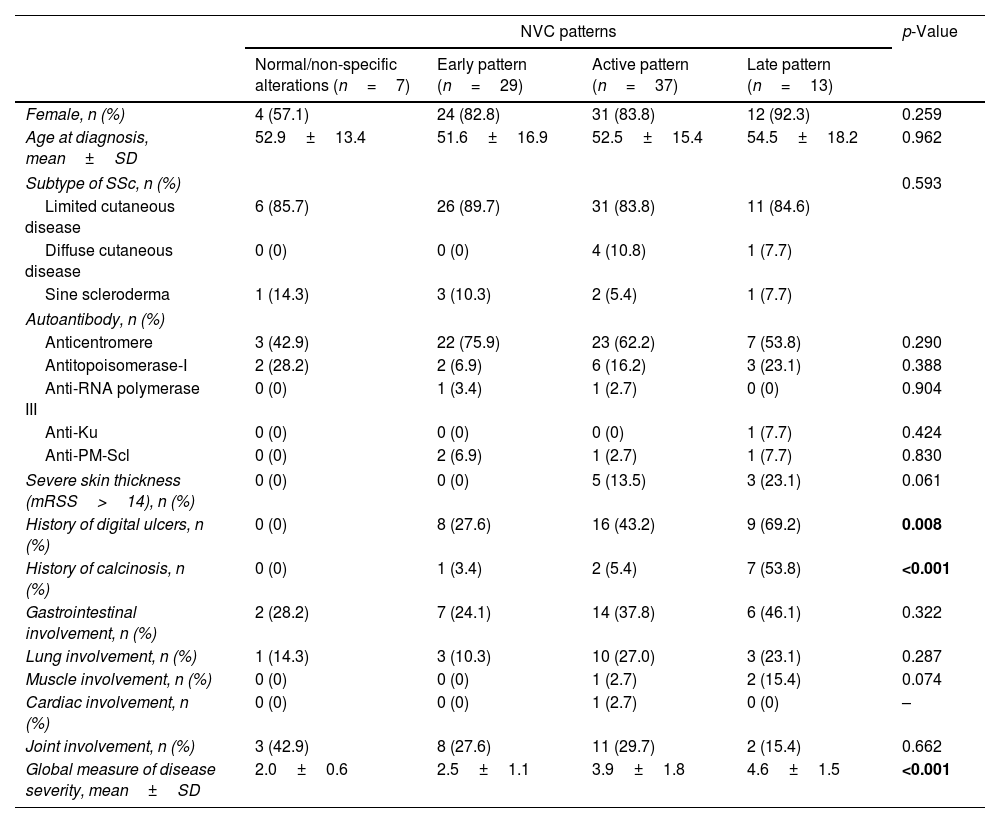
ResultsA total of 86 patients with SSc were included. A moderate correlation was found between the severity of microvascular damage and the global measure of disease severity (r=0.55, p<0.001), the severity of peripheral vascular involvement (r=0.43, p<0.001) and the severity of skin involvement (r=0.34, p=0.001).
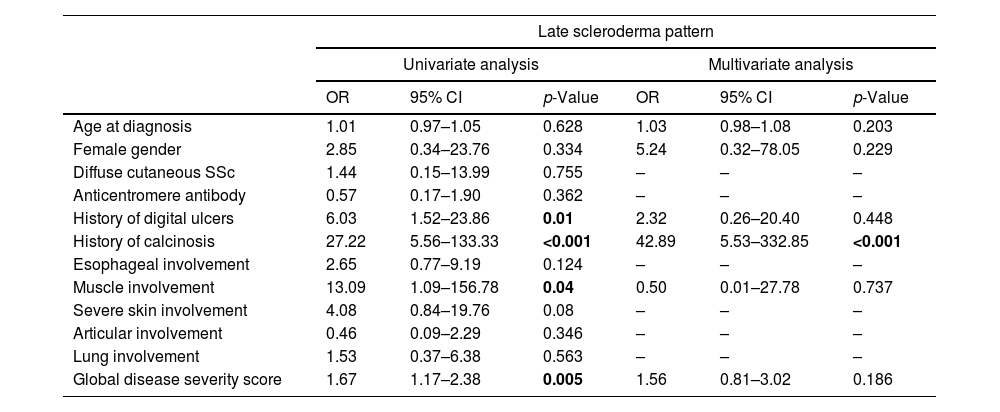
The presence of a late scleroderma pattern in NVC were predictive in univariate analysis of digital ulcers (OR 6.03, 95% CI 1.52–23.86, p=0.01), muscular involvement (OR 13.09, 95% CI 1.09–156.78, p=0.04), calcinosis (OR 27.22, 95% CI 5.56–133.33, p<0.001) and worse global disease severity score (OR 1.67, 95% CI 1.17–2.38, p=0.005). Multivariate analysis adjusted for disease duration and gender confirmed late pattern as an independent predictor of calcinosis (OR 42.89, 95% CI 5.53–332.85, p<0.001).
Discussion and conclusionIn this study, the worsening of NVC pattern in SSc was associated with the overall disease severity, the severity of peripheral vascular involvement and extension of skin involvement. This study highlights the importance of NVC as a prognostic tool and a possible predictor of systemic visceral involvement.
La esclerosis sistémica (ES) se caracteriza por fibrosis progresiva de la piel y órganos internos, daño microvascular y anomalías en la inmunidad celular y humoral. El daño microvascular puede detectarse fácilmente mediante la capilaroscopia periungueal (CPU).
Materiales y métodosUn estudio retrospectivo en pacientes con ES que realizaron una CPU en los primeros 6 meses después del diagnóstico. Se recopilaron los hallazgos de la CPU y el compromiso visceral en los primeros 3 años de la enfermedad. La gravedad del daño microvascular se clasificó en 4 categorías, según el empeoramiento de los patrones de la CPU. La gravedad del compromiso orgánico se evaluó mediante la escala de gravedad de la enfermedad de Medsger para cada órgano, y como medida global de la gravedad de la enfermedad, se utilizó la suma simple.
ResultadosSe incluyeron un total de 86 pacientes con ES. Se encontró una correlación moderada entre la gravedad del daño microvascular y la medida global de la gravedad de la enfermedad (r=0,55; p<0,001), la gravedad del compromiso vascular periférico (r=0,43; p<0,001) y la gravedad del compromiso cutáneo (r=0,34; p=0,001).
La presencia de un patrón esclerodérmico tardío en la CPU fue predictiva en el análisis univariado de úlceras digitales (OR: 6,03; IC 95%: 1,52-23,86; p=0,01), compromiso muscular (OR: 13,09; IC 95%: 1,09-156,78; p=0,04), calcinosis (OR: 27,22; IC 95%: 5,56-133,33; p<0,001) y peor puntuación global de la gravedad de la enfermedad (OR: 1,67; IC 95%: 1,17-2,38; p=0,005). El análisis multivariado, ajustado por la duración de la enfermedad y el género, confirmó el patrón tardío como un predictor independiente de la calcinosis (OR: 42,89; IC 95%: 5,53-332,85; p<0,001).
Discusión y conclusiónEn este estudio, el empeoramiento del patrón de la CPU en la ES se asoció con la gravedad global de la enfermedad, la gravedad del compromiso vascular periférico y la extensión del compromiso cutáneo. Este estudio destaca la importancia de la CPU como una herramienta pronóstica y un posible predictor del compromiso visceral sistémico.