Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) is a systemic vasculitis that is commonly associated with cutaneous involvement (40%–81%).1–3
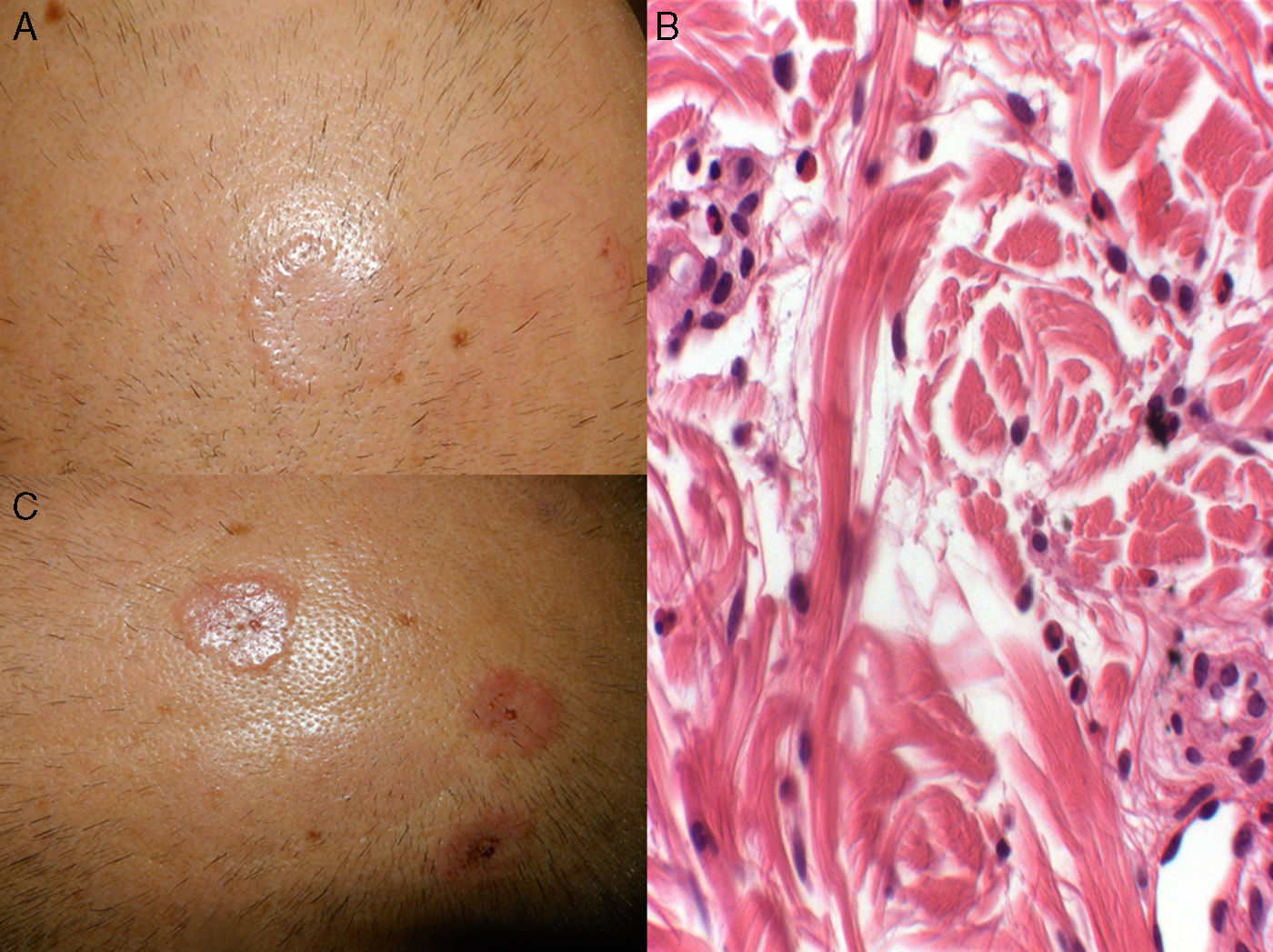
Case ReportThe patient was a 53-year-old man with a history of rhinitis, asthma and eosinophilic pneumonia, diagnosed 4 years earlier, who presented with pruritic lesions on the scalp that had developed 7 days before. There were 4 circular plaques measuring 2–4cm, that were skin-colored or erythematous, with an infiltrated border and small scabs (Fig. 1A and C). Biopsy revealed a superficial inflammatory infiltrate made up of lymphocytes and eosinophils; there were neutrophils in the vessel wall, with no fibrinoid necrosis; we also detected histiocytes interspersed with degenerated collagen in the superficial and reticular dermis (Fig. 1B). Direct immunofluorescence and Ziehl-Neelsen staining were negative. We found leukocytosis with 15,900cells/μL; eosinophilia (24.7%; 3900cells/μL); and complement C3 of 83.7mg/dL. Antinuclear antibodies, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (perinuclear ANCA and cytoplasmic ANCA) and urinalysis were normal. The diagnosis was EGPA, which ruled out cardiac and renal involvement. The patient was receiving prednisone at 10mg/day for a respiratory disease; the dose was increased to 30mg/day for 2 weeks, and resolution was achieved. During the last 6 months, he had a relapse in the form of parietal urticarial plaques, which were satisfactorily treated with a topical corticosteroid.
(A and C) Circular, skin-colored and erythematous plaques measuring 2–4cm, with a more infiltrated border and small scabs on the surface. (B) Histiocytes interspersed with bundles of degenerated collagen accompanied by an inflammatory infiltrate with abundant eosinophils (hematoxylin-eosin, 20×).
The most common lesions in EGPA are papules and nodules, palpable purpura and vesicles or blisters. The histological findings consist in extravascular granulomas (50%), with distinct clinical manifestations, followed by leukocytoclastic vasculitis.1 Churg-Strauss granuloma can be interstitial at first and subsequently be palisaded. The interstitium is characterized by epithelioid histiocytes intermingled with degenerated collagen and an inflammatory infiltrate with neutrophils, lymphocytes and eosinophils. The palisaded granuloma show images of leukocytoclastic vasculitis and degenerated collagen, with epithelioid histiocytes, multinucleated giant cells and eosinophils.4–6
The clinical signs of EGPA currently described do not include plaques mimicking granuloma annulare: this case reflects an unknown manifestation and points out the changing nature of these lesions, toward urticarial plaques.
Ethical DisclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work center on the publication of patient data.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors have obtained the written informed consent of the patients or subjects mentioned in the article. The corresponding author is in possession of this document.
FundingNone.
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Please cite this article as: Lozano-Masdemont B, Horcajada-Reales C, Gómez-Recuero Muñoz L, Parra-Blanco V. Lesiones granuloma anular-like como manifestación cutánea de granulomatosis eosinofílica con poliangitis. Reumatol Clin. 2017;13:357–358.