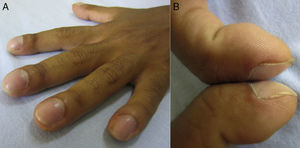
The patient is a 17-year-old man with a history of pulmonary tuberculosis treated for 6 months with the standard regimen [isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide for 2 months (intensive phase) followed by isoniazid and rifampin for 4 months (continuation phase)] with complete adherence and whose sputum smears at the end of his treatment were negative for acid-fast bacillus. Six months later, he presented to the emergency room complaining of pain and swelling of the ankles, knees and wrists for four weeks prior to admission with no constitutional (fever, night sweats, fatigue, weight loss) and respiratory symptoms. On physical examination, finger clubbing was evident and confirmed by observation of the Schamroth's sign (Fig. 1).
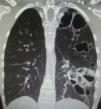
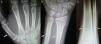
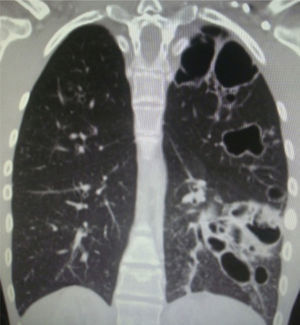
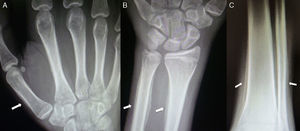
Chest computer tomography showed cystic bronchiectasis and cavitations in the left lower and upper lobes (Fig. 2). X-rays of wrists and legs showed periosteal reaction along the metacarpals, distal radius, ulna, tibia and fibula (Fig. 3) but not acro-osteolysis of the distal phalanges of the hands and feet. Human immunodeficiency virus antibody test was negative. Pharmacologic therapy with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs was effective in relieving pain from hypertrophic osteoarthropathy (HOA) during his hospital stay and after 3 months of follow-up.
HOA is a syndrome characterized by digital clubbing, periostosis of tubular bones and noninflammatory arthritis of large joints.1,2 Digital clubbing is characterized by an increase of the normal 160-degree angle between the nail bed and the proximal nail-fold (Lovibond's angle). In clubbing, this angle exceeds 180 degrees, while in pseudoclubbing it is preserved. Contrary to digital clubbing, finger involvement is asymmetrical in the majority of the reported cases of pseudoclubbing, and acro-osteolysis instead of an overgrowth of the phalangeal tufts seen in clubbing, is the typical radiographic finding in pseudoclubbing.3
HOA is classified as either primary (pachydermoperiostosis) or secondary to pulmonary, cardiac, liver or gastrointestinal diseases characterized by arteriovenous shunt.1,2 Pulmonary malignancies are the most common disorders associated with HOA (80%). Chronic infections associated with cystic fibrosis, subacute bacterial endocarditis, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and pulmonary tuberculosis are also associated with HOA.4 Our case illustrates the HOA as a rare late complication of pulmonary tuberculosis.
The pathogenesis of HOA is unknown, although an impaired lung function due to the exclusion of this organ from part of the circulation is common in most diseases associated with HOA. It has been suggested that in hypoxic conditions, megakaryocytes bypass the pulmonary circulation through arteriovenous shunts and directly reach the distal sites in the systemic circulation and interact with endothelial cells, releasing growth factors, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), resulting in angiogenesis and thus digital clubbing.1,5•8 VEGF is a platelet-derived factor induced by hypoxia that produces vascular hyperplasia, new bone formation, edema, and fibroblast/osteoblast proliferation, which are histological alterations of HOA.6•8
Although the association of HOA with pulmonary tuberculosis has been rarely reported,9•12 physicians should consider HOA as a complication of non-neoplastic diseases, such as pulmonary tuberculosis, an endemic infection of the world's population.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.