IgG4 related disease is a fibroinflammatory condition characterised by lymphoplasmocytic infiltration with predominance of IgG4+ plasma cells, fibrosis, and in most cases elevated IgG4 serum levels. It can affect any organ and result in varying clinical manifestations. Steroids are the cornerstone of treatment, however there is a high percentage of relapse. Recent studies have demonstrated favourable effects with rituximab.
ObjectiveTo evaluate effectiveness related to the response to treatment with rituximab in patients with IgG4 related disease refractory to steroids and other immunosuppressant therapies.
Materials and methodsWe undertook a systematic search of the specialist databases EMBASE, LILACS, PUBMED and OVID-Cochrane for publications up until December 2017.
ResultsAfter the quality analysis, we selected 27 articles (264 patients in total) for the final review, of which 23 were case reports and case series (105 patients), 3 were observational follow-up cohort studies (129 patients), and there was one clinical trial (30 patients). IgG4 related disease presents predominantly in male patients aged between 50 and 70 years on average. Multiple organs are compromised with an average of 3.5 compromised organs. Orbital, glandular and lymph-node compromise is most frequent. Patients in the different studies we included had received various treatments prior to starting rituximab, including glucocorticoids and disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. There was 90.7% response in the cases where rituximab was used as second line therapy; rituximab was used as first line treatment for 10% of the patients with a 100% response rate.
ConclusionThe use of rituximab for patients refractory to first-line treatments was associated with a high response percentage and less dependence on glucocorticoids.
La enfermedad relacionada con IgG4 es una condición fibroinflamatoria caracterizada por infiltración linfoplasmocítica con predominio de células plasmáticas IgG4+, fibrosis y en la mayoría de los casos niveles séricos elevados de IgG4. Puede afectar cualquier órgano y llevar a manifestaciones clínicas variables. El tratamiento con esteroides es la piedra angular, sin embargo, el porcentaje de recidivas es alto. Estudios recientes han mostrado efectos favorables con rituximab.
ObjetivoEvaluar la efectividad relacionada con la respuesta al tratamiento con rituximab en los pacientes con enfermedad relacionada con IgG4 refractarios a uso de esteroides y otras terapias inmunosupresoras.
Materiales y métodosSe realizó una búsqueda sistemática en bases de datos especializadas EMBASE, LILACS, PUBMED y OVID-Cochrane de publicaciones hasta diciembre de 2017.
ResultadosPosteriormente al análisis de calidad se seleccionaron 27 artículos (264 pacientes en total) para la revisión final de los cuales 23 correspondían a reportes de caso y series de caso (105 pacientes), 3 a estudios observacionales de seguimiento a una cohorte (129 pacientes) y un ensayo clínico (30 pacientes). La enfermedad relacionada con IgG4 se presenta predominantemente en pacientes de sexo masculino con una edad promedio entre 50 y 70 años. El compromiso orgánico es múltiple con un promedio de 3,5 órganos comprometidos, siendo lo más frecuente el compromiso orbitario, glandular y ganglionar. Los pacientes de los diferentes estudios incluidos recibieron diversos tratamientos previo al inicio de rituximab, entre ellos glucocorticoides y fármacos antirreumáticos modificadores de la enfermedad. El porcentaje de respuesta en aquellos casos donde el rituximab se empleó como terapia de segunda línea fue del 90,7%; en el 10% de los pacientes se empleó rituximab como primera línea con un porcentaje de respuesta del 100%.
ConclusiónEl uso de rituximab en pacientes refractarios a terapias de primera línea se asocia a un alto porcentaje de respuesta y a menor dependencia a glucocorticoides.
IgG4-related disease (ER-IgG4) is a fibroinflammatory condition characterised by lymphoplasmacytic infiltration with a predominance of IgG4+ plasma cells, fibrosis and in the majority of cases high levels of IgG4 in serum.1 It may essentially affect any organ, with a variable range of clinical manifestations, the most frequent of which are pancreatic and salivary gland compromise and adenopathies.2
Diagnosis is essentially histopathological, with characteristic findings of lymphoplasmacytic infiltration with a >40% proportion of IgG4/IgG, storiform fibrosis and obliterative phlebitis. Other diagnostic tools have also been used, such as imaging and IgG4 serum levels.1–4 There are 2 diagnostic scales (Umehara criteria5 and Okazaki criteria6) and an international consensus7 that makes it possible to reach the diagnosis. A series of organ-specific criteria have also been established, according to the organ that is involved (pancreatitis, sclerosing cholangitis, dacryoadenitis, ophthalmic, renal and pulmonary criteria associated with IgG4).8
Treatment is a field that has still hardly been explored. Steroids have formed the basis of treatment from the time it was described, although the relapse rate is high at 23–52%, especially when they are suspended.9,10 Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs are not effective in inducing remission, although they may be beneficial in maintenance therapy.11 Recent case reports, series of cases and cohort studies have shown the possible favourable effects of therapy with rituximab (RTX), although the evidence is not conclusive. This systematic review has the aim of evaluating the efficacy and response to treatment with RTX in patients with ER-IgG4 who do not respond to glucocorticoids (GCC) and relapse with other immunomodulating therapies.
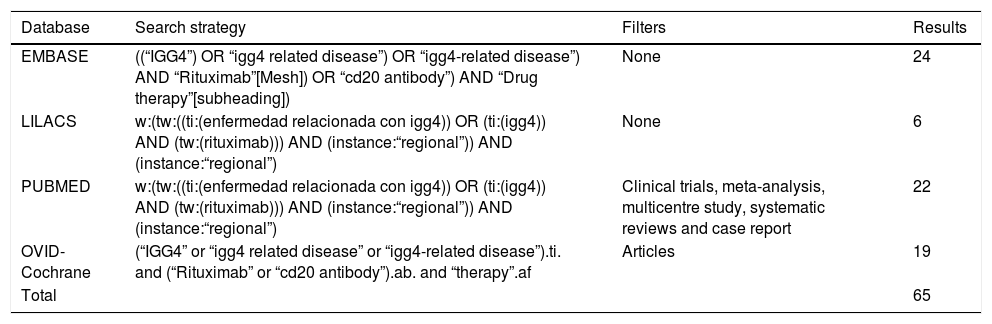
Materials and methodsSystematic searchA systematic search was conducted in the EMBASE, LILACS, PUBMED and OVID-Cochrane databases of publication until 28 December 2017. The PICO search strategy was followed to construct the question and structure the search (P, Definition of the problem or patient: ER-IgG4; I, Intervention: RTX; C, Intervention of comparison [when applicable]; O, Outcomes=Results: all of those reported in the papers to be selected). The following key words were used “IgG4”, “IgG4 related disease”, “igg4-related disease”, “Rituximab”, “cd20 antibody” and “drug therapy”, for the search in English, and “enfermedad relacionada con igg4”, “igg4” and “rituximab” for the search in Spanish in LILACS. Within this strategy the limits were to consider solely papers in English or Spanish. Table 1 shows the search strategies and filters that were applied, together with their respective results according to the different Boolean operators and qualifiers of fields or tags. PRISMA guide methodology was followed (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses)12 to develop the systematic review of the literature.
Search methodology.
| Database | Search strategy | Filters | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| EMBASE | ((“IGG4”) OR “igg4 related disease”) OR “igg4-related disease”) AND “Rituximab”[Mesh]) OR “cd20 antibody”) AND “Drug therapy”[subheading]) | None | 24 |
| LILACS | w:(tw:((ti:(enfermedad relacionada con igg4)) OR (ti:(igg4)) AND (tw:(rituximab))) AND (instance:“regional”)) AND (instance:“regional”) | None | 6 |
| PUBMED | w:(tw:((ti:(enfermedad relacionada con igg4)) OR (ti:(igg4)) AND (tw:(rituximab))) AND (instance:“regional”)) AND (instance:“regional”) | Clinical trials, meta-analysis, multicentre study, systematic reviews and case report | 22 |
| OVID-Cochrane | (“IGG4” or “igg4 related disease” or “igg4-related disease”).ti. and (“Rituximab” or “cd20 antibody”).ab. and “therapy”.af | Articles | 19 |
| Total | 65 |
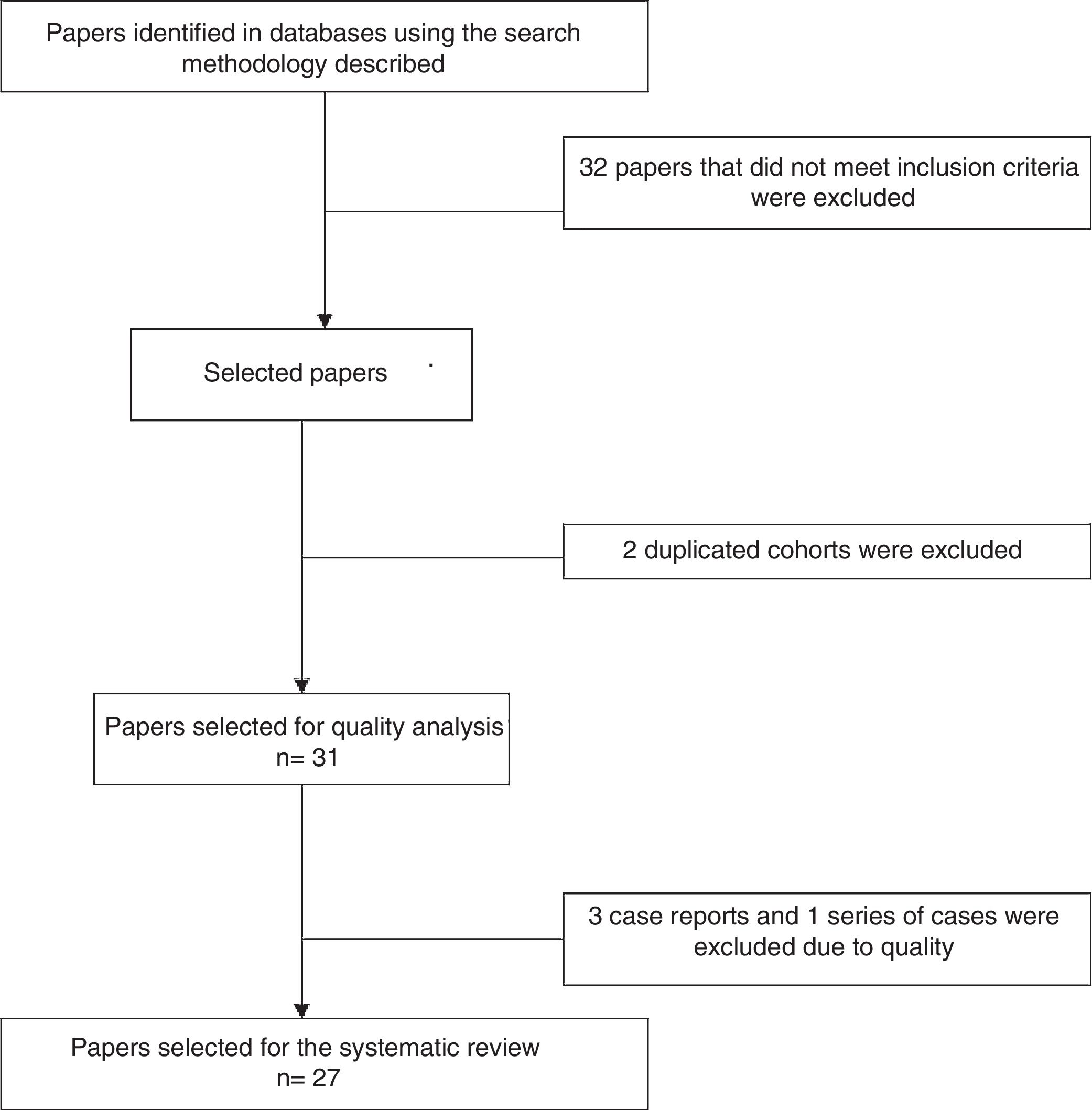
The title and abstract of each one of the papers that were selected in the search were evaluated, and the case reports, series of cases, cases and controls, observational studies and clinical trials that compared RTX with any other therapy for ER-IgG4 were selected. Following PICO strategy, the exclusion criteria were applied to papers that covered animal models as well as other subjects or outcomes unrelated to ER-IgG4. Papers in languages other than English or Spanish were excluded. When an observational follow-up study of a cohort study published several papers on the same cohort in different years, only the latest one was kept to prevent over-representation.
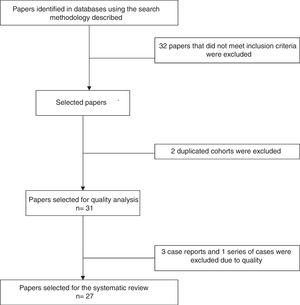
Analysis of the information and quality evaluationThe papers selected for review were independently examined by 2 researchers (JD, LB, DG, DA, SC, AR), and differences were resolved by consensus. Variables including average age, sex, clinical manifestations, diagnostic criteria used, therapeutic strategies and response to therapy were extracted from each study. CARE13 strategy was used to evaluate the quality of case reports and series of cases, while CASP14 was used for the observational studies and CONSORT15 was used for the clinical trials. Fig. 1 shows the PRISMA12 flow diagram for the selection of papers.
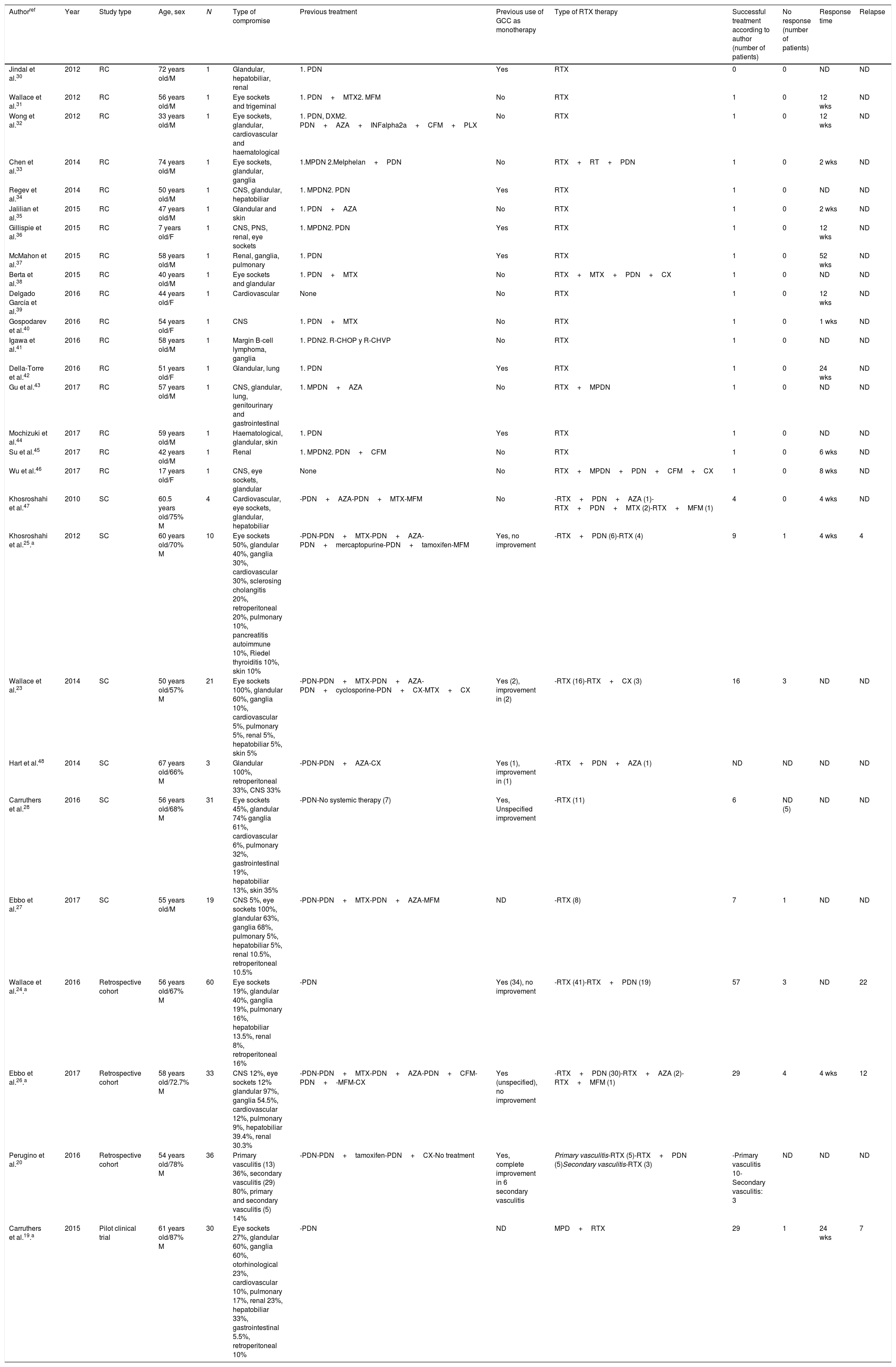
ResultsThe search criteria recovered 65 results. After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria and eliminating duplicated papers, 33 studies were selected. 2 studies were then eliminated because they were of duplicated cohorts, so that 31 papers were left for review, and they were subjected to quality analysis. 4 studies were excluded from the case reports and series of cases16–18 as they fulfilled fewer than 80% of CARE13 strategy criteria, while the observational studies met the CASP14 criteria except for the evaluation of confounding variables, while according to CONSORT15 the quality evaluation of the clinical trials gave optimum results. Finally 27 papers remained (with a total of 264 patients) for the final review, of which 23 corresponded to case reports and series of cases (105 patients), 3 corresponded to observational follow-up studies of a cohort (129 patients) and there was one clinical trial (30 patients). Table 2 describes the characteristics of the patients included in the studies, the type of clinical involvement depend on the affected system, previous treatments, type of RTX therapy, response to the same and relapses.
Characteristics of the patients included in the studies, type of clinical compromise, previous treatments, type of RTX therapy and response to the same.
| Authorref | Year | Study type | Age, sex | N | Type of compromise | Previous treatment | Previous use of GCC as monotherapy | Type of RTX therapy | Successful treatment according to author (number of patients) | No response (number of patients) | Response time | Relapse |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jindal et al.30 | 2012 | RC | 72 years old/M | 1 | Glandular, hepatobiliar, renal | 1. PDN | Yes | RTX | 0 | 0 | ND | ND |
| Wallace et al.31 | 2012 | RC | 56 years old/M | 1 | Eye sockets and trigeminal | 1. PDN+MTX2. MFM | No | RTX | 1 | 0 | 12 wks | ND |
| Wong et al.32 | 2012 | RC | 33 years old/M | 1 | Eye sockets, glandular, cardiovascular and haematological | 1. PDN, DXM2. PDN+AZA+INFalpha2a+CFM+PLX | No | RTX | 1 | 0 | 12 wks | ND |
| Chen et al.33 | 2014 | RC | 74 years old/M | 1 | Eye sockets, glandular, ganglia | 1.MPDN 2.Melphelan+PDN | No | RTX+RT+PDN | 1 | 0 | 2 wks | ND |
| Regev et al.34 | 2014 | RC | 50 years old/M | 1 | CNS, glandular, hepatobiliar | 1. MPDN2. PDN | Yes | RTX | 1 | 0 | ND | ND |
| Jalilian et al.35 | 2015 | RC | 47 years old/M | 1 | Glandular and skin | 1. PDN+AZA | No | RTX | 1 | 0 | 2 wks | ND |
| Gillispie et al.36 | 2015 | RC | 7 years old/F | 1 | CNS, PNS, renal, eye sockets | 1. MPDN2. PDN | Yes | RTX | 1 | 0 | 12 wks | ND |
| McMahon et al.37 | 2015 | RC | 58 years old/M | 1 | Renal, ganglia, pulmonary | 1. PDN | Yes | RTX | 1 | 0 | 52 wks | ND |
| Berta et al.38 | 2015 | RC | 40 years old/M | 1 | Eye sockets and glandular | 1. PDN+MTX | No | RTX+MTX+PDN+CX | 1 | 0 | ND | ND |
| Delgado García et al.39 | 2016 | RC | 44 years old/F | 1 | Cardiovascular | None | No | RTX | 1 | 0 | 12 wks | ND |
| Gospodarev et al.40 | 2016 | RC | 54 years old/F | 1 | CNS | 1. PDN+MTX | No | RTX | 1 | 0 | 1 wks | ND |
| Igawa et al.41 | 2016 | RC | 58 years old/M | 1 | Margin B-cell lymphoma, ganglia | 1. PDN2. R-CHOP y R-CHVP | No | RTX | 1 | 0 | ND | ND |
| Della-Torre et al.42 | 2016 | RC | 51 years old/F | 1 | Glandular, lung | 1. PDN | Yes | RTX | 1 | 0 | 24 wks | ND |
| Gu et al.43 | 2017 | RC | 57 years old/M | 1 | CNS, glandular, lung, genitourinary and gastrointestinal | 1. MPDN+AZA | No | RTX+MPDN | 1 | 0 | ND | ND |
| Mochizuki et al.44 | 2017 | RC | 59 years old/M | 1 | Haematological, glandular, skin | 1. PDN | Yes | RTX | 1 | 0 | ND | ND |
| Su et al.45 | 2017 | RC | 42 years old/M | 1 | Renal | 1. MPDN2. PDN+CFM | No | RTX | 1 | 0 | 6 wks | ND |
| Wu et al.46 | 2017 | RC | 17 years old/F | 1 | CNS, eye sockets, glandular | None | No | RTX+MPDN+PDN+CFM+CX | 1 | 0 | 8 wks | ND |
| Khosroshahi et al.47 | 2010 | SC | 60.5 years old/75% M | 4 | Cardiovascular, eye sockets, glandular, hepatobiliar | -PDN+AZA-PDN+MTX-MFM | No | -RTX+PDN+AZA (1)-RTX+PDN+MTX (2)-RTX+MFM (1) | 4 | 0 | 4 wks | ND |
| Khosroshahi et al.25.a | 2012 | SC | 60 years old/70% M | 10 | Eye sockets 50%, glandular 40%, ganglia 30%, cardiovascular 30%, sclerosing cholangitis 20%, retroperitoneal 20%, pulmonary 10%, pancreatitis autoimmune 10%, Riedel thyroiditis 10%, skin 10% | -PDN-PDN+MTX-PDN+AZA-PDN+mercaptopurine-PDN+tamoxifen-MFM | Yes, no improvement | -RTX+PDN (6)-RTX (4) | 9 | 1 | 4 wks | 4 |
| Wallace et al.23 | 2014 | SC | 50 years old/57% M | 21 | Eye sockets 100%, glandular 60%, ganglia 10%, cardiovascular 5%, pulmonary 5%, renal 5%, hepatobiliar 5%, skin 5% | -PDN-PDN+MTX-PDN+AZA-PDN+cyclosporine-PDN+CX-MTX+CX | Yes (2), improvement in (2) | -RTX (16)-RTX+CX (3) | 16 | 3 | ND | ND |
| Hart et al.48 | 2014 | SC | 67 years old/66% M | 3 | Glandular 100%, retroperitoneal 33%, CNS 33% | -PDN-PDN+AZA-CX | Yes (1), improvement in (1) | -RTX+PDN+AZA (1) | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Carruthers et al.28 | 2016 | SC | 56 years old/68% M | 31 | Eye sockets 45%, glandular 74% ganglia 61%, cardiovascular 6%, pulmonary 32%, gastrointestinal 19%, hepatobiliar 13%, skin 35% | -PDN-No systemic therapy (7) | Yes, Unspecified improvement | -RTX (11) | 6 | ND (5) | ND | ND |
| Ebbo et al.27 | 2017 | SC | 55 years old/M | 19 | CNS 5%, eye sockets 100%, glandular 63%, ganglia 68%, pulmonary 5%, hepatobiliar 5%, renal 10.5%, retroperitoneal 10.5% | -PDN-PDN+MTX-PDN+AZA-MFM | ND | -RTX (8) | 7 | 1 | ND | ND |
| Wallace et al.24.a | 2016 | Retrospective cohort | 56 years old/67% M | 60 | Eye sockets 19%, glandular 40%, ganglia 19%, pulmonary 16%, hepatobiliar 13.5%, renal 8%, retroperitoneal 16% | -PDN | Yes (34), no improvement | -RTX (41)-RTX+PDN (19) | 57 | 3 | ND | 22 |
| Ebbo et al.26.a | 2017 | Retrospective cohort | 58 years old/72.7% M | 33 | CNS 12%, eye sockets 12% glandular 97%, ganglia 54.5%, cardiovascular 12%, pulmonary 9%, hepatobiliar 39.4%, renal 30.3% | -PDN-PDN+MTX-PDN+AZA-PDN+CFM-PDN+-MFM-CX | Yes (unspecified), no improvement | -RTX+PDN (30)-RTX+AZA (2)-RTX+MFM (1) | 29 | 4 | 4 wks | 12 |
| Perugino et al.20 | 2016 | Retrospective cohort | 54 years old/78% M | 36 | Primary vasculitis (13) 36%, secondary vasculitis (29) 80%, primary and secondary vasculitis (5) 14% | -PDN-PDN+tamoxifen-PDN+CX-No treatment | Yes, complete improvement in 6 secondary vasculitis | Primary vasculitis-RTX (5)-RTX+PDN (5)Secondary vasculitis-RTX (3) | -Primary vasculitis 10-Secondary vasculitis: 3 | ND | ND | ND |
| Carruthers et al.19.a | 2015 | Pilot clinical trial | 61 years old/87% M | 30 | Eye sockets 27%, glandular 60%, ganglia 60%, otorhinological 23%, cardiovascular 10%, pulmonary 17%, renal 23%, hepatobiliar 33%, gastrointestinal 5.5%, retroperitoneal 10% | -PDN | ND | MPD+RTX | 29 | 1 | 24 wks | 7 |
AZA: azatioprine; CFM: cyclophosphamide; CX: surgery; DXM: dextromethorphan; ER-IgG4: IgG4-related disease; F: female; GCC: glucocorticoid; INFa2a: interferon alpha 2a subtype; M: male; MFM: micophenolate; MPDN: methylprednisolone; MTX: methotrexate; PDN: prednisolone; PLX: plasmapheresis, RC: case report; RT: radiotherapy; RTX: rituximab; R-CHOP: rituximab-cyclophosphamide-doxorubicin-vincristine-prednisone; R-CHVP: rituximab-cyclophosphamide-adriamycin-etoposide-prednisolone; SC: series of cases; ND: no data; CNS: central nervous system; PNS: peripheral nervous system.
The age of onset varied from 590 to 70 years old, although there was one case report of a paediatric patient. On average the distribution between the sexes was 75% men. There was a broad and variable range of clinical manifestations, and the majority of organs were involved. Glandular involvement was more frequent in the series of cases and observational studies (pancreas, tear glands, salivary and submandibular glands), lymphatic (ganglia) and involvement of the eye sockets. Involvement was predominantly multiorganic, with an average number of 3.5 organs being affected. The single organ forms were rare and were present in only 3 case reports (with cardiovascular, central nervous system and renal involvement).
Diagnostic strategiesDiagnosis was a challenge in all of the studies that were included, and in many of them another alternative diagnosis was first considered. The definitive diagnosis was histopathological, with criteria including lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates and associated fibrosis, although other diagnostic tools were used such as imaging techniques, serum levels of IgG4 and, in one case, plasmablasts.
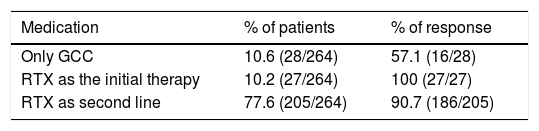
Therapeutic strategies and outcomesFirst line therapies27 studies with 264 patients were included, of whom 90% had received a previous treatment other than RTX. Of the previous treatments, GCC were used in 65.5% of cases (172/264 patients) and disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs were used in 36.7% (97/264 patients), with a 10% response to these therapeutic strategies. RTX was used in refractory patients. GCC were used as a monotherapy in 10.6%, with a 57% response rate. RTX was used as a first line therapy in 10% of cases, with a 100% response rate.
Rituximab as a second line therapyRTX was used as a second line therapy in patients, associated in the majority of cases with a steroid; there was a response in 77% of cases. Other therapies such as plasmapherisis and surgery were rarely used, although the latter was frequent in pure vasculitic forms. A higher proportion of patients were found who responded to RTX as a monotherapy or combined therapy than when it was used as a monotherapy with GCC. See Table 3.
Treatment regimesA range of regimes and doses were used, usually decided by the treating doctor. GCC was used in the majority of studies (in pulses in some cases) and with RTX the most frequent regime was 1g in 2 monthly or fortnightly doses.
Response estimationThe response to treatment was not measured in a uniform way in the studies. It was estimated subjectively by the researcher, considering resolution criteria such as clinical or imaging technique parameters, a fall in plasmablast levels or IgG4, fewer relapses or the possibility of ceasing to take GCC.
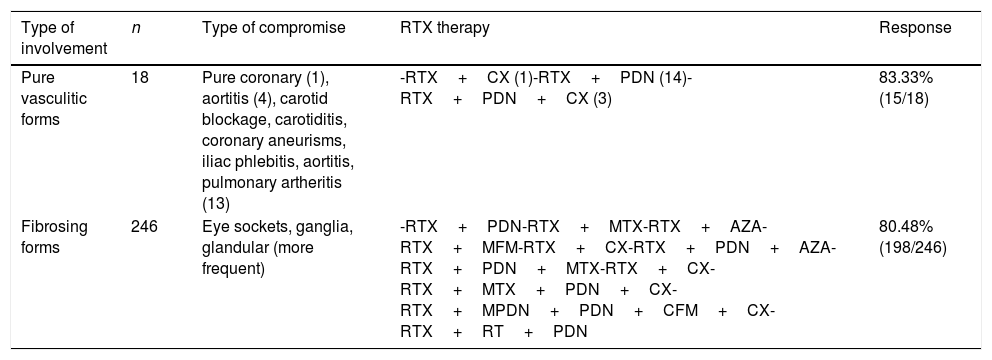
Clinical response according to type of involvementThere was a greater response to treatment in the patients with a predominance of eye socket, ganglion and glandular (including pancreatic) involvement. The response to treatment in vasculitic and fibrosing forms of the disease was also analysed and compared, without finding any significant differences in the proportions of the same. See Table 4.
Comparative analysis of the pure vasculitic forms vs fibrosing forms.
| Type of involvement | n | Type of compromise | RTX therapy | Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure vasculitic forms | 18 | Pure coronary (1), aortitis (4), carotid blockage, carotiditis, coronary aneurisms, iliac phlebitis, aortitis, pulmonary artheritis (13) | -RTX+CX (1)-RTX+PDN (14)-RTX+PDN+CX (3) | 83.33% (15/18) |
| Fibrosing forms | 246 | Eye sockets, ganglia, glandular (more frequent) | -RTX+PDN-RTX+MTX-RTX+AZA-RTX+MFM-RTX+CX-RTX+PDN+AZA-RTX+PDN+MTX-RTX+CX-RTX+MTX+PDN+CX-RTX+MPDN+PDN+CFM+CX-RTX+RT+PDN | 80.48% (198/246) |
AZA: azatioprine; CFM: cyclophosphamide; CX: surgery; MFM: micophenolate; MPDN: methylprednisolone; MTX: methotrexate; PDN: prednisolone; RT: radiotherapy; RTX: rituximab.
A total of 264 patients were documented, of which only 18 cases had pure vasculitic forms, where the predominant forms of involvement were vasculitis and aortitis with the formation of aneurisms. The primary form of involvement was defined as vessel inflammation as the main result of the disease, while the secondary form of involvement arose due to the effects of the adjacent inflammation. In this presentation it should be emphasised that the majority of these patients required surgery, independently of the use of RTX. Carruthers et al.19 even report a patient with ER-IgG4 centred at carotid level with a fleeting amaurosis-type manifestation that persisted in spite of RTX and resolved with endarterectomy. Of the patients who were not subjected to surgery, 3 showed an improvement in their vascular images subsequent to RTX.20
DiscussionAlthough ER-IgG4 was described around the year 2000, it is still an emerging condition. In recent years more publications have appeared in association with the clinical, serological and histopathological characteristics of the disease, although no strong recommendations have been made regarding its first and second line treatment. Although therapy with GCC is considered to be a first-line therapeutic option, the high relapse rate is also known (at 23–52%), especially when they are suspended.9,10,21 Due to this reason the literature describes a large number of immunosuppressor drug combinations, where the use of RTX seems to stand out as a single or combined therapy. It was decided to evaluate the existing evidence for the therapeutic efficacy of using RTX to treat patients with ER-IgG4, with the aim of supporting or rejecting its use in cases refractory to GCC and other therapies.
The International Consensus on the use of ER-IgG421 recommends GCC as the first line therapy, with a 94% interexpert agreement on a dose of 30–40mg/day prednisolone during 2–4 weeks, with a gradual levelling off over 3–6 months after starting the treatment. Considering the high rate of recurrence with this treatment and its high toxicity over the medium to long term, the consensus recommends the use of steroid sparing agents, especially when it is impossible to perform appropriate levelling due to the persistence of disease activity or relapses, although interexpert agreement on this point amounts to only 46%. A study of patients with relapsed autoimmune pancreatitis treated with azatioprine, micophenolate or 6 mercaptopurine compared to GCC as a monotherapy, showed no differences in relapse-free survival between the two groups.11
A systematic review of therapeutic interventions in ER-IgG4 that included 62 studies with 3034 patients found steroid use in 74%, non-pharmacological therapies such as radiotherapy and surgery in 11%, no intervention in 13% and other therapies in 2%. Treatment with steroids as monotherapy attained an efficacy of 97%, although there were 33% of relapses in spite of the short follow-up periods. Relapses were treated with GCC, which attained a response rate of 95%, azatioprine at 81% and RTX in 9 patients with a 100% response rate.22
Given that the majority of patients with ER-IgG4 have to use GCC to remain in remission, other therapeutic options have been used as GCC sparing agents with results that are not very encouraging. In a series of cases of 21 patients with ER-IgG4 the use of sparing agents such as methotrexate, cyclosporine and azatioprine did not attain the goal of levelling off GCC.23 These findings are consistent with those obtained by this systematic review, where 65.4% of the patients included in the papers reviewed received steroids as the initial therapy and in 36% of the studies reviewed sparing agents were included in different protocols. There was a 10% response rate to the latter therapeutic strategies. In patients who were refractory to these strategies RTX was used.
Large series of cases and cohort studies24,45,47 have shown a high response rate to RTX associated with fewer relapses of the disease and a major possibility of levelling off GCC over the long term. The results of the review confirm the benefits of therapy with RTX as the second line in patients who are refractory to other treatments such as GCC and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, among others, emphasising the response rate of 90.7% when it is used as a second line therapy. Analysis of the total number of cases reported even showed that 10% of patients were treated with RTX as the first line therapy, obtaining a response in 100% of the patients. This finding means that it is now possible to think of using RTX from early phases after diagnosis.
Few of the studies analysed in the review reported relapses with RTX, although it should be underlined that the short periods of follow-up may influence this finding. This contrasts with the proportions described in the literature, in ranges that run from 10% to 41%.19,24,27 Some factors have been found to be associated with the risk of relapse, including high concentrations in serum of IgG4, IgE and eosynophiles, the absence of regular doses of the medication and most especially a response rate index in ER-IGG4>9 prior to the use of RTX.27 This index was only applied and reported in 3 of the 27 studies included in the review.
A multicentre study undertaken in France found that the patients who received treatment, not necessarily associated with relapses, achieved greater survival free of the same (41 vs 21 months).27 Although the data of the present study do not make it possible to evaluate the effectiveness of RTX in terms of relapse-free time, it would be important to answer this question in a future work within the context of long-term maintenance.
The systematic review analysed the response to treatment with RTX depending on the form of presentation of the disease. Eye socket involvement was found in 30% of cases, glandular involvement in 53% and ganglion involvement in 32.5% of all the patients, and this is similar to the finding of other series.28 Although a high proportion of patients with these clinical manifestations responded to treatment, as they are the most common forms of presentation of the disease it is not possible to conclude that RTX has a greater effect in this group. A comparative analysis was also performed between pure vasculitic forms, in which similar response rates were found. Nevertheless, it is not possible to categorically conclude that primary vasculitic forms respond to treatment with RTX, as the majority of cases had received previous or concomitant surgery and therapies with GCC before or during the administration of RTX for severe vascular complications such as aneurisms. However, the good response to this multimodal approach in the majority of cases stands out.
Although it was not a research aim, it is important to mention the heterogeneity that was found in how the different authors defined improvement or remission after treatment with GCC, RTX or other therapies, together with the absence of objective measurements of therapeutic response throughout the studies. This was shown by the fact that the ER-IgG4 response index was only applied in 2 observational cohort follow-up studies and in one clinical trial. This instrument was designed to evaluate disease activity, and it considers the organs which are potentially involved and the levels of IgG4 in mg/dl. To validate this index it was applied retrospectively to a registry of 15 patients in Massachusetts Hospital, obtaining a Pearson coefficient of 0.93 between the 2 evaluating rheumatologists.29 Including IgG4 levels in the score has led to debate, given that the pathological role of the said molecule has not been clearly established, and that it seems to behave as an epiphenomenon of the disease, so that it could be explained by an unknown primary inflammatory stimulus.1 It is therefore necessary to generalise the detection of the response, especially in future clinical trials, to give results that make it possible make comparisons and draw more precise conclusions.
It may be concluded from this review that therapy with RTX in patients with ER-IgG4 who have relapsed with while using GCC or other disease-modifying therapies has benefits in terms of the therapeutic response. Its effect on relapses is less clear due to the duration of follow-up in the studies, although over the mid-term it gave better results than other therapies. It has also been shown to be effective as a first line therapy.
Randomised controlled clinical trials are required that make it possible to confirm what has been reported to date in the literature. Therapy with anti-CD20 seems to be one of the best therapeutic strategies in ER-IgG4, not only for recurrent and refractory disease, but also as the initial treatment, given the potential benefits in terms of therapeutic response, reducing the number of relapses and lowering GCC treatment toxicity.
Conflict of interestsThe authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Please cite this article as: Betancur-Vásquez L, Gonzalez-Hurtado D, Arango-Isaza D, Rojas-Villarraga A, Hernandez-Parra D, Carmona S, et al. Enfermedad relacionada con IgG4: ¿es el rituximab la mejor estrategia terapéutica en los casos refractarios a terapia convencional? Resultados de una revisión sistemática. Reumatol Clin. 2020;16:195–202.