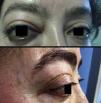
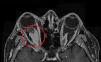
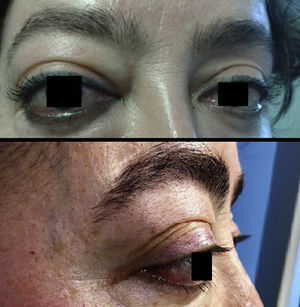
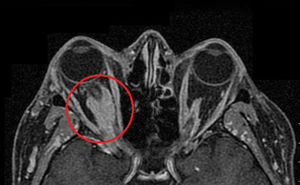
A 47 year-old woman with a background of total thyroidectomy from goitre with benign thyroid nodules presented with exophthalmos of several weeks onset (Fig. 1). There was no involvement of the ENT sphere, and no pulmonary, polyneuropathy, dry syndrome, arthralgias, photosensitivity or cutaneous lesions. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging revealed a solid retrobulbar mass which surrounded the optic nerve and was of fusiform morphology measuring 24×9mm (Fig. 2). We considered the need for biopsy but desisted, due to the high risk of complications. The ANAS, ANCAS, anti-DNA analysis, complement activity, proteinuria and ACE tested negative and the raising of immunoglobulin G4 860mg/dl was remarkable (normal: 10–140). The patient was diagnosed with a possible IgG4-related inflammatory orbital disease in keeping with clinical and serological criteria. Treatment with high doses of steroids and azatiorpine was initiated but suspended due to intolerance. The patient is currently being treated with mycophenolate mofetil and is responding favourably with no inflammatory activity. IgG4-related disease is a new entity which comprises several fibroinflammatory diseases which have not been previously linked to one another.1,2 Clinical features are highly varied and presentation is usually subacute.3,4 Ocular-orbital symptoms include: idiopathic orbital inflammation, pachymeningitis and sclerouveitis.5,6 Orbital pseudotumour is an uncommon presentation of IgG4 diseases.7 It is important to recognize this new disease to diagnoses it, since specific treatment may prevent complications.
Conflict of interestsThe authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Please cite this article as: Fernández Regueiro R, Fonseca Aizpuru EM, Estrada Menéndez C, Buznego Suárez L. Pseudotumor orbitario relacionado con IgG4. Reumatol Clin. 2020;16:245–246.