Osteopetrosis is a rare genetic disorder characterised by abnormal activity of osteoclasts, which leads to sclerosis and excessive growth of bony structures.1 There are 3 main clinical subtypes of osteopetrosis: the adult form (autosomal dominant), the infantile form (autosomal recessive) and the intermediate type (autosomal recessive).2
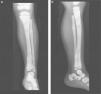
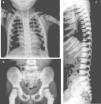
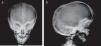
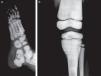
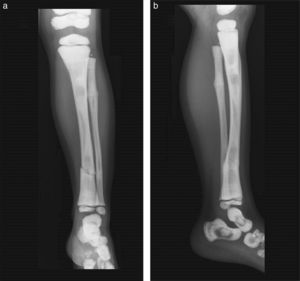
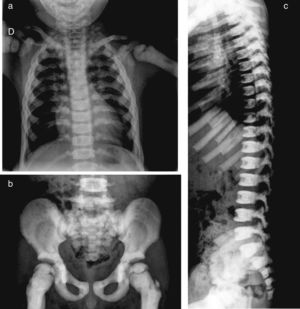
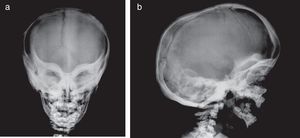
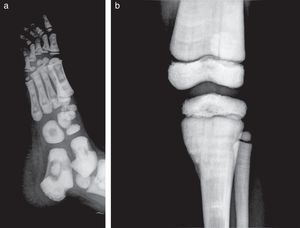
Presentation of the CaseA 4-year old male with a history of blindness in relation to congenital optic neuropathy of non-filiation aetiology and delayed growth. He presented at the emergency department after low intensity trauma in the right leg. An X-ray was taken which showed a fracture in the distal shaft of the tibia and fibula, together with a fracture callus in the proximal third of the fibula and general sclerosis of the visible bony structures which indicated sclerosing bone dysplasia (Fig. 1). The radiologic study was completed with a bone series, where a diffuse increase in bone density was highlighted with a “bone within bone” appearance and the enlargement of long bone metaphysis (Figs. 2–4). Radiologic findings determined the diagnosis of osteopetrosis.
X-rays of the right leg in anteroposterior (a) and lateral (b) projection. Transversal fracture in distal shaft of the right tibia and fibula. Fracture callus in proximal end of fibula. General sclerosis of the visible bony structures with poor differentiation between cortical and medullary cavity.
X-rays of the chest (a) and pelvis (b) show a diffuse and homogenous increase in bone density, more obvious in costal arcs and pelvic bones, also poor cortico-medullary differentiation and enlargement of long bone metaphysis. In the lateral projection of the spine (c), we observe sclerosis of the upper and lower plates of the vertebral bodies, in an image called a sandwich vertebral body.
No changes in blood analysis or abdominal ultrasound were detected.
A genetic study was undertaken which showed homozygotic mutation in gene SNX10, confirming the diagnosis of autosomal recessive infantile osteopetrosis.
At present the patient is not presenting with haematological changes and his blindness is irreversible. Medical follow-up and analysis every 6 months has been chosen as treatment. A histocompatibility study has been undertaken and the transplant of haematopoietic precursors will be assessed, depending on the patient's evolution.
DiscussionAutosomic recessive infantile osteopetrosis is the most aggressive form of osteopetrosis within its different subtypes.3,4
The main clinical symptoms of the disease are pancytopenia caused by the infiltration of bone marrow (increased risk of bleeding and repeated infections), which may be associated with extramedullary hematopoiesis, compression syndromes of cranial nerves (mainly optic and vestibucochlear nerves), pathologic fractures, dental problems and delayed growth.5
The transplant of haematopoietic progenitors is the only currently available lasting treatment.6 Treatment with vitamin D (calcitriol), gamma-interferon, erythropoietic and corticoid may also be useful.
Ethical DisclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that for this research no experimentation has been carried out on human beings or animals.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflict of InterestThe authors have no conflicts of interests to declare.
Please cite this article as: Gómez Varela C, Couto Rodríguez I, Durán Vila MD. Hallazgos radiológicos en la osteopetrosis infantil autosómica recesiva. Reumatol Clin. 2019;15:e153–e155.