The majority of the biological therapies used in the treatment of inflammatory diseases with an autoimmune component such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis are monoclonal antibodies whose target pharmacological molecules are involved in the pathophysiology of these entities. Patient satisfaction with these treatments is an important aspect to bear in mind, along with their effectiveness and safety, as this encourages greater adherence and better control of the disease.
The main objective of the study was to ascertain the degree of satisfaction of patients treated with biological drugs in a regional hospital with a catchment area of 109,530 inhabitants.
A descriptive and cross-sectional study was undertaken from October to December 2016. The patients were given a structured survey of approximately 15mins duration. The degree of satisfaction before and after the biological was evaluated from 0 to 10, where 0 was maximum dissatisfaction and 10 maximum satisfaction, and improvement in pain, where 0 was no improvement and 10 maximum improvement. All the patients who were treated with a rheumatology or dermatology biological drug during the months of the study were eligible for the study. There were no exclusion criteria. The questionnaire was given to all patients who attended the pharmacy service to collect medication or outpatient consultations in the case of treatments administered by a nurse. All the patients received a study fact sheet and signed their informed consent. A database was created with the responses to be handled using SPSS® v.22. The qualitative data were expressed as percentages and quantitative data as medians and 25–75 percentiles.
Of the total 149 patients undergoing biological treatment during the study, a total of 111 patients were included (response rate of 74.5%). Their demographic and clinical characteristics are shown in Table 1. Patient satisfaction before and after the biological treatment was 2 (0–5) and 8 (7–9) points, respectively. Of the patients, 90.1% stated that the decision to initiate treatment was made by the doctor for the most part. There were 64 (57.7) patients who self-administered the drug and 27 (24.3%) who attended a day hospital. Pain improvement scored 8 (7–9). Of the patients, 94.6% and 97.3% were comfortable with the route and frequency of administration, respectively, giving a score of 2 (0–6) pain during administration. Only 15 patients reported missed doses and of these, 53.3% reported to their doctor/pharmacist. Of the patients, 95.4% and 93.6% considered that the biological drug had controlled the disease and had improved their quality of life, respectively. Eighty-nine (80.2%) and 97 (87.4%) patients believed that they were sufficiently informed about the drug and their disease, respectively. The majority of patients (98.2%) considered that the language of the healthcare personnel was understandable. Only 4 (3.6%) patients claimed to belong to a patient association.
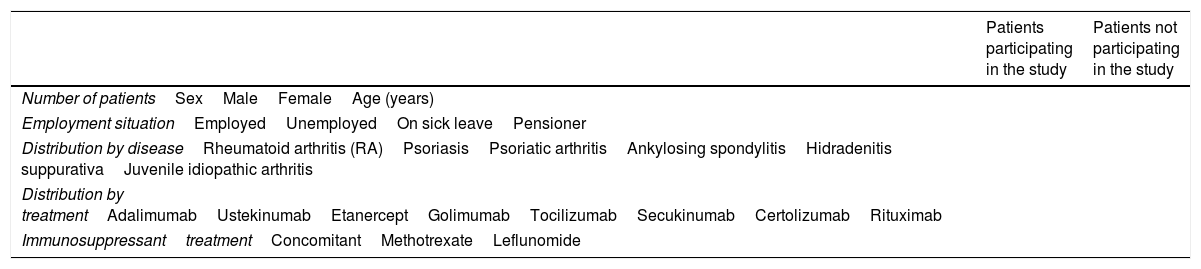
Baseline clinical and demographic characteristics of the patients included in the study.
| Patients participating in the study | Patients not participating in the study | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of patientsSexMaleFemaleAge (years) | ||
| Employment situationEmployedUnemployedOn sick leavePensioner | ||
| Distribution by diseaseRheumatoid arthritis (RA)PsoriasisPsoriatic arthritisAnkylosing spondylitisHidradenitis suppurativaJuvenile idiopathic arthritis | ||
| Distribution by treatmentAdalimumabUstekinumabEtanerceptGolimumabTocilizumabSecukinumabCertolizumabRituximab | ||
| ImmunosuppressanttreatmentConcomitantMethotrexateLeflunomide | ||
As a limitation, we know that no information was obtained on 38 patients, although we do not know the reason why they did not complete the survey, proportionally, women participated more than men in the study. The age of the patients is very similar in both groups. Regarding the employment situation, there is a higher percentage of employed patients and pensioners among the patients who did not respond to the survey. In terms of distribution by disease, in the patients who did not participate in the study there is a lower percentage of RA and a higher percentage of psoriasis, and the lower proportion of adalimumab is notable, at the expense of ustekinumab and etanercept, which increase.
As conclusions and in line with recent publications,1,2 the degree of patient satisfaction with biological treatments in our catchment area is very high irrespective of the route of administration. Of the patients, 94% consider that their quality of life has improved and that they are able to return to a normal life.
Please cite this article as: Grados D, Cucurell M, Bové F, Retamero A. Encuesta de satisfacción de tratamientos biológicos en un hospital comarcal. Reumatol Clin. 2020;16:428–429.