In patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), left ventricle diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) may be the only manifestation of cardiac involvement in anticipation of systolic dysfunction. It has been seen that myocardial deformation of the left atrium (LA), through the LA global longitudinal strain (LAGLS), may be useful in assessing diastolic function.
ObjectiveTo evaluate LA function through myocardial deformation in patients with LES, and compare the LA strain in patients with active, inactive and controls.
MethodsFifty patients with SLE were included and compared with 50 healthy controls paired by age and gender. Myocardial deformation was measured by transthoracic echocardiogram, to investigate the LAGLS, the strain of the three phases of the LA cycle and the strain rate. The differences between groups were compared in univariate analysis.
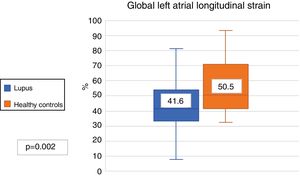
ResultsLAGLS in SLE patients was less than in the controls (41.6% vs 50.5%; p?=?.02), and in the 3 phases of the LA cycle. There were no differences in the LA strain rate in both groups (SLE 2.5 s-1 vs controls 2.75 s-1; p?=?.1). It was also found that the LAGLS was lesser in active patients than controls and inactive.
ConclusionsSLE patients have lower myocardial deformation of the LA, which is expressed as a lower diastolic function correlating with early subclinical myocardial damage.
En los pacientes con lupus eritematoso sistémico (LES) la disfunción diastólica del ventrículo izquierdo (DDVI) puede ser la única manifestación de involucro cardiaco anticipando una disfunción sistólica. Se ha visto que la deformación miocárdica de la aurícula izquierda (AI), mediante el strain longitudinal global de la AI (SLGAI), puede llegar a ser de utilidad en valorar la función diastólica.
ObjetivoEvaluar la función de la AI mediante la deformación miocárdica, en pacientes con LES. Comparar el strain de la AI en pacientes con LES activos, inactivos y controles.
MétodosSe incluyeron 50 pacientes con LES y se compararon con controles sanos (CS) pareados por edad y sexo. Se midió por ecocardiograma transtorácico la deformación miocárdica mediante el strain global de AI (SGAI), el strain de las tres fases del ciclo de la AI y tasa de strain (TSAI). La diferencia entre los grupos se analizó de forma univariante.
ResultadosEl SGAI en pacientes con lupus fue menor al de CS (41,6% vs 50,5%; p?=?0,02). Así como también fue menor en las 3 fases del ciclo de la AI. No hubo diferencias en la TSAI en ambos grupos (lupus 2,5 s-1 vs CS 2,75 s-1; p?=?0,1). También se encontró que en pacientes activos fue menor el SLGAI, en comparación con controles e inactivos.
ConclusionesLos pacientes con lupus tienen menor deformación miocárdica de la AI, lo que se expresa como una menor función diastólica correlacionando con daño miocárdico subclínico precoz.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an inflammatory immune disease characterised by the formation of autoantibodies and immune complex deposits. The presence of chronic inflammation may affect multiple organs, particularly the heart.1 Damage to the cardiovascular system, apart from being primarily caused by an autoimmune/inflammatory process, is also associated secondarily with disease activity and severity, in addition to immunosuppressant treatment mostly with steroids.2
One of the major complications of SLE is cardiac involvement and this may affect all heart structures including the pericardium, myocardium, valves and coronary vessels to differing levels of severity, with the reported prevalence in autopsy studies ranging between 40% to 70%. Symptomatic involvement detected ranged from 5% to 10% of patients, suggesting the subclinical nature of the damage to the myocardium.3 At present, the survival of patients with lupus has improved, but continuous cardiovascular morbimortality continues to be high, ranging between 17% and 76%, according to different studies.4
It has been suggested that some of the inherent SLE factors promote cardiovascular disease, such as the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies, reduced kidney function, disease duration, chronic damage to the organ reflected by the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology (SLICC/ACR) damage index, steroid duration and dose, and the use of azathioprine.5
Patients with SLE are 11 times more at risk of presenting with valvular changes than healthy individuals.6 The most frequent valvular changes are insufficiencies, mostly involving the aortic and mitral valves, and an association has been found with the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies and secondary antiphosphoipid syndrome. In some studies high levels of antiphospholipid antibodies have been reported which are strongly associated with cardiac abnormalities in patients with lupus.7,8
The left atrium plays a major role in maintaining heart function, because it acts as a reservoir, conductor and booster pump.9 In cases of diastolic dysfunction, changes occur in the ventricular inflow, triggering changes in the auricular phase to maintain ventricular systolic volume.
The echocardiogram is a simple and widely available tool for the diagnosis of cardiovascular disease which provide information of the haemodynamic structure, function and parameters.10 It has been reported that left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is common, occurs early and persistently in patients with SLE, and may be the only manifestation of cardiac involvement preceding large-scale systolic dysfunction.1
The enlargement and dysfunction of the left atrium has been considered as a subrogated marker of duration and severity of dyastolic dysfunction. It has also been identified as a potential indicator of several adverse cardiovascular events, such as major risk of acute infarction, heart failure, atrial fibrillation and mortality.11
Recently, myocardial deformation was introduced into the left atrium as a potential marker of diastolic function, using the global longitudinal strain of the left atrium (LAGLS) through the speckle tracking technique by echocardiography. It has the great advantage of being independent from the angle.
Myocardial deformation of the left atrium is an inherent mechanical property of the heart, which may be calculated using the echocardiogram software; this allows us to assess what percentage of movement in spatial position changes the myocardial fibre in each phase of the atrial cycle (reservoir, duct and booster pump); the higher the percentage of deformation, the greater the myocardial function. It has major clinical implications since it has been demonstrated that it begins to change prior to other parameters of heart function, such as the volume of the left atrium, the E/e' relationship and the fraction of expulsion of the left ventricle, which allows us to detect subclinical changes in the myocardium. This technique will be directly correlated with the diastolic function of the left ventricle, which generally presents with a dysfunction prior to systolic function.9,11,12 Studies exist which prove that the strain of the left atrium has been associated as a predictor of ischaemic cardiopathy, heart failure, atrial fibrillation and cardiovascular death.13–15
It has recently been described that the LAGLS is depressed in patients with SLE compared with controls,1 with our study being the second in the literature to research these parameters.
The main objective of this study was to evaluate left atrial function by strain through the speckle tracking echocardiographic technique in patients with SLE and associated-antiphospholipid syndrome and compare them with healthy controls. Our secondary objective was to determine whether risk factors existed for a depressed left atrial function in strain measurement in patients with SLE and antiphospholipid syndrome without cardiovascular symptoms.
MethodsPatients who attended the rheumatology unit of the Antiguo Hospital Civil de Guadalajara “Fray Antonio Alcalde” were recruited from March to August 2018. All patients had to be over 18 years of age and fulfil the SLE SLICC 201216 classification criteria and furthermore, they could have a diagnosis of secondary antiphospholipid syndrome according to the Sydney 200617 classification criteria of antiphospholipid antibody presence. The patients were paired with healthy controls by age and gender, defining themselves as a healthy control those patients without any type of comorbidity or disease.
Patients with badly controlled long duration high blood pressure were excluded, or those with a history of known valvular disease, atrial fibrillation or any other arrhythmia, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, a previous diagnosis of heart failure, ischaemic cardiopathy or patients who had overlap autoimmune diseases.
The patient medical characteristics were taken from their medical file. Laboratory data were obtained, such as blood biometry, blood chemistry, liver function tests, general urine examination, proteins in urine at 24?h, lipid profile, and antinuclear antibodies (ANA) (indirect immunofluorescence), specific antibodies (anti-Smith and double stranded anti-DNA), antiphospholipid antibodies (ELISA), lupus anticoagulant, IgG and IgM anticardiolipins and ß2 glycoprotein. Disease activity was calculated with the Mexican Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (Mex-SLEDAI)18 at the time of the visit, which was the day of inclusion into the study, and the SLICC/ACR damage index (SDI)19 scale was estimated to determine the presence of chronic damage caused by the disease. Activity was defined as Mex-SLEDAI?=?918 and SDI?=?1.
The treatment used in each patient was reported, such as immunosuppressant therapy, the use of steroids and anti-malaria drugs.
The echocardiographic images and calculations were performed in the echocardiographic laboratory of the Hospital Civil de Guadalajara “Fray Antonio Alcalde” by 5 cardiologists, with an interobserver variability of .85.
Conventional echocardiograms were made in a Siemens ACUSON SC2000 prime echocardiogram with a 4v1c sectorial of 1.25–4.5?MHz transducer. All the patients were evaluated with a two-dimensional echocardiogram. The expulsion fraction of the left ventricle was calculated using the biplanar Simpson method in the apical view 4 and 2 chambers. The indexed volume of the left atrium was determined at the end of the ventricular systole (maximum size of the left atrium) by the area-longitude biplanar method in the apical view of 4 and 2 chambers, indexing its result with the body surface area. The E/e' relationship was obtained using the proportion of the E wave of the transmitral flow and the average of the septal and lateral waves. The expulsion fraction of the left atrium was calculated using the software of the strain calculation. The valvulopathy was defined as the presence of a degree of valvular failure seen with the color doppler flow mapping in the aortic, mitral, pulmonary and tricuspid valves. The presence of the pericardial effusion was sought at the apical4 chamber axis.
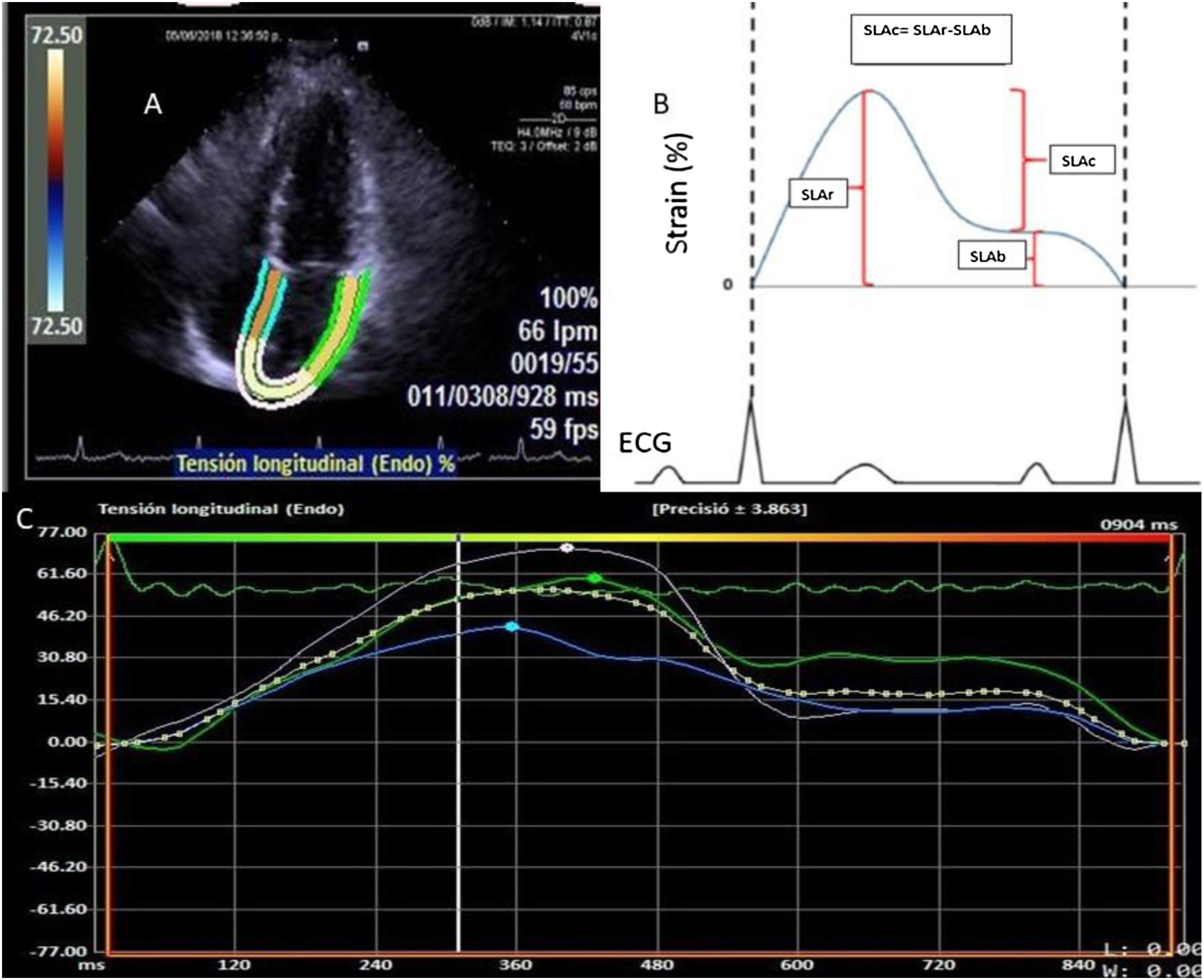
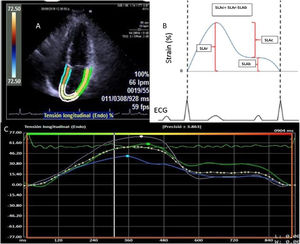
Deformation of the left atrium was determined (Fig. 1) using the syngo® Velocity Vector Imaging technology software. The echocardiographic view for the study was the apical 4-chamber. The endocardium of the left atrium was manually traced at the end-systole, and the edges of the endocardium were traced by the software through the cardiac cycle. The software took the R-R interval of the electrocardiogram pattern for deformation calculation. The deformation was evaluated as the global longitudinal strain and 3 values were calculated in the atrial deformation called: atrial longitudinal strain reservoir (ALSr),duct (ALSc) and booster pump (ALSb). The ALSr corresponded to the value from the highest peak of the reservoir phase, the ALSb to the highest peak of the booster pump phase and the ALSc to the difference between the ALSr and the ALSb. Furthermore, the value of the rate of deformation was reported, defined as the strain rate. The LAGLS under 35% was used to define a deformation of the depressed atrium reflecting a change in the atrial contraction and stiffness.20
A) Four-chamber apical view image where the edges of the left atrium are determined for strain calculation. B) Graphical representation of the left atrium strain in the whole atrium cycle. The ALSr corresponded to the value from the highest peak of the reservoir phase, the ALSb to the highest peak of the booster pump phase and the ALSc to the difference between ALSr and ALSb. C) Representation of the strain report of the left atrium of the VVI software.
The numerical variables were presented as means and standard deviations or medians and interquartile ranges, according to their distribution by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. The categorical variables were expressed as absolute numbers and proportions. The Student’s t-test and Mann-Whitney U test were used to compare the continuous variables. To compare the categorical variables the ?2 was used. To compare multiple quantitative variables with normal distribution the ANOVA was used and for non parametric distribution the Kruskal-Wallis was used. Univariate and multivariate analyses was performed using logistic regression. The variables were significant in the univariate analysis analysed in the multivariate to identify the predictors of an abnormal left atrial strain; the left atrial strain was taken as the dependent variable and the independent ones were: gender, age, body mass index, time of evolution, presence of antiphospholipid antibodies, diabetes mellitus, high blood pressure, lupus dyslipidaemia, use of steroids, antimalarials, azathioprin, methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate mofetil, rituximab, disease activity and damage index. The Medcalc statistical package version 18.9 was used to assess data. A p value of .05 was considered to be statistically significant.
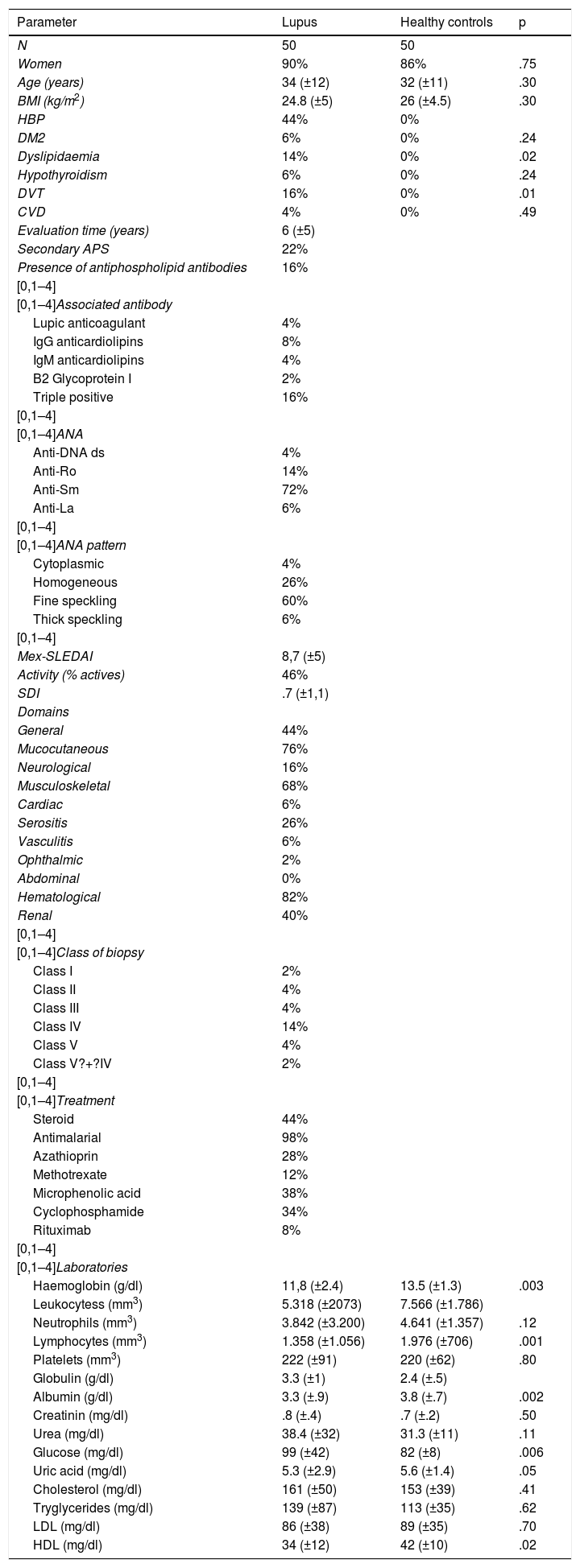
ResultsDuring the study period 50 patients with SLE and 50 healthy controls were included. Females were more preponderant in both groups (90% and 86%, respectively). Mean patient age with SLE was 34 years (SD?±12 years). There were no differences in body mass index between the patients with SLE and healthy controls. The most frequent comorbidity was high blood pressure, at 44%. Mean evolution time of the illness was 6 years (SD?±5 years). 22% of patients had secondary antiphospholipid syndrome and 16% of patients presented with circulating antiphospholipid antibodies without any antiphospholipid syndrome criteria, and 16% of the patients being triply positive. 72% of the patients had positive ANA 1:640 rates, with the fine speckled pattern being the most common. 46% of the patients with SLE were active on presenting with a above 9 Mex-SLEDAI. The most frequently affected domains were haematological (82%), mucocutaneous (76%), musculoskeletral (68%). 40% of the sample patients presented with lupic nephritis, with class IV being most common, in 14%. Regarding treatment, 44% took steroids, 98% antimalarials, 28% azathioprin, 12% methotrexate, 38% microphenolic acid, 34% cyclophosphamide and 8% rituximab. Significant differences were found in haemoglobin, leukocytes, neutrophils, lymphocytes, albumin, glucose, uric acid and high density lipoproteins (HDL) among the patients with SLE and health controls (Table 1).
Demographic and clinical characteristics of the patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and controls.
| Parameter | Lupus | Healthy controls | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 50 | 50 | |
| Women | 90% | 86% | .75 |
| Age (years) | 34 (±12) | 32 (±11) | .30 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.8 (±5) | 26 (±4.5) | .30 |
| HBP | 44% | 0% | |
| DM2 | 6% | 0% | .24 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 14% | 0% | .02 |
| Hypothyroidism | 6% | 0% | .24 |
| DVT | 16% | 0% | .01 |
| CVD | 4% | 0% | .49 |
| Evaluation time (years) | 6 (±5) | ||
| Secondary APS | 22% | ||
| Presence of antiphospholipid antibodies | 16% | ||
| [0,1–4] | |||
| [0,1–4]Associated antibody | |||
| Lupic anticoagulant | 4% | ||
| IgG anticardiolipins | 8% | ||
| IgM anticardiolipins | 4% | ||
| B2 Glycoprotein I | 2% | ||
| Triple positive | 16% | ||
| [0,1–4] | |||
| [0,1–4]ANA | |||
| Anti-DNA ds | 4% | ||
| Anti-Ro | 14% | ||
| Anti-Sm | 72% | ||
| Anti-La | 6% | ||
| [0,1–4] | |||
| [0,1–4]ANA pattern | |||
| Cytoplasmic | 4% | ||
| Homogeneous | 26% | ||
| Fine speckling | 60% | ||
| Thick speckling | 6% | ||
| [0,1–4] | |||
| Mex-SLEDAI | 8,7 (±5) | ||
| Activity (% actives) | 46% | ||
| SDI | .7 (±1,1) | ||
| Domains | |||
| General | 44% | ||
| Mucocutaneous | 76% | ||
| Neurological | 16% | ||
| Musculoskeletal | 68% | ||
| Cardiac | 6% | ||
| Serositis | 26% | ||
| Vasculitis | 6% | ||
| Ophthalmic | 2% | ||
| Abdominal | 0% | ||
| Hematological | 82% | ||
| Renal | 40% | ||
| [0,1–4] | |||
| [0,1–4]Class of biopsy | |||
| Class I | 2% | ||
| Class II | 4% | ||
| Class III | 4% | ||
| Class IV | 14% | ||
| Class V | 4% | ||
| Class V?+?IV | 2% | ||
| [0,1–4] | |||
| [0,1–4]Treatment | |||
| Steroid | 44% | ||
| Antimalarial | 98% | ||
| Azathioprin | 28% | ||
| Methotrexate | 12% | ||
| Microphenolic acid | 38% | ||
| Cyclophosphamide | 34% | ||
| Rituximab | 8% | ||
| [0,1–4] | |||
| [0,1–4]Laboratories | |||
| Haemoglobin (g/dl) | 11,8 (±2.4) | 13.5 (±1.3) | .003 |
| Leukocytess (mm3) | 5.318 (±2073) | 7.566 (±1.786) | |
| Neutrophils (mm3) | 3.842 (±3.200) | 4.641 (±1.357) | .12 |
| Lymphocytes (mm3) | 1.358 (±1.056) | 1.976 (±706) | .001 |
| Platelets (mm3) | 222 (±91) | 220 (±62) | .80 |
| Globulin (g/dl) | 3.3 (±1) | 2.4 (±.5) | |
| Albumin (g/dl) | 3.3 (±.9) | 3.8 (±.7) | .002 |
| Creatinin (mg/dl) | .8 (±.4) | .7 (±.2) | .50 |
| Urea (mg/dl) | 38.4 (±32) | 31.3 (±11) | .11 |
| Glucose (mg/dl) | 99 (±42) | 82 (±8) | .006 |
| Uric acid (mg/dl) | 5.3 (±2.9) | 5.6 (±1.4) | .05 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dl) | 161 (±50) | 153 (±39) | .41 |
| Tryglycerides (mg/dl) | 139 (±87) | 113 (±35) | .62 |
| LDL (mg/dl) | 86 (±38) | 89 (±35) | .70 |
| HDL (mg/dl) | 34 (±12) | 42 (±10) | .02 |
ANA: Antinuclear Antibodies; APS: Antiphospholipid Syndrome; BMI: Body Mass Index; CVD: Cerebral Vascular Disease; DM2: Diabetes Mellitus 2; DVT: Deep Vein Thrombosis; HBP: High Blood Pressure; HDL: High Density Lipoprotein; LDL: Low Density Lipoprotein; Mex-SLEDAI: Mexican Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index; SDI: SLICC/ACR Damage Index.
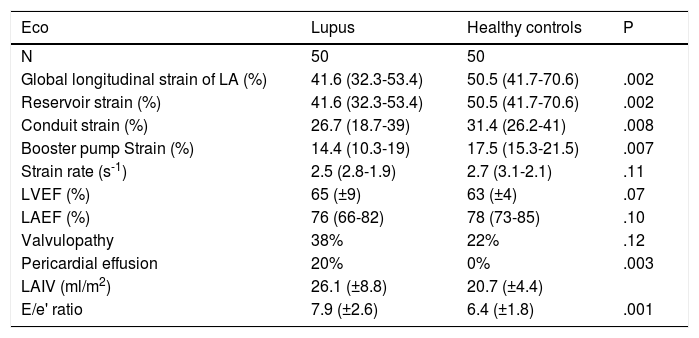
Among the echocardiographic variables studied, we found that the systolic function of the left atrium in both groups was similar, and also that of the systolic function of the left atrium (Table 2). A greater proportion of pericardial effusion was reported in patients with SLE (20% vs. 0%, p?=?.003). There were no differences in the presence of any level of valvulopathy between both groups.
Echocardiographic parameters of the patients with systemic lupus erythematosus compared with healthy controls.
| Eco | Lupus | Healthy controls | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 50 | 50 | |
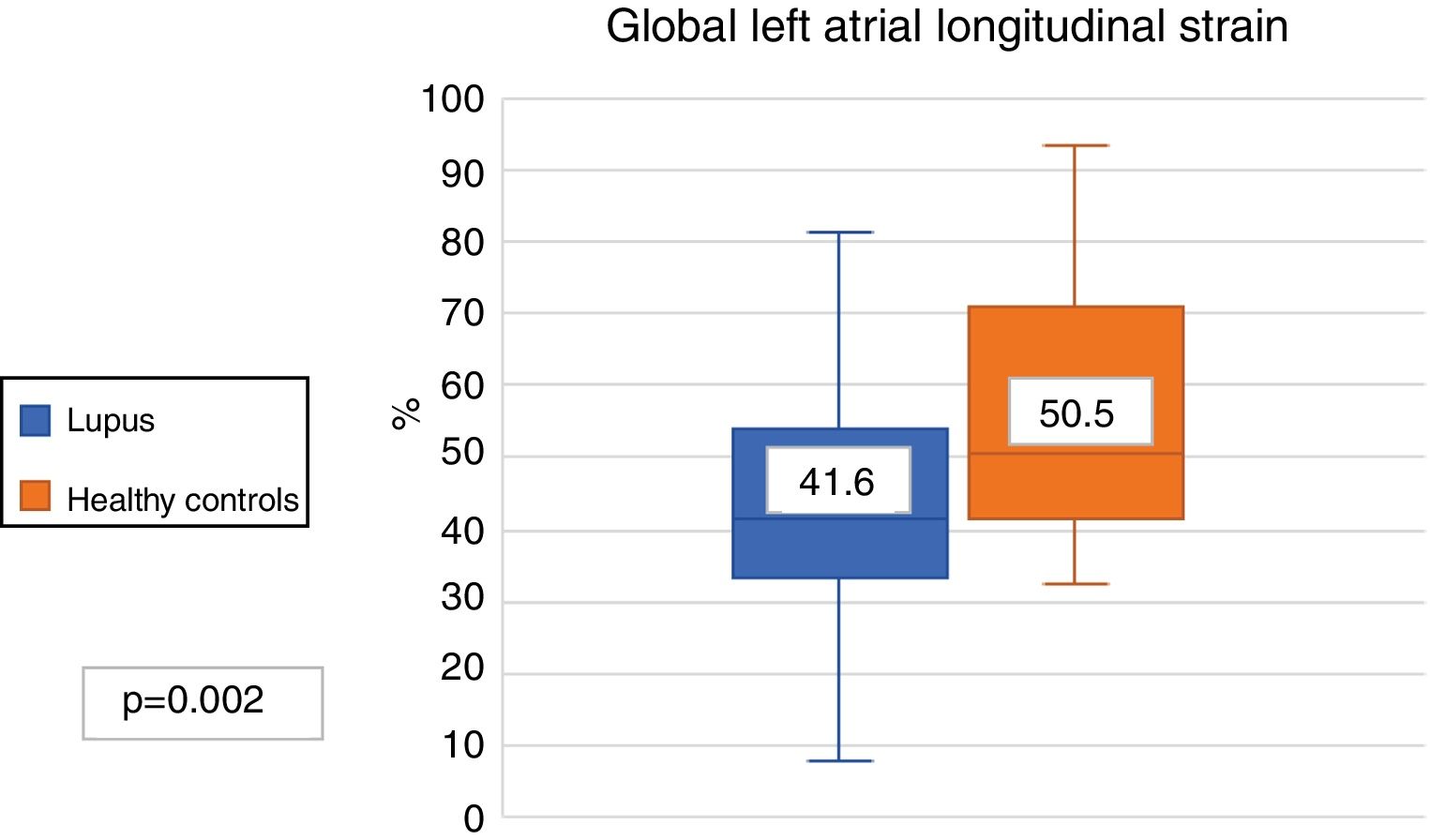
| Global longitudinal strain of LA (%) | 41.6 (32.3-53.4) | 50.5 (41.7-70.6) | .002 |
| Reservoir strain (%) | 41.6 (32.3-53.4) | 50.5 (41.7-70.6) | .002 |
| Conduit strain (%) | 26.7 (18.7-39) | 31.4 (26.2-41) | .008 |
| Booster pump Strain (%) | 14.4 (10.3-19) | 17.5 (15.3-21.5) | .007 |
| Strain rate (s-1) | 2.5 (2.8-1.9) | 2.7 (3.1-2.1) | .11 |
| LVEF (%) | 65 (±9) | 63 (±4) | .07 |
| LAEF (%) | 76 (66-82) | 78 (73-85) | .10 |
| Valvulopathy | 38% | 22% | .12 |
| Pericardial effusion | 20% | 0% | .003 |
| LAIV (ml/m2) | 26.1 (±8.8) | 20.7 (±4.4) | |
| E/e' ratio | 7.9 (±2.6) | 6.4 (±1.8) | .001 |
E: Early diastolic fillup transmitral flow speed; e´: Tissue speed of the transmitral flow at mitral annulus level; LA: Left Atrium; LAEF: Left Atrium Ejection Fraction; LAIV: Left Atrium Indexed Volume; LVEF: Left Ventricle Ejection Fraction.
Within the parameters of the diastolic function, patients with SLE presented with higher pressure of fill out of the left ventricle, expressed through the E/e' (7,5 vs. 6,3, p?=?.0003) and the indexed volume of the left atrium (24?ml/m2 vs. 21?ml/m2, p?=?.0007).
The LAGLS was lower in patients with SLE compared with the controls (41.6% vs. 50.5%, p?=?.002) (Fig. 2). The 3 phases of the left atrium cycle was also lower; ALSr (41.6% vs. 50.5%, p?=?.002), ALSc (26.7% vs. 31.4%, p?=?.008) and ALSb (14.4% and 17.5%, p?=?.007). No differences were found in the strain rate in patients with SLE and healthy controls (2.5?s-1 vs. 2.7?s-1). The results round in the LAGLS expressed a lower diastolic function in patients with SLE.
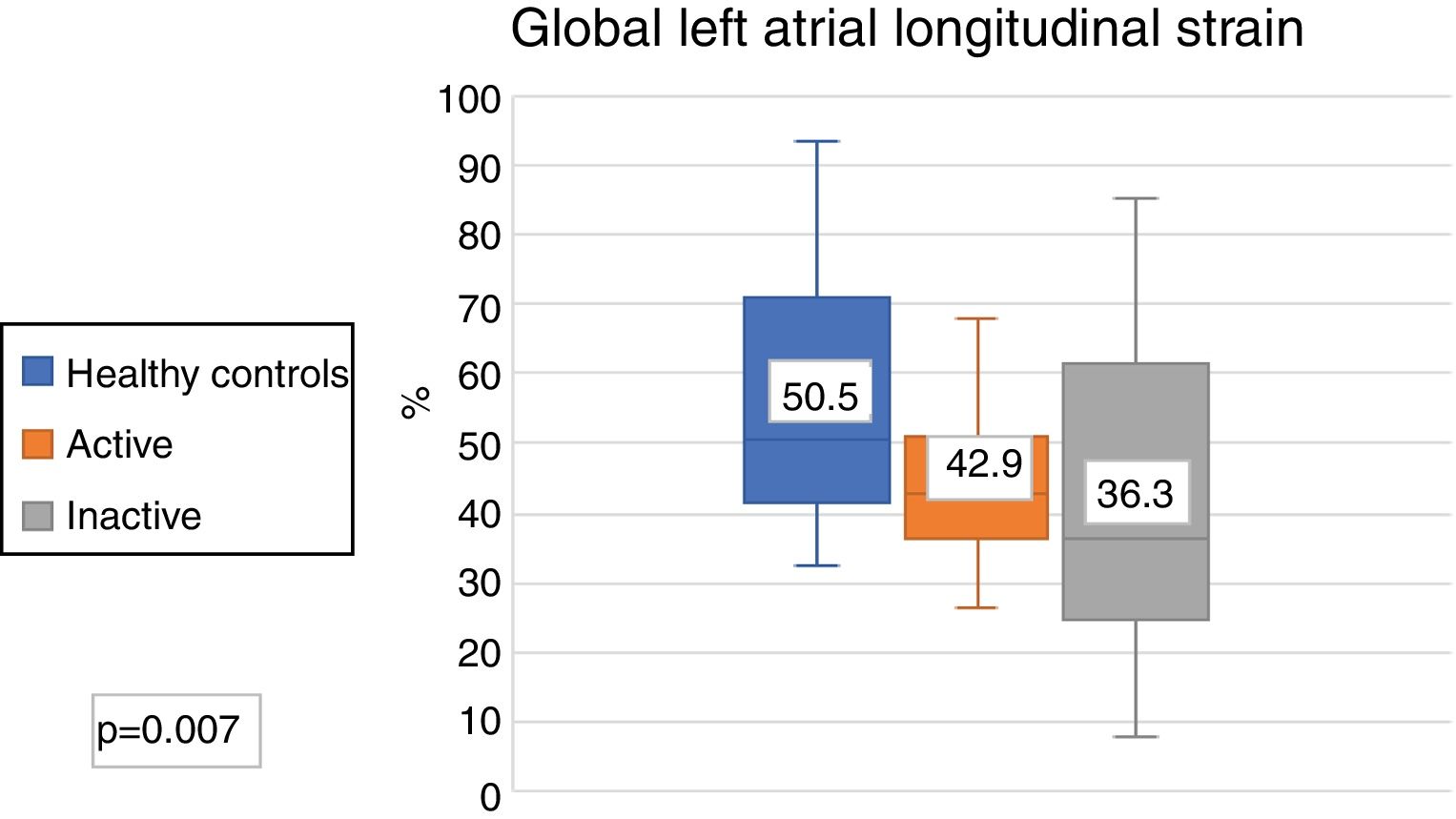
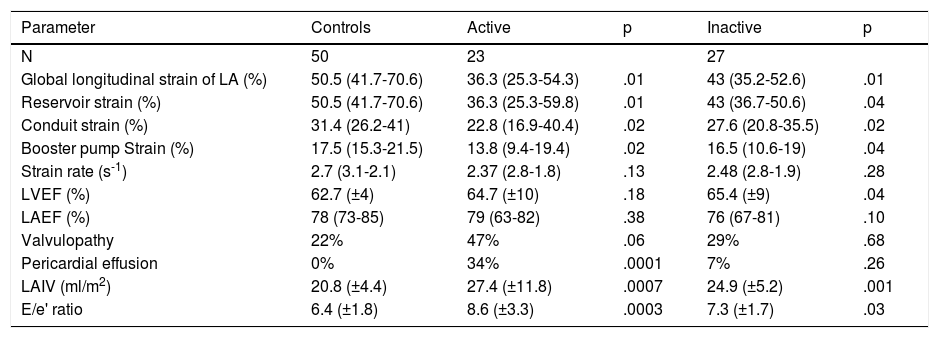
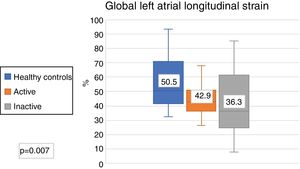
The echocardiographic parameters between the healthy controls and active SLE and healthy controls and inactive SLE were compared; significant differences were found in the LAGLS (healthy controls 50.5% vs. inactive 43% vs. actives 36.3%) (Fig. 3); in the strain of the 3 phases of the left atrium and in the indexed volume of the left atrium and E/e'. No difference was found in the strain rate (Table 3).
Comparison of echocardiographic parameters between controls and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus by disease activity according to the Mex-SLEDAI (active?>?9).
| Parameter | Controls | Active | p | Inactive | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 50 | 23 | 27 | ||
| Global longitudinal strain of LA (%) | 50.5 (41.7-70.6) | 36.3 (25.3-54.3) | .01 | 43 (35.2-52.6) | .01 |
| Reservoir strain (%) | 50.5 (41.7-70.6) | 36.3 (25.3-59.8) | .01 | 43 (36.7-50.6) | .04 |
| Conduit strain (%) | 31.4 (26.2-41) | 22.8 (16.9-40.4) | .02 | 27.6 (20.8-35.5) | .02 |
| Booster pump Strain (%) | 17.5 (15.3-21.5) | 13.8 (9.4-19.4) | .02 | 16.5 (10.6-19) | .04 |
| Strain rate (s-1) | 2.7 (3.1-2.1) | 2.37 (2.8-1.8) | .13 | 2.48 (2.8-1.9) | .28 |
| LVEF (%) | 62.7 (±4) | 64.7 (±10) | .18 | 65.4 (±9) | .04 |
| LAEF (%) | 78 (73-85) | 79 (63-82) | .38 | 76 (67-81) | .10 |
| Valvulopathy | 22% | 47% | .06 | 29% | .68 |
| Pericardial effusion | 0% | 34% | .0001 | 7% | .26 |
| LAIV (ml/m2) | 20.8 (±4.4) | 27.4 (±11.8) | .0007 | 24.9 (±5.2) | .001 |
| E/e' ratio | 6.4 (±1.8) | 8.6 (±3.3) | .0003 | 7.3 (±1.7) | .03 |
E: Early diastolic fillup transmitral flow speed; e´: Tissue speed of the transmitral flow at mitral annulus level; LA: Left Atrium; LAEF: Left Atrium Ejection Fraction; LAIV: Left Atrium Indexed Volume; LVEF: Left Ventricle Ejection Fraction; Mex-SLEDAI: Mexican Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index.
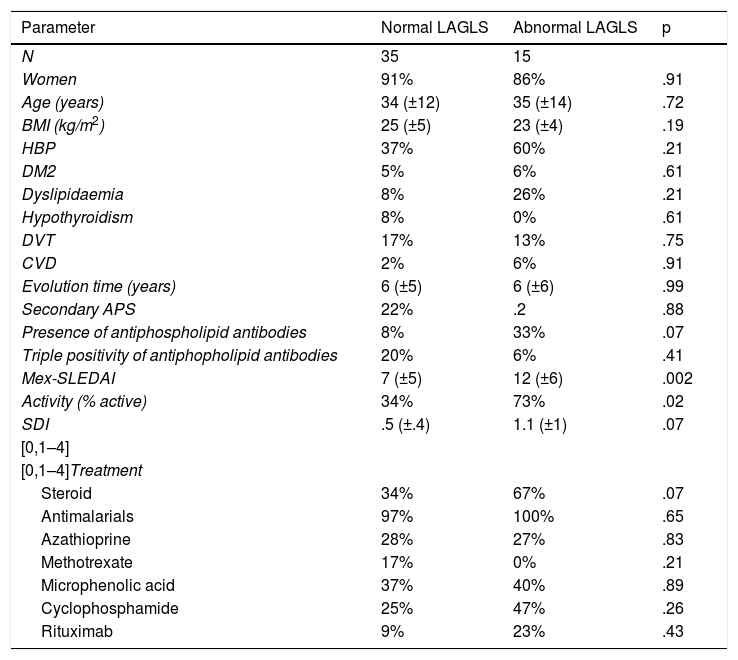
Clinical variables were contrasted between the patients with SLE who presented with an abnormal LAGLS vs. normal (35% cut-off point); in this they found 35 patients with normal LAGLS and 15 with abnormal (Table 4); significant differences were only found regarding the patients with abnormal LAGLS who presented with a higher score on the Mex-SLEDAI scale and therefore a higher percentage of active patients.
Comparison of clinical characteristics of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus who presented with normal left atrial global longitudinal strain (>?35%) and abnormal (
| Parameter | Normal LAGLS | Abnormal LAGLS | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 35 | 15 | |
| Women | 91% | 86% | .91 |
| Age (years) | 34 (±12) | 35 (±14) | .72 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25 (±5) | 23 (±4) | .19 |
| HBP | 37% | 60% | .21 |
| DM2 | 5% | 6% | .61 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 8% | 26% | .21 |
| Hypothyroidism | 8% | 0% | .61 |
| DVT | 17% | 13% | .75 |
| CVD | 2% | 6% | .91 |
| Evolution time (years) | 6 (±5) | 6 (±6) | .99 |
| Secondary APS | 22% | .2 | .88 |
| Presence of antiphospholipid antibodies | 8% | 33% | .07 |
| Triple positivity of antiphopholipid antibodies | 20% | 6% | .41 |
| Mex-SLEDAI | 7 (±5) | 12 (±6) | .002 |
| Activity (% active) | 34% | 73% | .02 |
| SDI | .5 (±.4) | 1.1 (±1) | .07 |
| [0,1–4] | |||
| [0,1–4]Treatment | |||
| Steroid | 34% | 67% | .07 |
| Antimalarials | 97% | 100% | .65 |
| Azathioprine | 28% | 27% | .83 |
| Methotrexate | 17% | 0% | .21 |
| Microphenolic acid | 37% | 40% | .89 |
| Cyclophosphamide | 25% | 47% | .26 |
| Rituximab | 9% | 23% | .43 |
APS: Antiphospholipid Syndrome; BMI: Body Mass Index; CVD: Cerebral Vascular Disease; DM2: Diabetes Mellitus 2; DVT: Deep Vein Thrombosis; HBP: High Blood Pressure; LAGLS: Left Atrium Global Longitudinal Strain; Mex-SLEDAI: Mexican Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index; SDI: SLICC/ACR Damage Index.
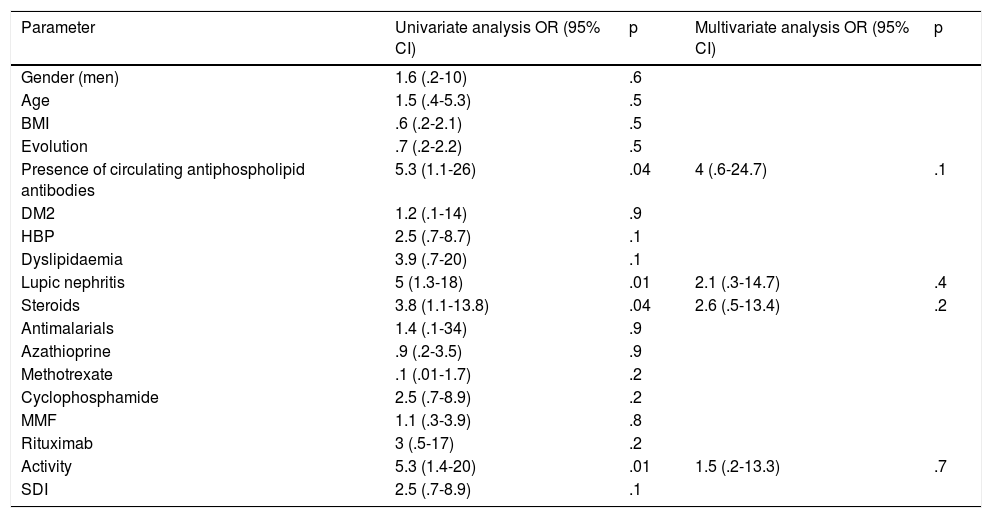
Univariate and multivariate analysis was performed (Table 5) to determine whether the variables were independently influenced in the LAGLS. It was reported that in the univariate analysis the presence of circulating antiphospholipid antibodies was significant, together with the presence of lupic nephritis, the use of steroids and the disease activity. However, in the multivariate analysis no significant differences of any of these were found.
Univariate and multivariate analysis of the factors associated with LAGLS?
| Parameter | Univariate analysis OR (95% CI) | p | Multivariate analysis OR (95% CI) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (men) | 1.6 (.2-10) | .6 | ||
| Age | 1.5 (.4-5.3) | .5 | ||
| BMI | .6 (.2-2.1) | .5 | ||
| Evolution | .7 (.2-2.2) | .5 | ||
| Presence of circulating antiphospholipid antibodies | 5.3 (1.1-26) | .04 | 4 (.6-24.7) | .1 |
| DM2 | 1.2 (.1-14) | .9 | ||
| HBP | 2.5 (.7-8.7) | .1 | ||
| Dyslipidaemia | 3.9 (.7-20) | .1 | ||
| Lupic nephritis | 5 (1.3-18) | .01 | 2.1 (.3-14.7) | .4 |
| Steroids | 3.8 (1.1-13.8) | .04 | 2.6 (.5-13.4) | .2 |
| Antimalarials | 1.4 (.1-34) | .9 | ||
| Azathioprine | .9 (.2-3.5) | .9 | ||
| Methotrexate | .1 (.01-1.7) | .2 | ||
| Cyclophosphamide | 2.5 (.7-8.9) | .2 | ||
| MMF | 1.1 (.3-3.9) | .8 | ||
| Rituximab | 3 (.5-17) | .2 | ||
| Activity | 5.3 (1.4-20) | .01 | 1.5 (.2-13.3) | .7 |
| SDI | 2.5 (.7-8.9) | .1 |
BMI: Body Mass Index; DM2: Diabetes Mellitus 2; HBP: High Blood Pressure; 95% CI: 95% confidence interval; LAGLS: Left Atrium Global Longitudinal Strain; MMF: mycophenolate mofetil; OR: Odds Ratio; SDI: SLICC/ACR Damage Index.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the function of the left atrium through two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography, which is a non-invasive method in patients with SLE with no cardiac symptoms. The main findings from this study were that the deformation of the left atrium was altered and reduced in patients with SLE compared with healthy people of the same age and sex. There was also higher diastolic dysfunction. Furthermore, we found that in the patients with SLE, the atrium deformation was lower when greater disease activity presented.
In this study, we found that patients with SLE had an global depressed longitudinal strain compared with the healthy controls, and that they also presented with a reduction of the strain in the 3 phases of the atrium cycle, which may be interpreted as an altered dynamic in the contraction of myocardial fibres of the atrium secondary to ventricular diastolic dysfunction and to the stiffness of the myocardial fibres of the atrium through the chronic inflammatory status and deposit of immunocomplexes.21
Our results are similar to those of a study in which the speckle tracking technique was used in the left atrium of patients with SLE and was compared with healthy controls, including 60 patients in each group. The mean age of the patients with SLE was 35.8?±?8.1, the mean of SLEDAI was 2.3?±?1.0 and the mean of SDI was 2.4?±?1.2. It was found that the patients with SLE presented with a lower global strain compared with the healthy controls (26.2?±?9.5% vs. 32.5?±?9.8%, both p?1; however, in our study this was not similar, since in the multivariate analysis it was not significant. This may be due to our patients having a lower SDI and evolution time of the disease.
We found that another of the standard parameters of diastolic function of the left ventricle, like those of the E/e' and the indexed volume of the left atrium, was higher in patients with SLE, unlike in the controls; even in active ones, both values were also higher, correlating with a greater diastolic dysfunction. This fact has already been previously described by Gusetu et al. in a study carried out with 75 patients with SLE, where they were compared with 73 healthy controls.22 This was also reported by Barutcu et al., who studied 50 patients with SLE compared with 30 controls and reported higher values of E/e' and indexed volume of the left atrium. Of relevance was that this study also reported that the patients with SLE and positive anticardiolypin antibodies had higher diastolic dysfunction levels.23 In a study with 102 patients with lupus and 32 control individuals, Li et al., used 3D echocardiography to rate the volume and function of the left atrium and found that the patients with SLE had greater volume and a more impaired left atrium function, with it being greater in those patients with elevated SDI and a higher disease activity.24 This is similar to our results, where it was reported that the patients with a higher activity had a more impaired left atrial function.
We report that patients with lupic nephritis could have an association with higher depression of the strain; this could explain already that the majority of patients classified as active had a higher presence of lupic nephritis. It has been reported25 that patients with chronic kidney disease have a depressed LAGLS compared with healthy controls, secondary to the activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone pathway causing myocardial fibrosis, and this could explain that the lupic nephritis was related to greater depression of the left atrial strain in our study.
In our study it was found that the presence of circulating antiphospholipid antibodies could be related to the univariate analysis with the presentation of a depressed strain, which indicates higher diastolic dysfunction. These findings coincide with those described by Tufano et al. in a study with 69 patients with antiphospholipid syndrome and 69 healthy controls, in which the presence of diastolic dysfunction was demonstrated to correlate with higher rates of lupic anticoagulant and with greater age. Moreover, it was found that the patients with secondary antiphospholipid syndrome presented with a higher left atrial volume.26
We found that the use of steroids could be associated with the univariate analysis on presenting with depressed LAGLS. Hattori et al.27 had described the effect of steroids at cardiac level, in one study with murine models, finding that they produced hypertension, ventricular fibrosis, and induced diastolic dysfunction of the left ventricle, due to the increase in the oxidative stress, deficiency in nitric oxide, acting through the mineral corticoid receptors (MR) and glucocorticoids (CR) widely distributed in the cardiovascular system. We also observed the presence of atrophy of the cardiac fibres, regardless of the receptor activation. It was found that these effects diminished when spironolactone was administered.
Impairment of left atrial function in patients with SLE could be due to the presence of chronic systemic subclinical inflammation, even with low levels of activity, in keeping with existing indexes, secondary to the presence of circulating pro-inflammatory cytokines. In one study with patients with rheumatoid arthritis28 and in another study with patients with ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis29 it was observed that by administrating anti-TNF the left atrial function improved.
Literature is scarce on the use of left atrial strain in patients with SLE and its application in the detection of change to the left atrial function. Only one study was found which compared the function of the left atrium by strain in patients with SLE and control individuals. This study was useful for describing the possible value of this new strain technique on the left atrium in patients with SLE, to determine subclinical change or incipient diastolic dysfunction and its early detection. As a result, actions could be implemented to reduce heart failure progression with the future preservation of systolic function. However, further studies are required with long term follow-up and on a grand scale to validate the use of this technique in the follow-up with patients with SLE.
The limitations of this study are mainly the modest sample size and that there was no long-term follow-up for the patients with echocardiograms using the left atrial strain technique for posterior control to treatment modifications and change in activity. Providing follow-up to these patients during their evolution with this technique would be of interest, as would assessment of the changes in parameter and patient outcome. Moreover, the strain technique depends on the quality of the image and on the operator, and is not widely found in all centres, although it is a technique which has acquired an importance for the cardiac evaluation of the patients.
ConclusionThe SLE is a multi-organ entity which also affects the heart. In the study it was found that the deformation of the left atrium and all the phases of the cycle were altered, indicating subclinical involvement of the heart, in asymptomatic patients, within the disease evolution and activity. It is therefore recommended that periodical cardiac evaluation be carried out, even in asymptomatic patients, so that early modifications to treatment may be made and comprehensive care may be offered to patients, preventing the remodelling of the atrium and avoiding development of arrhythmias and heart failure with ejection fraction preserved.
Conflict of interestThe authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Please cite this article as: Pérez-Topete SE, Miranda-Aquino T, Hernández-del Río JE, Cerpa-Cruz S, Gutiérrez-Ureña SR, Martínez-Bonilla G, et al. Deformación miocárdica de la aurícula izquierda en pacientes con lupus eritematoso sistémico. Reumatol Clin. 2021;17:74–81.