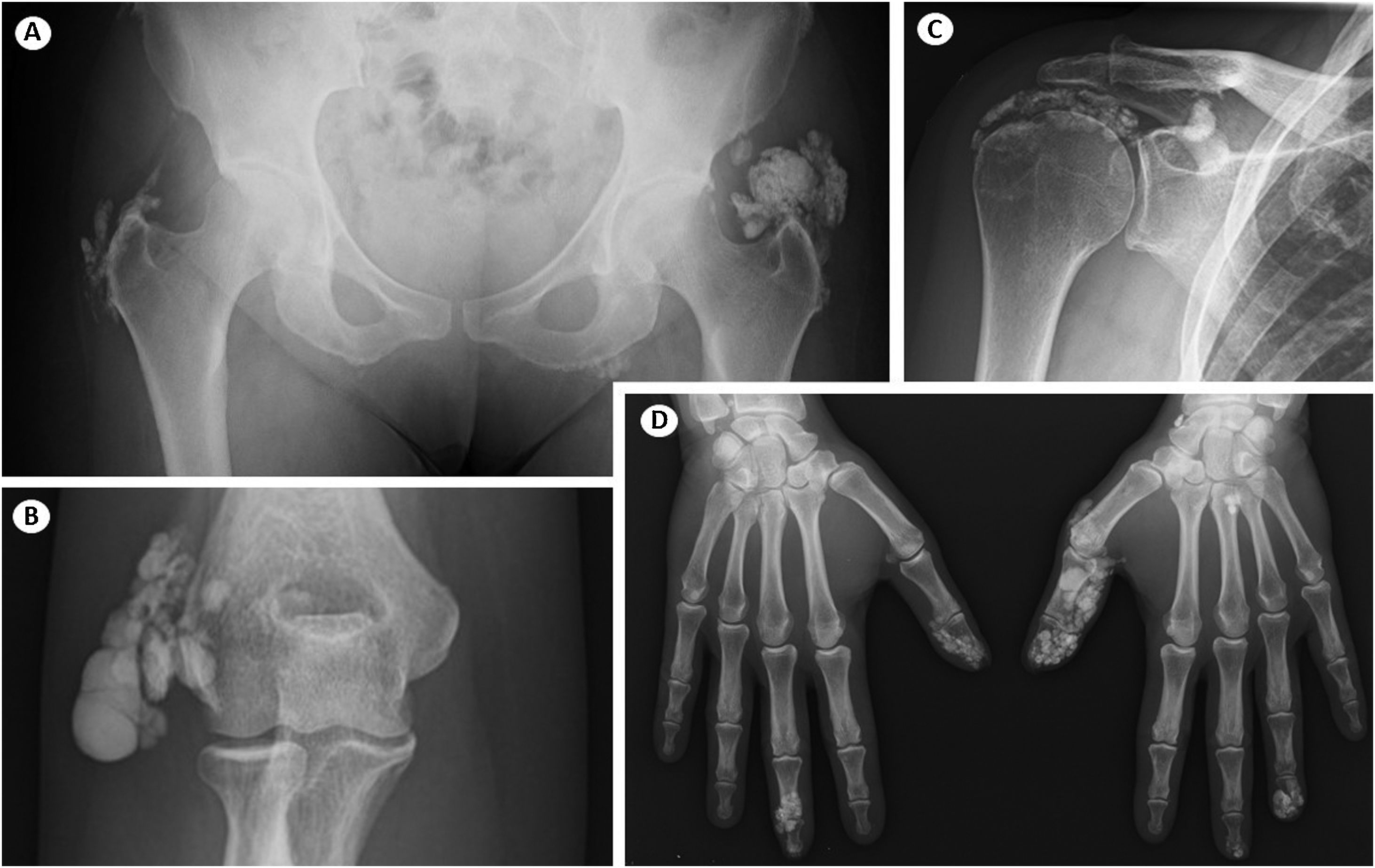
A 68-year-old woman presented to the rheumatology clinic with complaints of progressive pain and oedema in the fingertips, sometimes with ulceration and extrusion calcium-like material.
The patient had a 12-year history of limited Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) with symptoms of Raynaud, dyspnoea, heartburn, pain and swelling in the fingertips. By the time of diagnosis physical examination revealed telangiectasias, sclerodactyly and subcutaneous nodularities in the tip of the 1st and 3rd fingers of the right hand. Laboratory analyses were positive for Topoisomerase I/Scl-70.
During the 12 years of follow-up, the most prominent complaints were related to the function limitation caused by calcinosis cutis. She also developed exuberant widespread calcinosis in other fingers, right elbow, right shoulder and hips. Several therapies were tried, including bisphosphonates, diltiazem, colchicine, minocycline and intravenous immunoglobulin, without any benefit. Three surgeries on the 1st and 3rd fingers of her right hand were performed to excise calcium deposits; despite that, calcinosis returned at the same locations. Current radiographic images show the ineffectiveness of treating calcinosis cutis (Fig. 1).
SSc-related calcinosis is a common and debilitating manifestation. Frequent complications are ulceration, infection, pain and impaired function. The scarcity of effective options makes the treatment of calcinosis a major clinical challenge. Together, these factors make calcinosis a major contributor to the disease burden in SSc patients.1,2
EthicsThis article was written in compliance with the Helsinki Declaration.
FundingThe authors declare no funding sources.
Authors’ contributionsAll authors contributed for the care of the patient and equally contribute to the article.
Conflict of interestWe declare no conflict of interest.