To assess the association between the HLA-B*51 allele and Behçet Disease (BD) in Argentinean patients.
MethodsWe enrolled 34 consecutive Argentinean patients with definitive diagnosis of BD between October 2016 and March 2017. None of the patients had the HLA-B*51 allele determined at study entry. Unrelated controls (n=240) were randomly obtained from the national cadaveric donor database. Demographic and clinical features of the patients were recorded by attending physicians through a questionnaire.
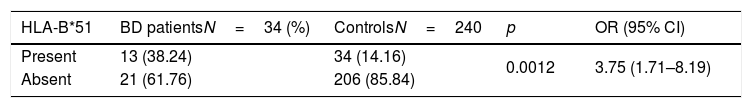
ResultsMean age of cases was 42 years old. Nineteen (55.8%) were male, and the mean age at diagnosis was 35 years old; twenty (58.8%) were Mestizos, 8 (23.5%) were Caucasian, and 6 (17.6%) were Amerindians. Thirteen (38.2%) of 34 cases were HLA-B*51 allele positive; 11 were heterozygous and 2 homozygous for the allele. Thirty-four (14.2%) of 240 controls were positive for the HLA-B*51 allele. The association between BD and HLA-B*51 allele was greater than that of control group (OR=3.75; p=0.0012).
ConclusionsThe HLA-B*51 allele is strongly associated with BD in Argentinean patients. Our finding is consistent with previous studies indicating that the HLA-B*51 allele is an important susceptibility gene in BD regardless the geographical region and ethnicity.
Evaluar la asociación entre el alelo HLA-B*51 y la enfermedad de Behçet (EB) en pacientes argentinos.
MétodosIncluimos en forma consecutiva 34 pacientes argentinos con diagnóstico definitivo de EB entre los meses de octubre de 2016 y marzo de 2017. Ninguno de los pacientes tenía el alelo HLA-B*51 determinado al inicio del estudio. Los controles no relacionados (n=240) se obtuvieron al azar de la base nacional de datos de donantes cadavéricos. Las características demográficas y clínicas de los pacientes fueron registradas por los médicos asistentes a través de un cuestionario.
ResultadosLa edad promedio de los casos fue de 42 años. Diecinueve (55,8%) fueron varones, y la edad promedio en el momento del diagnóstico fue de 35 años; 20 (58,8%) fueron mestizos, 8 (23,5%) caucásicos y 6 (17,6%) amerindios. Trece (38,2%) de los 34 casos fueron positivos para el alelo HLA-B*51; 11 de ellos fueron heterocigotas y 2 homocigotas para dicho alelo. Treinta y cuatro (14,2%) de los 240 controles fueron positivos para el alelo HLA-B*51. La asociación entre la EB y el alelo HLA-B*51 fue mayor que en el grupo control (OR=3,75; p=0,0012).
ConclusionesEl alelo HLA-B*51 está fuertemente asociado con la EB en pacientes argentinos. Nuestro hallazgo es consistente con estudios previos que indican que el alelo HLA-B*51 es un gen de susceptibilidad importante en la EB independientemente de la región geográfica y la etnia.
Behçet disease (BD) is a systemic inflammatory disease of unknown etiology. It is characterized by recurrent oral aphthous and genital ulcers, uveitis, and skin lesions. Vascular injury, hyper-coagulability, hyper-function of neutrophils, and autoimmune response are pathological findings of the disease.1,2
BD is a complex clinical entity where genetic and environmental factors influence disease’ susceptibility. Several previous studies showed that immunogenetics factors (mainly HLA class A and B) are present in the development of BD.3
HLA-B*51 allele is the most strongly associated genetic risk factor linked with BD.1,2,4–6 This association is present along different geographical regions and ethnic groups.7 So far, two studies from Mexico are the only evidence on the association between the HLA-B51 allele and BD in Latin American countries; however, the results are contradictory.8,9
The aim of this study was to assess the association between BD and the HLA-B*51 allele in Argentinean patients.
Materials and MethodsStudy Design and SettingWe carried out a case–control study. The researchers who participated in the study work in reference Hospitals, and they belong to the Vasculitis Study Group of the Argentinean Society of Rheumatology.
ParticipantsThirty-four consecutive BD Argentinean patients were included for the study between October 2016 and March 2017. All of them had a definitive diagnosis of BD according to the International Study Group for Behçet Disease criteria, and they did not have the HLA-B*51 allele determined at study entry.10 Unrelated controls (n=240), and their HLA-B*51 status, were randomly obtained from the cadaveric donor database from the “Instituto Nacional Central Único Coordinador de Ablación e Implante del Ministerio de Salud de La Nación (INCUCAI)” the official national institution for transplant allocation in Argentina.
VariablesDemographic and clinical features of the patients were recorded by attending physicians through a questionnaire. Ethnicity was defined according to definitions made by the “Grupo Latinoamericano de Estudio del Lupus (GLADEL)”.11
HLA Class I TypingFor cases HLA class I typing was performed using a polymerase chain reaction sequence-specific oligonucleotide (PCR-SSO) coupled with a Luminex platform using a medium resolution LABType SSO class I B locus typing test (One Lambda Inc., California, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The controls were typed by a PCR with sequence-specific primers (PCR-SSP).
Statistical AnalysisDescriptive statistics including percentages, mean, standard deviation (SD), median and range were calculated. The frequencies of the alleles and genotypes among patients and controls were compared by chi-squared tests. Odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals were calculated. A p level of ≤0.05 was considered significant in all analysis. Statistical analysis was done using Stata 14.0 (StataCorp 2015, TX, USA).
Ethics ApprovalThe study was approved by all local ethical committees of the corresponding hospitals, and all the study participants gave their written informed consent to participate. The research methods were in compliance of the tenets of the Declarations of Helsinki.
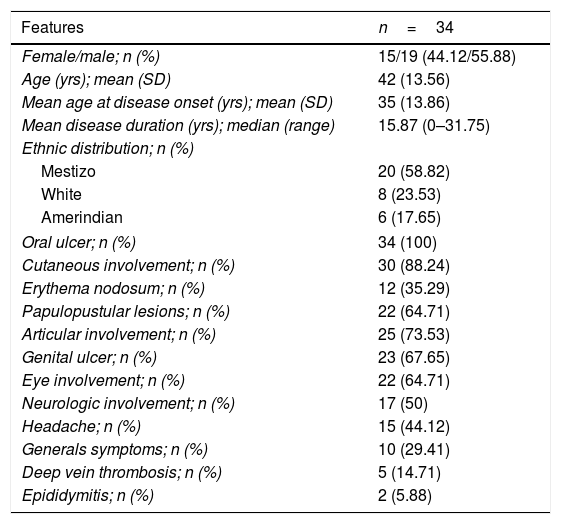
ResultsDemographics and Clinical FeaturesMain demographic characteristics are shown in Table 1. BD was slightly more prevalent in males, with a mean age at diagnosis of 35 years old. Mestizo population accounted for the majority of ethnicity, followed by White and Amerindians subjects. Most frequent clinical manifestations were oral and genital ulcers, followed by cutaneous, articular, ocular, and neurological involvement.
Demographic and Clinical Features of 34 Argentinean Patients With Behçet's Disease.
| Features | n=34 |
|---|---|
| Female/male; n (%) | 15/19 (44.12/55.88) |
| Age (yrs); mean (SD) | 42 (13.56) |
| Mean age at disease onset (yrs); mean (SD) | 35 (13.86) |
| Mean disease duration (yrs); median (range) | 15.87 (0–31.75) |
| Ethnic distribution; n (%) | |
| Mestizo | 20 (58.82) |
| White | 8 (23.53) |
| Amerindian | 6 (17.65) |
| Oral ulcer; n (%) | 34 (100) |
| Cutaneous involvement; n (%) | 30 (88.24) |
| Erythema nodosum; n (%) | 12 (35.29) |
| Papulopustular lesions; n (%) | 22 (64.71) |
| Articular involvement; n (%) | 25 (73.53) |
| Genital ulcer; n (%) | 23 (67.65) |
| Eye involvement; n (%) | 22 (64.71) |
| Neurologic involvement; n (%) | 17 (50) |
| Headache; n (%) | 15 (44.12) |
| Generals symptoms; n (%) | 10 (29.41) |
| Deep vein thrombosis; n (%) | 5 (14.71) |
| Epididymitis; n (%) | 2 (5.88) |
SD: standard deviation; yrs: years.
Out of 34 patients with BD, 13 (38.2%) of them were positive for the HLA-B*51 allele; 11 (32.3%) were heterozygous and 2 (5.8%) were homozygous. In the control group, 34 out of 240 subjects had the HLA-B*51 allele (14.2%). None of the controls were homozygous for the allele HLA-B*51. The association between BD and HLA-B*51 allele was greater than that of control group (OR=3.75; 95%IC=1.71–8.19; p=0.0012) (Table 2).
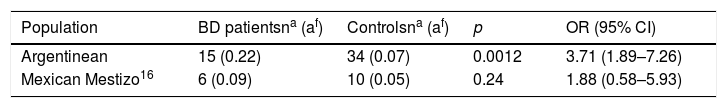
DiscussionThe most significant finding in our study is a strong association between HLA-B*51 allele and Behçet disease in Argentinean patients. This association is well known in patients belonging to Asian and Eurasian populations from Japan to the Middle East.7 However, there is less data on Caucasian patients with BD from other regions, such as North Western Europe and North America.12–16 Furthermore, there are two Latin American studies focusing on the association between HLA-B*5 allele and BD. Lavalle, et al. found that the HLA-B*5 allele was more frequent in Mexican Mestizo patients with BD than ethnically matched controls (70% vs. 31%, p<0.05).8 On the other hand, Soto Vega et al., found no association between HLA-B*51 allele and BD among Mexican Mestizo patients and controls [9% vs. 5%, OR=1.88 (95%CI=0.58–5.93, p=0.24)].9Table 3 shows the HLA-B*51 allele frequencies in our BD patients and the Mexican Mestizo patients from Soto Vega study.
HLA-B*51 Allele Frequencies in Argentinean BD Patients, Mexican Mestizo BD Patients and Controls.
| Population | BD patientsna (af) | Controlsna (af) | p | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Argentinean | 15 (0.22) | 34 (0.07) | 0.0012 | 3.71 (1.89–7.26) |
| Mexican Mestizo16 | 6 (0.09) | 10 (0.05) | 0.24 | 1.88 (0.58–5.93) |
BD: Behçet’ disease; OR: odds ratio; CI: confidence interval; na: number of alleles; af: allele frequencies.
In our study the frequency of the HLA-B*51 allele in BD patients was 38.2% as compared to 14.2% in controls. Strikingly, our data are quite similar to the pooled prevalence estimated for HLA-B*51 allele in the Northern/Eastern regions of Europe (BD=39%; 95%CI=28.2–51.1 vs. controls=11.2%; 95%CI=8.1–15.3) and North America (BD=34.2%; 95%CI=6.0–80.8 vs. controls=18%; 95%CI=7.6–37.1), but lower than the pooled prevalence estimated in the Southern Europe (BD=60.6%; 95% CI=51.9–68.7 vs. controls=16.8%; 95% CI=13.3–21.0) where the biggest proportion of Argentine immigration comes from.7 This finding could be partially explained by the fact that our studied population was predominantly Mestizo, a mixture of European (Caucasian) and native ancestors (Amerindians). Two studies showed low prevalence of HLA-B*51 in Amerindian tribes of South America (mainly Argentine natives). Fernandez-Viña et al.,17 analyzed the prevalence of HLA antigens in a Toba tribe, finding an HLA-B*51 allele frequency of 3%. Parham et al.,18 studied the prevalence of HLA antigen in a Guarani tribe, finding an HLA-B*51 allele frequency of 6.6%. Therefore, we assume that the admixture between European and South American Amerindian could explain that mixed populations have more HLA class I allele diversity than each ethnic group separately.
LimitationsOur study has limitations. Classical case-control studies designed to evaluate gene association are exposed to bias due to the existence of population substructures that cannot be certainly determined. It is possible that our cases are not representative of all BD patients from an Argentinean population as a consequence of a selection bias. Finally, as we did not have the sex and ethnicity data of the controls, we could not match both groups for these variables.
ConclusionsThe HLA-B*51 allele is strongly associated with BD in Argentinean patients. Individuals carrying HLA B*51 allele have a 4-fold susceptibility risk increase of BD compared to non-carrier individuals of the allele. Our finding is consistent with previous studies indicating that the HLA-B*51 allele is an important susceptibility gene in BD regardless the geographical region and ethnicity.
FundingThis research was funded by an Argentinean Rheumatology Society grant.
Conflicts of InterestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.